
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Below is the perspective drawings for XeF2. Below the structure are arrows indicating the overall direction of polarity or a “0” if the molecule is non polar.
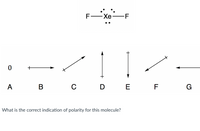
Transcribed Image Text:### Exploring Molecular Polarity
#### Molecule Representation:
The image displays a Lewis structure of a xenon difluoride (\( \text{XeF}_2 \)) molecule. In the structure, a central xenon atom (Xe) is single-bonded to two fluorine atoms (F) on either side. The xenon atom has three lone pairs of electrons.
#### Polarity Indicators:
Below the Lewis structure are several vectors labeled A to G, representing different possible directions and magnitudes of molecular polarity.
- **A:** No arrow (indicates non-polarity)
- **B:** Horizontal arrow pointing right
- **C:** Diagonal arrow pointing towards the upper right
- **D:** Vertical arrow pointing up
- **E:** Vertical arrow pointing down
- **F:** Diagonal arrow pointing towards the lower left
- **G:** Horizontal arrow pointing left
#### Question:
What is the correct indication of polarity for this molecule?
#### Explanation:
The indicated task is to determine the polarity direction for the \(\text{XeF}_2\) molecule using the vectors provided. The molecular geometry of \(\text{XeF}_2\) is linear. Due to symmetry, the dipoles of the F atoms cancel each other out, resulting in no net dipole moment. Therefore, indicator A, which denotes a non-polar molecule, is the correct one.
---
This type of analysis is crucial for understanding molecular interactions, solubility, and physical properties in chemical compounds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the following molecule, indicate the positive and negative ends of the dipole, using the symbol →→→→→→→. Refer to a table of the Pauling electronegativity scale as needed. Select the single best answer. CO The arrow points to the left. The arrow points to the right.arrow_forwardFollowing is a molecule with polar bonds whose shape was obtained using the VSEPR theory. Specify the molecular shape of this molecule, and whether the molecule is polar or nonpolar. (Hint: In terms of polarity, see whether the dipoles in the molecule cancel or not. A molecule containing polar bonds can be nanpolar if the dipoles cancel each other. You can imagine the dipoles as ropes pulling on the central atom–If the pulls cancel each other, that is, the central atom cannot move, then the molecule is nonpolar. If on the other hand the opposite is true, then the molecule is polar.) O trigonal pyramidal shape, nonpolar O trigonal planar shape, nonpolar O tetrahedral shape, polar O trigonal pyramidal shape, polar O trigonal planar shape, polararrow_forwardThe VSEPR diagram for PC15 is shown below. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. :ĊI: :CI—P™ :CI: CI: CI: a) Name the VSEPR shape. b) Identify the polarity of the bonds. Explain how you know. (AEN for P = 2.1, AEN for Cl = 3.0) c) Identify the polarity of the molecule. Explain how you know. d) Identify the dominant intermolecular force present between molecules of PCI 5. Explain how you know.arrow_forward
- Mark the following statements as true or false. A molecule with very polar bonds can be nonpolar. blank The electrons in a polar bond are found nearer to the more electronegative element. blank Fluorine is very polarizable. blank Covalent bonds are partially ionic because of polarizability of atoms. blank Kr and Sr2- are isoelectronic.arrow_forward3. Draw the Lewis structure for SH₂F3 (S is central). Predict the molecular geometry and bond polarity. Draw two perspective drawings, one where the SH₂F3 molecule is polar and one where the SH₂F3 molecule is nonpolar.arrow_forwardFor each of the compounds below, A , C and D state whether the molecule is polar or nonpolar. H. Ö=c=Ö ÇI ÇI C D Cll Cl ci Harrow_forward
- Below is the perspective drawings for SiCl4. Below the structure are arrows indicating the overall direction of polarity or a “0” if the molecule is non polar.arrow_forwardplease don't provide hand writtin solution....arrow_forwardIn 3-5 sentences, describe the differences between molecules that are polar and those that are non polar.arrow_forward
- [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Draw a Lewis structure for the C₂H6O molecule, using the connectivity shown in the spacefilling model in the window. (Gray = C; white = H; red = 0; blue = N; dark green = Cl; brown = Br; light green= F; purple = I; yellow = S; orange = P.) The number of C-H bonds = Submitted The number of O-H bonds = 20 The number of C-C single bonds = The number of C-O single bonds = The total number of lone pairs = $ 4 R F 288 V %6 5 PA T Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support 6 I G MacBook Air B pe Y H & 7 N F7 U J H 8 1 M ( 9 K V 1 ) O L P Previous ¡ Email Instructor Save and Exit Next [ 11 1 Darrow_forwardPredict the ideal bond angles around each central atom in this molecule. carbon: O : N=C—Ñ—H nitrogen: -I Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY