
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Based on the zinc / copper electrochemical cell in Table 10.1, which statement is
correct?
O Zinc is the anode, copper is the cathode and the overall cell voltage is negative.
O Zinc is the cathode, copper is the anode and the overall cell voltage is negative.
Zinc is the cathode, copper is the anode and the overall cell voltage is positive.
O Zinc is the anode, copper is the cathode and the overall cell voltage is positive.
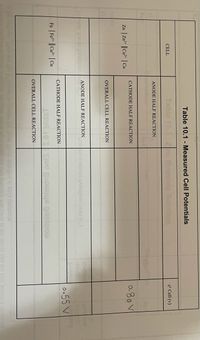
Transcribed Image Text:Table 10.1 - Measured Cell Potentials
Solution
CELL
8° Cell (v)
ANODE HALF REACTION
CATHODE HALF REACTION
Zn | Zn || Cu²* | Cu
o.80 V
OVERALL CELL REACTION
ANODE HALF REACTION
(a dire) anobosl oborlis ol
0.55 V
CATHODE HALF REACTION
Fe | Fe2 || Cu² | Cu
noituloa ohimo18 onisS.or bldsT
OVERALL CELL REACTION
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Write the cell notation for an electrochemical cell consisting of an anode where Cr (s) is oxidized to Cr3+ (aq) and a cathode where Cr3+ (aq) is reduced to Cr2+ (aq) at a platinum electrode . Assume all aqueous solutions have a concentration of 1 mol/L and gases have a pressure of 1 bar.arrow_forwardIn a electrochemical cell, which of the following statements is true? In a galvanic cell, the substance at the anode loses electrons but in a electrolytic cell, the substance at the cathode loses electrons. The substance at the anode loses electrons. The substance in the salt bridge loses electrons. The substance at the cathode loses electrons.arrow_forwardA galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2103 (aq) +12H (aq)+5Co (s) → I2 (s)+6H₂O (1)+5Co²+ (aq) + Suppose the cell is prepared with 0.361 MIO3 and 7.57 M H in one half-cell and 2.53 M Co Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ☐ μ ロ・ロ 2+ in the other.arrow_forward
- A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3 Ca(s) → 2Cr(s) + 3Ca²+ (aq) Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.35 M Cr³+ in one half-cell and 0.492 M Ca2+ in the other half. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Cr3+ (aq) + 3e → Cr(s) Ered = -0.744 V Ca2+ (aq) + 2e → Ca(s) Ered = -2.868 V The standard cell potential (E°) for this galvanic cell is [Select] V. There are [ Select] + moles of electrons transferred during to operate this galvanic cell. Under these conditions, the reaction quotient is [Select] and the cell volatage is [Select] V. In order to increase the cell voltage for this cell, [Select ]arrow_forwardA galvanic (voltaic) cell consists of an electrode composed of aluminum in a 1.0 M aluminum ion solution and another electrode composed of gold in a 1.0 M gold(III) ion solution, connected by a salt bridge. Calculate the standard potential for this cell at 25 °C. Refer to the list of standard reduction potentials. Excell Varrow_forwardA galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ Cu2+ (aq) + Zn (s) → Cu (s) + Zn²+ (aq) 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 3.51 M Cu²*+ in one half-cell and 1.20 M Zn²+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 日 ☐ x10 ☐ μ ロ・ロarrow_forward
- Thomas Edison invented an electric meter that was nothing more than a simple coulometer, a device to measure the amount of electricity passing through a circuit. In this meter, a small, fixed fraction of the total current supplied to a household was passed through an electrolytic cell, plating out zinc at the cathode. Each month the cathode could then be removed and weighed to determine the amount of electricity used. If 0.25% of a household’s electricity passed through such a coulometer and the cathodeincreased in mass by 1.83 g in a month, how many coulombs of electricity were used during that month?arrow_forwardCalculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardWhat is the maximum voltage that can be produced by a galvanic cell with the following electrodes? Copper and Lead Zinc and Lithiumarrow_forward
- How long would it take to deposit 7.54 g of copper (molar mass 63.55 g/mol) at the cathode of an electrolytic cell, if a current of 15.9 A is passed through an aqueous solution of CuSOa? 19.4 min 32.2 min 24.0 min 33.9 min 26.8 minarrow_forward7. Fig. 7.1 shows a simplified diagram of the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution, used to produce chlorine in industry. concentrated sodium chloride solution anode cathode gas 111 chlorine gas permeable membrane hydrogen Fig. 7.1 The balanced equation for the overall chemical change that occurs in the process shown in Fig. 7.1 is 2NaCl + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + Cl₂ + H₂ a. Show that the relative formula mass of sodium chloride is 58.5 sodium hydroxide solution b. Calculate the number of moles in 234g of sodium chloride. Show your working. Number of moles= Volume= c. Calculate the volume of chlorine molecules produced at room temperature and pressure, when 234g of sodium chloride are electrolysed. (1 mole of chlorine molecules has a volume of 24 dm³ at room temperature and pressure). Show your workingarrow_forwardYou are a bioengineer designing a new type of pacemaker. Which type of Galvanic cell would be best for you to use in this new device?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY