
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
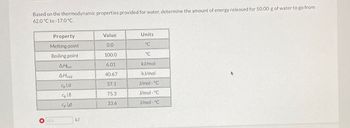
Transcribed Image Text:Based on the thermodynamic properties provided for water, determine the amount of energy released for 50.00 g of water to go from
62.0 °C to -17.0 °C.
Property
Melting point
Boiling point
12.3
AHfus
Hvap
Cp (s)
Cp (1)
Cp (g)
kJ
Value
0.0
100.0
6.01
40.67
37.1
75.3
33.6
Units.
°C
°C
kJ/mol
kJ/mol
J/mol · °C
J/mol · °C
J/mol °C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Steps involved in the process!
VIEW Step 2: Calculation for number of moles of water!
VIEW Step 3: Energy lost in cooling of water up to its melting point
VIEW Step 4: Energy during freezing of water
VIEW Step 5: Energy lost in cooling of ice up to its final temperature
VIEW Step 6: Calculation for total energy lost!
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Based on the thermodynamic properties provided for methanol (below), select from the following list the equation(s) necessary to calculate the amount of energy needed for 5.0 kg of methanol to go from -64°C to 88°C. Property Value Units Melting point -94 °C Boiling point 65 °C AHus 3.18 kJ/mol ΔHap 37 kJ/mol G (s) 48.7 J/mol ·°C 81.1 J/mol °C Go (8) 43.8 J/mol ·°Carrow_forwardBased on the thermodynamic properties provided for water, determine the amount of energy needed for 2.20 kg of water to go from -14.0 °C to 74.0 °C. 6.50 Property Melting point Boiling point AHfus AHvap Cp (s) Cp (1) Cp (g) kJ Value 0.0 100.0 6.01 40.67 37.1 75.3 33.6 Units °C °℃ kJ/mol kJ/mol J/mol • °C J/mol • °C J/mol • °Carrow_forwardBased on the thermodynamic properties provided for water, determine the amount of energy needed for 2.20 kg of water to go from -17.0 °C to 78.0 °C. Property Melting point Boiling point AHfus AHvap C(s) 5(1) 5 (8) kJ Value 0.0 100.0 6.01 40.67 37.1 75.3 33.6 Units °C °C kJ/mol kJ/mol J/mol - °C J/mol · °C J/mol · °Carrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamic properties provided for methanol (below), select from the following list the equation(s) necessary to calculate the amount of energy needed for 5.0 kg of methanol to go from -64°C to 88°C. Property Value Units Melting point -94 °C Boiling point 65 °C AHfus 3.18 kJ/mol AHvap 37 kJ/mol 615) 48.7 J/mol.°C Cp (1) 81.1 J/mol.°C 5 (8) 43.8 J/mol °C Choose one or more: A. q = n(43.8 J/mol °C)AT, where AT is negative B. q=n(48.7 J/mol ·°C)AT, where AT is negative C. q= n(81.1 J/mol -°C)AT, where A Tis negative D. q = n(43.8 J/mol °C)AT, where A Tis positive E. q=n(-3.18 kJ/mol) F. q- n(37 kJ/mol) G. q=n(-37 kJ/mol) H. q- n(3.18 kJ/mol) 1.q=n(48.7 J/mol °C)AT, where AT is positive J.q=n(81.1 J/mol °C)AT, where A Tis positivearrow_forwardBased on the thermodynamic properties provided for water, determine the amount of energy needed for 2.00 kg of water to go from -16.0 °C to 69.0 °C. Property Melting point Boiling point AHfus AHvap Cp (s) Cp (1) Cp (8) kJ Value 0.0 100.0 6.01 40.67 37.1 75.3 33.6 Units °℃ °C kJ/mol kJ/mol J/mol. °C J/mol • °C J/mol. °Carrow_forwardPlease answer question 3.arrow_forward
- Octane(C3H18) is a hydrocarbon found in crude oil. Thermochemical data for octane is provided below. The total change in enthalpy is 15.94 kJ when heating 0.2500 moles of octane from -70.00°C to 100.0°C. Determine the AHfusion. Melting point: -57.00 °C Boiling point: 126.0 °C J Csolid : 185.0 °C mol J Cliquid: 254.0 °C mol J Cgas: 250.0 °C mol AHvap: 34.40 kJ/ mol Molar mass: 114.23 g/mol 0.2693 kJ/mol 4.720 kJ/mol O 21.50 kJ/mol 0.2540 J/molarrow_forwardBased on the thermodynamic properties provided for water, determine the energy change when the temperature of 1.05 kg of water decreased from 117 °C to 56.5 °C. Property Value Units Melting point 0 °C Boiling point 100.0 °C ΔHfus 6.01 kJ/mol ΔHvap 40.67 kJ/mol cp (s) 37.1 J/mol · °C cp (l) 75.3 J/mol · °C cp (g) 33.6 J/mol · °Carrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 55.0 g of liquid water from 25°C to 99°C. The specific heat of liquid water is 1.00 cal/g °Carrow_forward
- How many joules of heat are required to heat 25.2 g of ethyl alcohol from the prevailing room temperature, 22.5 oC, to its boiling point, 78.5 oC?arrow_forwardCalculate the heat required to bring 10.0 g CCl2F2 from -29.8°C as a liquid to the gas phase at 10.0°C. (molar mass = 120.91 g/mol) Cs (gas) = 0.074 kJ/mol·K ΔHvap = 20.1 kJ/mol ΔHfus = 4.14 kJ/molarrow_forwardBased on the thermodynamic properties provided for water, determine the energy change when the temperature of 1.45 kg of water decreased from 109 °C to 40.5 °C. Property Value Units Melting point 0 °C Boiling point 100.0 °C ΔHfus 6.01 kJ/mol ΔHvap 40.67 kJ/mol cp (s) 37.1 J/mol · °C cp (l) 75.3 J/mol · °C cp (g) 33.6 J/mol · °C kJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY