
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A uniform board of length L and mass M lies near a boundary that separates two regions. In region 1, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the board and the surface is μ1, and in region 2, the coefficient is μ2. The positive direction is shown in the figure.
Find the net work W done by friction in pulling the board directly from region 1 to region 2. Assume that the board moves at a constant velocity.b Express your answer in terms of M, g, L, μ1, and μ2.
What is the total work done by the external force in pulling the board from region 1 to region 2? (Again, assume that the board moves at constant velocity.)
Express your answer in terms of M, g, L, μ1, and μ2.
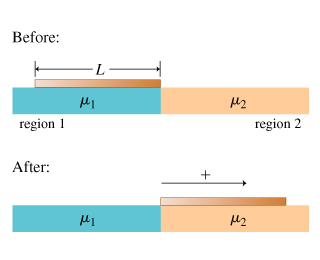
Transcribed Image Text:Before
L
region
region
After:
+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- H, Please explain and answer this question for me:thank you! Why does the shape of the ramp not affect the Total Energy in the non-friction case and Why does the shape of the ramp affect the Total Energy in the friction case?arrow_forwardAn archery bow is drawn a distance d = 0.75 m and loaded with an arrow of mass m = 0.067 kg. The bow acts as a spring with a spring constant of k = 195 N/m, and the arrow flies with negligible air resistance. To simplify your work, let the gravitational potential energy be zero at the initial height of the arrow. a. How fast, in meters per second, will the arrow be traveling as it leaves the bow? b. If the arrow is shot at an angle of θ = 45° above the horizontal, how high, in meters above the initial height, will the arrow be when it reaches its peak?arrow_forwardA process occurs in which a system's potential energy decreases while the system does work on the environment. Does the system's kinetic energy increase, decrease, or stay the same? Or is there not enough information to tell? Explain. Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. positive negative zero unknown ‒‒‒‒‒‒‒‒‒‒ only the potential energy does the work the system does work on the environment Submit the mechanical energy does not change the change in potential energy may be greater as well as less than the work the system does on the environment the body cannot do more work than the change of its potential energy Request Answer The change in kinetic energy is because Reset Helparrow_forward
- A 100 kg block is pulled at a constant speed of 5.5 m/s across a horizontal floor by an applied force of 137 N directed 37° above the horizontal. What is the rate at which the force does work on the block? Warrow_forwardConsider a system of a cliff diver and the earth. The gravitational potential energy of the system decreases by 23,000 J as the diver drops to the water from a height of 44.0 m. Determine her weight in newtons. Narrow_forwardLearning Goal: Recall that the work W done by a constant force Fat an angle to the displacement Ar is W = F· A7 = FAr cos 0. The vector magnitudes F and Ar are always positive, so the sign of Wis determined entirely by the angle between the force and the displacement. Figure AP 1 of 1arrow_forward
- What's the answer for all the parts?arrow_forwardUsing energy considerations, calculate the average force (in N) a 63.0 kg sprinter exerts backward on the track to accelerate from 2.00 to 7.00 m/s in a distance of 25.0 m, if he encounters a headwind that exerts an average force of 30.0 N against him. N Additional Materials O Readingarrow_forwardA factory worker pushes a 31.2 kg crate a distance of 4.9 m along a level floor at constant velocity by pushing downward at an angle of 28° below the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and floor is 0.25. Part C How much work is done on the crate by friction during this displacement? Express your answer using two significant figures. W₁ = 416.30 Submit 1 ( Templates Symbols undo rado reset keyboard shortcuts help ΑΣΦΑ / С Part D X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Wnf= Previous Answers Request Answer How much work is done by the normal force? Submit Templates Symbols undo do reset keyboard shortcuts help ΑΣΦΑ / C Request Answer J Jarrow_forward
- A small block with mass 0.0400 kg is moving in the xy-plane. The net force on the block is described by the potential-energy function U(x, y) = (5.70 J/m²)x² − (3.90 J/m³)y³. Part A What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block when it is at the point x = 0.27 m, y = 0.55 m? Express your answer with the appropriate units. a = Submit Part B Value 0 = Request Answer Units ΑΣΦ www. What is the direction of the acceleration of the block when it is at the point x = 0.27 m, y = 0.55 m? Express your answer in degrees. ? ? counterclockwise from the +x-axisarrow_forwardA mechanic pushes a 3.20 × 103 - kg car from rest to a speed of v, doing 5, 340 J of work in the process. During this time, the car moves 20.0 m. Neglecting friction between car and road, find v and the horizontal force exerted on the car. (a) the speed v m/s (b) the horizontal force exerted on the car (Enter the magnitude.) Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON