
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
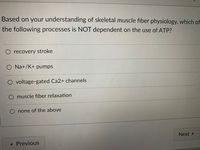
Transcribed Image Text:Based on your understanding of skeletal muscle fiber physiology, which of
the following processes is NOT dependent on the use of ATP?
O recovery stroke
O Na+/K+ pumps
O voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
O muscle fiber relaxation
none of the above
Next
« Previous
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- One of your colleagues has obtained a sample of muscle phonghorytaseb that is known to be relatvely inactive She has approached you for advice on how to set up an appropriate anay. She has the following items avalable, not al of which are appropriate for thi study. Help her out by selecting the items that she should une and what their purpose in the y. and then eplain why each of the oer item wodnot be uset 1. 100 MAMP 2. 100 uM GTP 1. 100 M ge 4. 100 uM gose phesphate S. Branched gon 4Unbranched gvoopen 7.50 m HEPES buffer, p75 a.50 m potansium phonghate bufter, piH75 wite outa short elanation for each of the above items, and upload vour anwers by the due dane.arrow_forwardResistance-trained skeletal muscles show O Increased size and increased mitochondrial density O Increased size and decreased twitch contraction time Increased size and increased type II fiber proportion O Decreased size and decreased mitochondrial densityarrow_forwardIn which type of muscle fibers is ATP synthesized aerobically in mitochondria? smooth cardiac skeletal all of the above 2. In which types of muscle fibers are action potentials transmitted from one cell to the next through gap junctions? unitary smooth and cardiac cardiac and skeletal skeletal and smooth 3. All types of muscle have actin and myosin, but not all types have sarcomeres." True Falsearrow_forward
- Seconds Put the steps of excitation-contraction in order: 1 Myosin "heads" pivot, cause [ Choose ] Calcium is taken back up and the muscle relaxes Action potential triggers Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum ACh produces large EPSP in muscle fiber 4 Muscle contracts Binding of Ca2+ to troponin causes myosin to bind to actin 5. EPSP evokes muscle action potential Alpha motor neurons release ACh Myosin "heads" pivot, cause filaments to walk along filament 7 [ Choose ) 8. [Choose ]arrow_forwardIn which of the following locations would you most likely find the tissue known as perimysium? O surrounding the biceps brachii muscle O wrapped around a myofilament O surrounding a muscle fascicle O around an individual muscle cellarrow_forward44.arrow_forward
- The muscle fibers with the fastest contractions are O slow oxidative O fast oxidative O fast glycolytic O fasciclesarrow_forwardDetermine whether the following description is common to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle or both skeletal and cardiac muscle. increase in tension during contraction of the muscle organ involves recruitment of other cells is primarily under the control of the autonomic nervous system all cells depolarize and contract during every contraction of the muscle organ different neurotransmitters can increase or decrease the rate of contraction action potentials begin electrical depolarization by a voltage-gated Na+ channel 1. skeletal muscle 2. cardiac muscle increase in cytosolic 3. skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle calcium increases tension in muscle cells prolonged depolarization is due to Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane contraction is not under the control of hormones relaxation occurs when cytosolic calcium is reduced to resting levels increase in tension during contraction of single cells is associated with a higher frequency of action potentialsarrow_forwardWhich of the following would NOT occur as a result of regular exercise to a specific muscle group (assume you are resting now, but have been working this muscle group)? more capillaries will grow into the area the muscle cells will build more mitochondria O the muscle cells will build fewer contractile proteins O the muscle cells will increase their glycogen storesarrow_forward
- As an action potential moves along the sarcolemma, the brief opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels will allow Na+ to rush into the muscle cell, causing the inside of the membrane at that location to become more ________. positive negativearrow_forward61.arrow_forwardIn which type(s) of muscle cells does each cell have its own neuromuscular junction? skeletal only unitary smooth and skeletal skeletal and cardiac 2. The follow is NOT true of CARDIAC muscle fibers: - connected by gap junctions - include pacemaker cells that can produce produce action potentials at regular intervals without innervation - without calcium cross bridge cycles will not occur and fibers will not shorten - each cell in a motor unit has a neuromuscular junction with the same motor neuron actin and myosin filaments are arranged in sarcomeres produce greater force when stretched than at resting length 3. Match the following: -Skeletal muscle -Cardiac muscle -Smooth muscle Can maintain prolonged isometric contractions with very little energy Striated muscle fibers with gap…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education