
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:rch
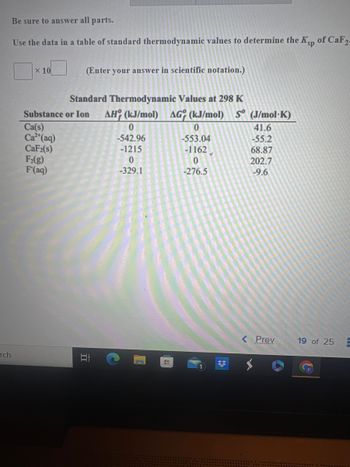
Be sure to answer all parts.
Use the data in a table of standard thermodynamic values to determine the Ksp of CaF2-
X 10
Substance
Ca(s)
Ca²+ (aq)
CaF2(s)
F₂(g)
F(aq)
(Enter your answer in scientific notation.)
Standard Thermodynamic Values at 298 K
or Ion AH (kJ/mol) AG (kJ/mol) S (J/mol-K)
II
0
-542.96
-1215
0
-329.1
HI
0
-553.04
-1162
0
-276.5
3
41.6
-55.2
68.87
202.7
-9.6
< Prev
19 of 25 E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Do not give handwriting solution. Calculate the entropy change, ΔS, for the following processes. If needed, Cp(O2)= 29.4 J mol-1 K-1 and Cp(CO2) = 37.1 J mol-1 K-1.(a) The pressure of one mole of O2(g) is increased from P to 2P at 298 K.(b) The temperature of one mole of CO2(g) is increased from 298 K to 355 K at aconstant volume of 20.0 L.arrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2NH3(g) + 3N₂O(g) → 4N₂ (9) + 3H₂O(g) for which AH° = − 879.5 kJ and AS° = 288.1 J/K at 298.15 K. 1. Calculate the entropy change of the UNIVERSE when 2.344 moles of NH3(g) react under standard conditions at 298.15 K. ASuniverse = J/K 2. Is this reaction reactant or product favored under standard conditions? 3. If the reaction is product favored, is it enthalpy favored, entropy favored, or favored by both enthalpy and entropy? If the reaction is reactant favored, choose 'reactant favored'.arrow_forwardIce cubes at 0°C are poured into a glass that initially contains 150 g of liquid water at 20°C. The contents of the glass are gently stirred. After a short time, some of the ice melts, and the liquid cools to 0°C. No appreciable heat exchange occurs between matter inside the glass with matter outside the glass during this process. (a) Calculate the entropy change of the universe during the process. Use only the following data: the constant pressure heat capacity of liquid water is approximately 4.18 J/(g K) over the temper- ature range of interest. You may further presume that the density of water is constant over the temperature range. (b) If the same process were performed reversibly, how much useful work would be obtained from it? Any required heat exchange to achieve the same final state reversibly should be with matter outside the glass, which are at 20°C.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)—2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) for which AH° = 368.6 kJ and AS° = 15.30 J/K at 298.15 K. (1) Calculate the entropy change of the UNIVERSE when 1.759 moles of NaOH(aq) react under standard conditions at 298.15 K. ASuniverse= J/K (2) Is this reaction reactant or product favored under standard conditions? (3) If the reaction is product favored, is it enthalpy favored, entropy favored, or favored by both enthalpy and entropy? If the reaction is reactant favored, choose 'reactant favored'. Submit Answerarrow_forwardPlease provide fullarrow_forwardConsider the reaction Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl₂ (s) + H₂(g) for which AH = -7.400 kJ and AS = 107.9 J/K at 298.15 K. 1. Calculate the entropy change of the UNIVERSE when 2.385 moles of Fe(s) react under standard conditions at 298.15 K. ASuniverse J/K 2. Is this reaction reactant or product favored under standard conditions? 3. If the reaction is product favored, is it enthalpy favored, entropy favored, or favored by both enthalpy and entropy? If the reaction is reactant favored, choose 'reactant favored'. Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
- What would the entropy be for a system with 6.05E+1 microstates, in J/mol-K?arrow_forwardThe pressure dependence of G is quite different for gases and condensed phases. Calculate ΔGm for the process (C,solid,graphite,1bar,298.15K)→(C,solid,graphite,300.bar,298.15K) The density for graphite is 2250 kg⋅m−3 Calculate ΔGm for the process (He,g,1bar,298.15K)→(He,g,300.bar,298.15K)arrow_forward"M" represents a metallic element. "X" represents a nonmetallic element. Calculate ΔH for the process M3X4(s) ⟶ 3M(s) + 2X2(g) from the following information: M(s) + ½X2(g) ⟶ MX(s) ΔH°= -286.2 kJ 3MX(s) + ½X2(g) ⟶ M3X4(s) ΔH°= -84.3 kJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY