Question
thumb_up100%
Below is a simplified diagram of a generator, looking at it head-on. The coil is rotating clockwise.
(a) At what position is it cutting the field lines fastest?
(b) At what position is its vertical velocity zero?
(c) Why is no current induced when the coil is vertical?
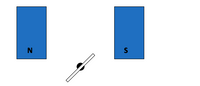
Transcribed Image Text:N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The figure below is a graph of the induced emf versus time for a coil of N turns rotating with angular speed w in a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular to the coil's axis of rotation. Copy thi sketch (on a larger scale), and on the same set of axes show the graph of emf versus t. On the same graph, plot the following changes and provide answers to the corresponding questions. & (mV) 10 -5 -10 V 2 3 t (ms) (a) The number of turns in the coil is doubled which causes the amplitude to ---Select--- (b) The angular speed is doubled which causes the amplitude to ---Select--- and the period to ---Select--- and the period to ---Result--- 0 (c) The angular speed is doubled while the number of turns in the coil is halved which causes the amplitude to ---Result--- and the period to ---Result--- Garrow_forwardWhen you move a magnet through a 1 loop coil you detect a voltage of 0.001 volts, what voltage would you read if you move the same magnet at the same velocity through a coil with 1000 loops (assume the radius of the loops in the coil is the same as the one in the single loop wire)arrow_forwardShown in the following figure is a long, straight wire and a single-turn rectangular loop, both of which lie in the plane of the page. The wire is parallel to the long sides of the loop and is 0.5 m away from the closer side. At an instant when the voltage induced in the loop is 2.5 V, what is the time rate of change of the current in the wire? 0.50 m] 3.0 m 0.50 m a. What is the expression for magnetic field B due to the current I in the long, straight wire, at distance r away from the wire? B = . Give your answer in terms of given variables (I, r) and physical and numerical constants (o, T, ke, and/or c). Spell out Greek letters and use underscore ("_") for subscripts. b. Because the magnetic field is not uniform, you will have to use integration to calculate the magnetic flux, = = [₁ BdA. Find the magnetic flux through the loop as a function of I ( will be proportional to I, as shown below; find the coefficient, in base SI units). Hint for (b) Φ I. Give your answer in terms of given…arrow_forward
- Two coils are placed near each other as shown in the figure below. The coil on the left is connected to a battery and a switch, and the coil on the right is connected to a resistor. (i) What is the direction of the current in the resistor at an instant immediately after the switch is thrown closed? left right The current is zero. (ii) What is the direction of the current in the resistor after the switch has been closed for several seconds? left right The current is zero. (iii) What is the direction of the current in the resistor at an instant after the switch has then been thrown open? left right The current is zero.arrow_forwardInduced EMF Below is a closed conducting loop within a magnetic field (for direction see picture). The loop is a circle with a radius of r = 5.00 cm. The magnetic field is decreasing in the direction shown at a rate of dB/dt = 157.0 mT/s. The circle wire has 305.0 loops around it. The wire has a total resistance of R = 2.80 Ohms. Magnetic Field (into the page) 8) What is the induced current around the wire in this system? (use a negative value for a clockwise current) Make sure to give your answer in an appropriate number of significant figures as well as including units with your answer. Your Answer: Answer units PLEASE TAKE OUT TRASH AT EOS IGarrow_forwardA 40 turn conductive loop encloses an area of 0.55 m?. At what constant rate should the magnetic field directed perpendicular to the loop change with time if the induced emf is to be 4.25 Volts? Consider only positive numbers here in your answer.arrow_forward
- What is the direction of the induced emf in the circular loop below? wire is entering a constant magnetic field region (A) ▼ (B) radially outward (C) clockwise (D) counterclockwise (E) radially inwardarrow_forwardThe current in a long solenoid of radius 6 cm and 22 turns/cm is varied with time at a rate of 3 A/s. A circular loop of wire of radius 8 cm and resistance 7 0 surrounds the solenoid. Find the electrical current induced in the loop (in HA). HAarrow_forwardImagine that we have a rectangular loop of wire (with a total resistance of 1.6 ohms) placed in a magnetic field that dies off as: 0.3*e-10t T into the page. What is the induced current in the coil at 0.002 s? The loop has a length of 1.7 m and a width of 1.7 m.arrow_forward
- A 36 turn conductive loop encloses an area of 0.69 m2. At what constant rate should the magnetic field directed perpendicular to the loop change with time if the induced emf is to be 4.12 Volts? Consider only positive numbers here in your answer.arrow_forwardSuppose that a 0.25 m radius, 500 turn coil produces an average emf of 11300 V when rotated one-fourth of a revolution in 4.09 ms, starting from its plane being perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the peak emf generated by this coil, in volts?arrow_forwardScreenshots of the physics problem are provided belowarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios