
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781305156050
Author: N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
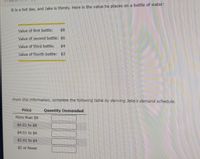
Transcribed Image Text:It is a hot day, and Jake is thirsty. Here is the value he places on a bottle of water:
Value of first bottle:
$8
Value of second bottle: $6
Value of third bottle:
$4
Value of fourth bottle: $2
From this information, complete the following table by deriving Jake''s demand schedule.
Price
Quantity Demanded
More than $8
$6.01 to $8
$4.01 to $6
$2.01 to $4
$2 or fewer
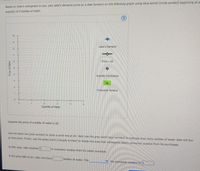
Transcribed Image Text:Based on Jake's willingness to pay, plot Jake's demand curve as a step function on the following graph using blue points (arcle symbol) beginning at a
quantity of 0 bottles of water.
10
Jake's Demand
Price = $5
Quantity Purchased
3.
Consumer Surplus
21
13
Quantity of Water
Suppose the price of a bottle of water is $5.
Use the black line (plus symbol) to draw a price line at $5. Next use the grey point (star symbol) to indicate how many bottles of water Jake will buy
at that price. Finally, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area that represents Jake's consumer surplus from his purchases.
In this case, Jake receives S
in consumer surplus from his water purchase.
If the price falls to $2, Jake now buys
bottles of water. This
his consumer surplus to S
Price of Water
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Since we only answer up to 3 sub-parts, we’ll answer the first 3. Please resubmit the question and specify the other subparts (up to 3) you’d like answered
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Maria has decided always to spend one third of her income on clothing. a. What is her income elasticity of clothing demand? b. What is her price elasticity of clothing demand? c. It Marias tastes change and she decides to spend only one fourth of her income on clothing, how does her demand curve change? What is her income elasticity and price elasticity now?arrow_forwardIncome Effects depend on the income elasticity of demand for each good limit you buy. If one of the goods you buy has a negative income elasticity, that is, it is an inferior good, what must be true of the income elasticity of the other good you buy?arrow_forwardWhat does a downward-sloping demand curve mean about how buyers in a market will react to a higher price?arrow_forward
- Economists define normal goods as having a positive income elasticity. We can divide normal goods into two types: Those whose income elasticity is less than one and those whose income elasticity is greater than one. Think about products that would fall into each category. Can you come up with a name for each category?arrow_forwardIf a 10 decrease in the price of one product that you buy causes an 8 increase in quantity demanded of that product, will another 10 decrease in the price cause another 3 increase (no more and no less) in quantity demanded?arrow_forwardProblems 7-4 It is a hot day, and Larry is thirsty. Here is the value he places on a bottle of water: Value of first bottle: $7 Value of second bottle: $5 Value of third bottle: $3 Value of fourth bottle: $1 From this information, complete the following table by deriving Larry’s demand schedule. Price Quantity Demanded More than $7 $5.01 to $7 $3.01 to $5 $1.01 to $3 $1 or fewerarrow_forward
- 1)It is a hot day, and Carlos is thirsty. Here is the value he places on a bottle of water: Value of first bottle: $9 Value of second bottle: $7 Value of third bottle: $4 Value of fourth bottle: $1 From this information, complete the following table by deriving Carlos’s demand schedule. Price Quantity Demanded More than $9 $7.01 to $9 $4.01 to $7 $1.01 to $4 $1 or fewer 2)Based on Carlos's willingness to pay, plot Carlos's demand curve as a step function on the following graph using blue points (circle symbol) beginning at a quantity of 0 bottles of water. Please do the graph 3)Suppose the price of a bottle of water is $6. Use the black line (plus symbol) to draw a price line at $6. Next use the grey point (star symbol) to indicate how many bottles of water Carlos will buy at that price. Finally, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area that represents Carlos's consumer surplus from his…arrow_forwardAn individual sets aside a certain amount of his income per month to spend on his two hobbies, collecting wine and collecting books. Given the information below, illustrate the demand curve for wine. Wine Price Book Price $15 $12 $30 $12 $60 $12 Books 100- 90- Wine 40 20 10 LOTB FO- Books 50 50 50 80- 70- 60- 50- 40- 30- 20- 10- 0- 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Wine PCG Budget $1200 $1200 $1200 N Using the three-point curved line drawing tool, draw the demand curve for wine in the figure to the right. Label this curve 'Demand". Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required object. CULDarrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying figures. If Mallory and Rick are the only two consumers in this market, then the market demand for soda will be 90 cans per month when the price of a can of soda is Mallory's Demand for Soda Price ($/can) 1.501 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (cans of soda/month) Select one: O a. $1.50 O b. $0.50 O c. $1.25 O d. $0.75 Price ($/can) 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0 0 Rick's Demand for Soda 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (cans of soda/month)arrow_forward
- An individual sets aside a certain amount of his income per month to spend on his two hobbies, collecting wine and collecting books. Given the information below, illustrate the demand curve for wine. 70- TTTTI Wine Price Book Price Wine Вooks Budget $1200 $1200 60- $15 $12 $12 $12 40 50 $30 $60 20 50 50- 10 50 $1200 40- 100- 90- 30- 80- 70- 20- 60- A 50- PCC 10- 40- 30- 0- 20- 10 20 30 40 50 10- Wine 0+ 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Wine Using the three-point curved line drawing tool, draw the demand curve for wine in the figure to the right. Label this curve 'Demand'. Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required object. Books Pricearrow_forward4 Refer to Table below. The table above shows the demand schedules for Kona coffee of two individuals (Luke and Ravi) and the rest of the market. At a price of $6, the quantity demanded in the market would be Kona Coffee Price per lb. (dollars) Luke's Quantity Demanded (lbs.) Ravi's Quantity Demanded (lbs.) Rest of Market Quantity Demanded (lbs.) Market Quantity Demanded (lbs.) $10 3 0 23 8 9 3 32 6 14 7 68 5 18 12 85 4 22 18 110 a. 123 lbs b. 89 lbs c. 36 lbs d. 68 lbsarrow_forwardQuestion 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning