
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Based on the experience of Russia and China over the past few years, Western businesses are
concerned that the budget and the inflation rate in Freedonia will spiral out of control. Because
of these fears, they have been hesitant to invest in Freedonia. In an attempt to reassure foreign
investors, the Freedonian government has published an economic plan for the next several
years.
The government thinks that real GDP can continue to grow at a rate of 3.5 percent for at least
the next decade. All tax revenue is generated by a value-added tax that collects 20 percent of
GDP. The government proposes to keep this tax rate constant far into the future, and also to let
its purchases and transfer payments grow by 3.5 percent per year in real terms, so that they
remain fixed as a fraction of GDP. The government promises to bring the inflation rate down to
2.5 percent per h 2.5 percent inflationyear within two years, and it has already adopted a
money growth rate that is consistent wit
a. What rate of money growth is consistent with 2.5 percent inflation? Why?
b.
Given this rate of money growth, how much revenue will the government
generate from money growth this year?
Calculate the conventional government budget deficit.
C.
d.
Calculate the primary government budget deficit.
e.
Calculate the real government budget deficit.
f.
Do you think the government can keep all of the promises listed above? If
yes, why? If no, why not, and how might the actual results differ from the promised
results?
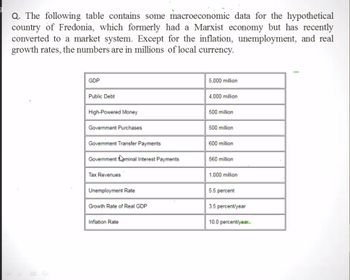
Transcribed Image Text:Q. The following table contains some macroeconomic data for the hypothetical
country of Fredonia, which formerly had a Marxist economy but has recently
converted to a market system. Except for the inflation, unemployment, and real
growth rates, the numbers are in millions of local currency.
GDP
Public Debt
High-Powered Money
Government Purchases
Government Transfer Payments
Government Nominal Interest Payments
Tax Revenues
Unemployment Rate
Growth Rate of Real GDP
Inflation Rate
5,000 million
4,000 million
500 million
500 million
600 million
560 million
1,000 million
5.5 percent
3.5 percent/year
10.0 percent/year.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following is FALSE? The classical dichotomy would suggest that money has no long-run effect on economic growth. Neoliberalism is the best economic system. Price controls can often work to improve productivity and growth. Corporate taxes always reduce inflation.arrow_forwardShould countries with stable economies, like Germany, be responsible for bailing out countries that have mismanaged their finances and assumed massive debt levels?arrow_forwardSuppose that a vaccine manufacturing company owned entirely by U.S. citizens opens a new facility in Canada. Answer all three parts below. In each case, carefully explain your answer. a) What sort of foreign investment would this represent? b) What would be the effect of this investment on current Canadian Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and U.S. GDP? c) What would be the effect of this investment on future per capita incomes in Canada?arrow_forward
- Van manages a grocery store in a country experiencing a high rate of inflation. He is paid in cash twice per month. On payday, he immediately goes out and buys all the goods he will need over the next two weeks in order to prevent the money in his wallet from losing value. What he can't spend, he converts into a more stable foreign currency for a steep fee. This is an example of the______________ of inflationarrow_forwardWhat causes inflation in the industrial and developing globe after COVID?arrow_forwardSolve the problem. Show work and do not use AI.arrow_forward
- Why do leaders of less-developed countries often run very large deficits and print entirely too much money creating excessive inflation, even though they are aware of the consequences of their policies? How might these inflationary policies damage these countries chances for growth and development?arrow_forwardSuppose that the central bank in the UK (The Bank of England) decides to raise interest rates because it is worried about high inflation. As a result, interest rates in the UK become higher than interest rates in the REST OF EUROPE. This acts as an incentive for EUROPEAN investors to increase the amount of funds they invest in British (UK) interest bearing assets. In order to increase their purchases of those UK assets, which are priced in PST, EUROPEAN investors have to convert EUR into PST. This conversion, in turn, increases the demand for PST. Based on the above information, please explain what will happen to the EUR–‐‑PST exchange rate. In other words, will the increased demand for PST, make PST gain value (appreciatearrow_forwardCountry A has a natural climate that is perfect for growing strawberries - long sunny seasons and plenty of rich, well drained soil. Country A also has a big labor force with agriculture knowledge and can produce 80,000 baskets of strawberries in one growing season. By contrast, Country B’s climate is less well-appointed for strawberries - a shorter summer season with large areas of red clay. They also have a smaller population trained in agriculture. Country B can only produce 30,0000 baskets of strawberries in one growing season. In this scenario and with this information, Country A has Group of answer choices A)Absolute advantage for producing strawberries B)Comparative advantage for producing strawberries C)The lowest synthetic advantage for producing strawberries D)Elastic advantage for producing strawberriesarrow_forward
- Peru is growing relatively quickly and has begun to attract large inflows of foreign direct investment. While Peru relishes the benefit of the inflows, it is concerned about the potential negative effects if the foreign investors pull out their investments quickly. One particular reason for Peru to be concerned is that its banks have taken out large loans denominated in U.S. dollars and European euros from foreign banks. If the foreign direct investment is withdrawn quickly from Peru, what will be the effect on each of these items? A. Peru's money supply - B. Peru's exchange rate with other countries - C. Peru's exports - D. Peru's trade deficit - Answer Bank: No Effect, Increase or Decreasearrow_forwardInitially, real interest rates in the United States, South Africa, and Mexico are all equal, at 6 percent. Then the central banks alter their policies so that the American interest rate rises to 8 percent, the South African rate falls to 4 percent, and the Mexican rate stayed at 6 percent. Select one of the following: A. Capital will flow to countries with high interest rate. In this case, the United States will attract more inflows than South Africa and Mexico. South Africa will face maximum capital outflow. Balance of trade will deteriorate for the country with the highest rate of capital inflow B. Capital will flow to countries with the low-interest rate. In this case, South Africa will have the highest rate of capital inflow, Mexico will have the second highest, and the United States the least. The balance of trade will deteriorate for the country with the highest rate of capital outflow. C. Capital will flow to the United States not…arrow_forwardHow do you think the GDP, the unemployment rate and the inflation rate are related to each other in the emerging markets? Do you think these relationships are different in the Turkish context? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education