
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
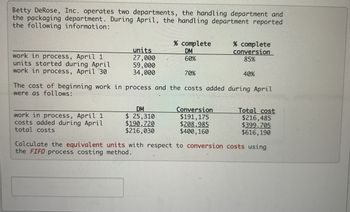
Transcribed Image Text:Betty DeRose, Inc. operates two departments, the handling department and
the packaging department. During April, the handling department reported
the following information:
work in process, April 1
units started during April
work in process, April 30
units
27,000
59,000
34,000
work in process, April 1
costs added during April
total costs
% complete
DM
60%
DM
$ 25,310
$190,720
$216,030
70%
The cost of beginning work in process and the costs added during April
were as follows:
% complete
conversion
85%
Conversion
$191, 175
$208,985
$400, 160
40%
Total cost
$216,485
$399, 705
$616, 190
Calculate the equivalent units with respect to conversion costs using
the FIFO process costing method.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use this information about the Assembly Department to answer the question that follows. The debits to Work in Process-Assembly Department for April, together with data concerning production, are as follows: April 1, work in process: Materials cost, 3,000 units $ 7,500 Conversion costs, 3,000 units, 80% completed 6,000 Materials added during April, 10,000 units 29,000 Conversion costs during April 35,000 Goods finished during April, 11,500 units — April 30 work in process, 1,500 units, 60% completed — All direct materials are added at the beginning of the process, and the average cost method is used to cost inventories. The cost per equivalent unit for April is a.$2.70 b.$6.74 c.$6.25 d.$6.40arrow_forwardCarlberg Company has two manufacturing departments, Assembly and Painting. The Assembly department started 12,200 units during November. The following production activity in both units and costs refers to the Assembly department's November activities. Assembly Department Beginning work in process inventory. Units started this period Units completed and transferred out Ending work in process inventory Cost of beginning work in process Direct materials Conversion Costs added this month Direct materials Conversion Cost per Equivalent Unit of Production Costs added this period Costs of beginning work in process Total costs + Equivalent units of production Cost per equivalent unit of production Units 3,000 12,200 10,000 5,200 Direct Materials $ Percent. Complete for Direct Materials 70% $ 1,484 804 12,936 16,926 85% Calculate the Assembly department's cost per equivalent unit of production for materials and for conversion for November. Use the weighted average method. 1,484 1,484 $ $ 2,288…arrow_forwardHoneybutter Pty Ltd manufactures a product that goes through two departments prior to completion—the Mixing Department followed by the Packaging Department. The following information is available about work in the first department, the Mixing Department, during June. Percent completed Units Materials Conversion Work in process, beginning 70,000 70% 40% Units started during June 460,000 Completed and transferred out 450,000 Work in process, ending 75% 25% Work in process, beginning $36,550 $13,500 Cost added during June $391,850 $287,300 Required: Assume that the company uses the weighted-average method. (a) Determine the physical units of the ending inventory in June for the Mixing Department (b) Determine the equivalent units for June for the Mixing Department (c) Compute the costs per equivalent unit…arrow_forward
- The following information concerns production in the Forging Department for June. All direct materials are placed into the process at the beginning of production, and conversion costs are incurred evenly throughout the process. The beginning inventory consists of $18,000 of direct materials. ACCOUNT Work in Process-Forging Department Debit Credit Date Item June 1 Bal., 1,800 units, 60% completed 30 Direct materials, 25,800 units 30 Direct labor 30 Factory overhead 30 Goods transferred, ? units 30 Bal., 2,800 units, 70% completed Cost per equivalent units of $9.60 for Direct Materials and $3.00 for Conversion Costs. Based on the above data, determine each of the following amounts. If required, round your interim calculations to two decimal places. Round final answers (a-c) to the nearest dollar. a. Cost of beginning work in process inventory completed in June $ 247,680 43,300 33,740 b. Cost of units transferred to the next department during June $ c. Cost of ending work in process…arrow_forwardShirley Processing, Incorporated (SPI) makes adhesive tape. The following information on the physical flow of units and costs for month of March: Quantities Beginning work-in-process Started To account for Transferred out Ending work in process Accounted for Physical units Percentage Complete. Materials 107,000 100% Conversion 40% 957,000 1,064,000 975,500 100% 100% 88,500 100% 20% 1,064,000 Cost Beginning work-in-process Current period Total $ 186,570 1,871,298 Direct Materials $ 167,180 1,234,530 Conversion $ 19,390 636,768 Total $ 2,057,868 $ 1,401,710 $ 656,158 Required: a. Compute the equivalent units for the conversion cost calculation for March assuming Shirley Processing. Incorporated uses the weighted-average method. b. Compute the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs for March assuming Shirley Processing, Incorporated uses the weighted-average method. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Compute…arrow_forwardPrepare a Production Cost Report Troika Company The production information for Troika's Smoothing department for August is as follows: Work in process Beginning balance: materials Beginning balance: conversion Materials Labor Overhead Cost $ 1,550 2,500 7,441 14,520 7,930 Beginning units Transferred in Transferred in Transferred out Units 650 1,780 1,810 All materials are added at the beginning of the period. The ending work in process is 30% complete as to conversion. Prepare a production cost report for August for the Smoothing Department.arrow_forward
- Mercier Manufacturing produces a plastic part in three sequential departments: Extruding, Fabricating, and Packaging. Mercier uses the weighted-average process costing method to account for costs of production in all three departments. The following information was obtained for the Fabricating Department for the month of September. Work in process on September 1 had 15,000 units made up of the following: Amount Degree of Completion Prior department costs transferred in from the Extruding Department $ 80,250 100% Costs added by the Fabricating Department Direct materials $ 40,500 90% Direct labor 10,200 70% Manufacturing overhead 9,420 35% $ 60,120 Work in process, September 1 $ 140,370 During September, 75,000 units were transferred in from the Extruding Department at a cost of $446,250. The Fabricating Department added the following costs: Direct materials $ 214,200 Direct labor 64,800 Manufacturing overhead 34,380 Total costs added $ 313,380…arrow_forwardThe debits to Work in Process—Assembly Department for April, together with data concerning production, are as follows: April 1, work in process: Materials cost, 3,000 units $ 8,142 Conversion costs, 3,000 units, 40% completed 5,220 Materials added during April, 10,000 units 25,698 Conversion costs during April 32,143 Goods finished during April, 12,000 units 0 April 30 work in process, 1,000 units, 40% completed 0 All direct materials are added at the beginning of the process, and the first-in, first-out method is used to cost inventories. The conversion cost per equivalent unit for April is a.$3.21 b.$2.47 c.$2.80 d.$2.87arrow_forwardCosts per Equivalent Unit and Production Costs The following information concerns production in the Forging Department for June. All direct materials are placed into the process at the beginning of production, and conversion costs are incurred evenly throughout the process. The beginning inventory consists of $18,000 of direct materials. ACCOUNT Work in Process-Forging Department Debit Credit Date Item June 1 Bal., 1,800 units, 60% completed 30 Direct materials, 25,800 units 30 Direct labor 30 Factory overhead 30 Goods transferred, 2 units 30 Bal., 2,800 units, 70% completed Cost per equivalent units of $9.60 for Direct Materials and $3.00 for Conversion Costs. Based on the above data, determine each of the following amounts. If required, round your interim calculations to two decimal places. Round final answers (a-c) to the nearest dollar. 247,680 43,300 33,740 Change in direct materials cost per equivalent unit Change in conversion cost per equivalent unit ACCOUNT NO. Balance Balance…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education