
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
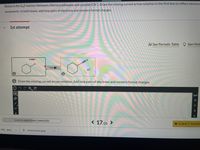
Transcribed Image Text:**Topic: SN2 Reaction Mechanism**
Below is the SN2 reaction between chlorocyclohexane and cyanide (CN⁻). The task is to draw the missing curved arrow notation in the first box to reflect electron movements. In both boxes, you are required to add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- **Left Box**:
- Reactants include chlorocyclohexane with a chlorine (Cl) atom attached to a cyclohexane ring, and a cyanide ion (CN⁻) depicted with a negative charge.
- The curved arrow needs to be drawn to indicate the nucleophilic attack by the cyanide ion on the cyclohexane carbon that is bonded to chlorine, demonstrating the electron movement.
- **Right Box**:
- Products show the cyanide ion now bonded to the cyclohexane ring, with chlorine (Cl⁻) having a negative charge as it leaves.
**Instructions:**
- Add the appropriate curved arrows to depict the electron shifts.
- Include lone pairs of electrons on relevant atoms.
- Denote nonzero formal charges where applicable.
Interactive tools and hints are available to aid in solving the problem. To continue with similar questions, proceed through the sequence.
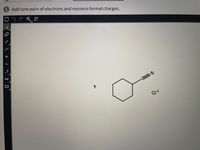
Transcribed Image Text:This image contains a chemical structure along with a task prompt. The prompt says: "Add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges."
### Description of the Chemical Structure:
1. **Ring Structure:**
- The main feature is a six-membered carbon ring, which is a cyclohexane structure.
2. **Functional Groups:**
- Attached to one of the carbon atoms in the ring is a triple bond (alkyne) leading to a nitrogen atom, which is indicative of a nitrile group (C≡N).
3. **Chlorine Ion:**
- Nearby, there is a "Cl" symbol with a negative charge (Cl⁻), indicating the presence of a chloride ion.
### Explanation for Educational Context:
The structure outlines a cyclohexyl nitrile with a chloride counterion. When adding lone pairs of electrons and formal charges, consider:
- **Nitrogen in Nitrile Group:** Typically has one lone pair of electrons.
- **Chloride Ion (Cl⁻):** Should have three lone pairs of electrons as it is in a negatively charged state.
- **Carbon Atoms:** Usually do not carry lone pairs, but it's essential to show any necessary hydrogen atoms for full representation.
- **Formal Charges:** Check all atoms to ensure they have the correct number of valence electrons based on typical bonding patterns (e.g., carbon typically forms four bonds).
Adding these details accurately reflects a full understanding of structural representation for organic compounds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Don't use hand raiting pleasearrow_forwardUsing a electrons and/or lone pairs in the following conjugated system, create a resonance form by moving electrons as far as possible. Be sure to include all lone pairs and charges. Add curved arrow notation to show how electrons will move to form a different resonance form. Ö. Ć G 13arrow_forwardFrom the following list select all the correct statements about the following molecule.arrow_forward
- Resonance structures Maximum allowed tries per question: 5 (15) In the box on the right, draw the best resonance structure of the compound on the le structure on the left to indicate how the electrons reorganize to give the structure on the Launch MarvinJS™ viewer or click image to copy source DI H₂Carrow_forwardK Problem 7 of 25 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. 0:0 :0: H Select to Add Arrows 0:0 :0: Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwarde which of the following benzene compounds will be more reactive than ben vill be less reactive than benzene. (1 point) NO2 NH3 NH2arrow_forward
- Draw two resonance structures better than this. Include curvy arrows to show how you determined the structures. Lone pairs are not shown so include lone pairs in the original and subsequent structures. Label the major, minor, and very minor contributors.arrow_forwardI got step two wrongarrow_forwardThree resonance structures are possible for the structure shown. One resonance form is given. Draw the remaining resonance structures, in any order, including nonbonding electrons. Omit curved arrows. H Structure A H H H Select Draw Rings More C H Erase Structure B Select Draw Rings с More H Erasearrow_forward
- To preview image Click here For the following bonds indicated below, choose which one would have the smallest and highest bond dissociation energy. 1. Smallest Bond Dissociation Energ: ✔ [Select] 2. Highest Bond Dissociation Energy :0 C B C H ΤῊ H A Barrow_forwardStep 3: When a curved arrow starts from a lone pair and points to an adjacent bond, a new z bond will form. Several examples are shown. A- -B* A=B alternatively, in some books A-B" A=B B AEB alternatively, in some books A=B" AEB Read the curved arrow in the mechanism shown and draw the product. Be sure to draw lone pairs. Select Draw Rings More Erasearrow_forwardIn each case below, draw the correct curved arrow(s) that generate(s) the resonance structure(s) shown:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY