
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
a. What is the
b. What is the kinetic energy before and after the collision?
c. What is the total linear momentum before and after the collision?
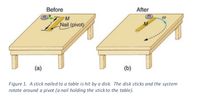
Transcribed Image Text:Before
After
m
M
Nail (pivot)
(a)
(b)
Figure 1. Astick nailed to a table is hit by a disk. The disk sticks and the system
rotate around a pivot (a nail holding the stick to the table).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 5 kg car traveling at 3 m/s collides with a 4 kg cart traveling towards it at 4 m/s. After the bounce collision the 5 kg cart is traveling at 1 m/s in the opposite direction. a. Draw an IF Chart of the scenario. b. Calculate the change in momentum for the 5 kg car. c. What is the final speed of the 4 kg car?arrow_forward1. A 1.50 kg cart on an air track collides with a 0.500 kg cart that is stationary. The initial velocity of the heavier cart is measured to be 2.00 m/s. After the collision, the heavier cart velocity is measured at 1.05 m/s and the lighter cart has a velocity of 2.95 m/s. Calculate the total momentum of the carts before and after this collision and do the same for the kinetic energy of the carts. Allowing for 5% experimental error, was this an elastic or inelastic collision? Explain your reasoning. Pinitial = Pfinal = KEinitial = KE final =arrow_forward4. A golf ball of mass 50 grams is struck and has a velocity of 70 m/s when it leaves the tee. The golf ball then hits a fence and comes to a stop in 0.02 seconds.a. What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it comes off the tee?b. What is the momentum of the ball as it comes off the tee?c. What is the stopping force acting on the ball?arrow_forward
- A 1.0 kg sphere moves to the right at 3.0 m/s and collided head on with a 3kg sphere moving at 1.0 m/s in the opposite direction. If the collision is elastic, the velocity of the heavier sphere after the collision is equal to what? A. 1.0 m/s to the left B. 3.0 m/s to the left C. 1.0 m/s to the right D. 3.0 m/s t o the right E.0arrow_forward4. A 2kg block and a 3kg block collide with the velocities shown. a) Find the momenta of the blocks before and after the collision, and fill in the table. Include the correct sign. b) Find the velocity of the 3kg block after the collision. 2kg 7m/s 8m/s 2kg 1m/s 3kg B 3kg V PAi P Bi PAf P Bfarrow_forward7. For a given experiment, the students know how much the angular momentum of the system has changed after a specific time interval. The students create a series of graphs for each experiment. The students must determine if the change in angular momentum of a given system is equal to the angular impulse applied to the system. How should the students use data from a particular graph to make the determination by using only the graph? A Calculate the slope of an angular velocity versus time graph and see if it equals the angular acceleration. Calculate the slope of an angular position versus time graph and see if it equals the average angular velocity. Calculate the slope of a graph of the change in angular momentum versus the product of the net torque and C the time interval and determine if the slope is equal to one. Calculate the slope of an angular momentum versus time graph and see if it equals the net torque.arrow_forward
- An empty freight car with a mass of 10,000 kg rolls at 5 m/s along a level track and collides with a loaded car with a mass of 20,000 kg, standing at rest with brakes released. Friction can be neglected. If the cars couple together, find their speed after the collision. a. Find the decrease in kinetic energy as a result of the collision. b. With what speed should the loaded car be rolling towards the empty car for both to be brought to rest by the collision? (full solution)arrow_forwardA spring with relaxed length 0.30 m and spring constant 1.8 N/m rests horizontally on a frictionless table and is anchored frmly to a wall on one side. You press a 400 g block into the other side until the spring length is 0.16 m and then let go. a.) What will the momentum of the block be when it departs from the spring? (Assume contact ceases when the spring is relaxed.) b.) If the table were no longer frictionless and the block-table interface had a kinetic coeffcient of friction of 0.1 what then would the momentum of the block be when it departs from the spring?arrow_forwardConsider a medicine ball with mass 2kg and initial velocity of 1.2 m/s. During 1.5s a force of 12N is applied to the ball during an exercise prescribed for an elderly patient recovering muscle strength after a surgery. a. Determine the initial momentum of the ball b. Determine the impulse applied to the ball c. Determine the change of momentum of the ball after the force was applied d. What is the final velocity of the ballarrow_forward
- As part of a carnival game, a mp 0.578 kg ball is thrown at a stack of 17.3 cm tall, 0.343 kg objects and hits with a = 11.8 m/s. Suppose that the ball strikes the topmost object. Immediately after the collision, m. perfectly horizontal velocity of vp.i the ball has a horizontal velocity of Ub.f = 3.85 m/s in the same direction, the topmost object has an angular velocity of @. = 2.43 rad/s about its center of mass, and all the remaining objects are undisturbed. Assume that the ball is not rotating and that the effect of the torque due to gravity during the collision is negligible. If the object's center of mass is located r = 12.1 cm below the point where the ball hits, what is the moment of inertia I, of the object about its center of mass? b,i I, = 0.228 kg-m2arrow_forwardA car is stopped for a traffic signal. when the light turns green, the car accelerates, increasing its speed from 0 to 4.90 m/s in 0.812 s. A. what is the magnitude of the linear impulse experienced by a 72.0 -kg passenger in the car during the time the car accelerates? B. what is the magnitude of the average total force experienced by a 72.0-kg passenger in the car during the time the car accelerates?arrow_forwardAn empty freight car with a mass of 10,000 kg rolls at 5 m/s along a level track and collides with a loaded car with a mass of 20,000 kg, standing at rest with brakes released. Friction can be neglected. If the cars couple together, find their speed after the collision. a. Find the decrease in kinetic energy as a result of the collision. b. With what speed should the loaded car be rolling towards the empty car for both to be brought to rest by the collision? Solution FBD and Formula Requiredarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON