
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
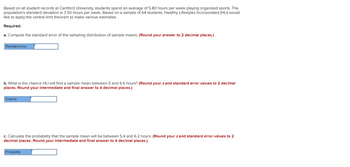
Transcribed Image Text:Based on all student records at Camford University, students spend an average of 5.80 hours per week playing organized sports. The
population's standard deviation is 3.50 hours per week. Based on a sample of 64 students, Healthy Lifestyles Incorporated (HLI) would
like to apply the central limit theorem to make various estimates.
Required:
a. Compute the standard error of the sampling distribution of sample means. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Standard error
b. What is the chance HLI will find a sample mean between 5 and 6.6 hours? (Round your z and standard error values to 2 decimal
places. Round your intermediate and final answer to 4 decimal places.)
Chance
c. Calculate the probability that the sample mean will be between 5.4 and 6.2 hours. (Round your z and standard error values to 2
decimal places. Round your intermediate and final answer to 4 decimal places.)
Probability

Transcribed Image Text:d. How strange would it be to obtain a sample mean greater than 7.80 hours?
O This is very unlikely.
This is very likely.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- See attachedarrow_forwardSuppose the price for pomegranates in NYC have a mean of $1.25 with a standard deviation of $0.15. Suppose you sample 1 pomegranate for different stores in NYC for a total of 50 pomegranates. What is the resulting sampling distribution (mean, standard deviation) for this sample? Assume a random sample. a. None of these b. ($0.18, $0.02) c. ($1.25, $0.02) d. Whatever the mean and standard deviation of the sample is. e. ($1.25, $0.15)arrow_forwardA variable of a population has a mean of u=89 and a standard deviation of o=18. A. Identify the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 36. B. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable? C. Can you answer part (a) if the sample size is 25 instead of 36? Why or why not? what is the mean of the sampling distribution?arrow_forward
- The average annual rainfall in New York City follows a normal distribution with a mean of 49.9 inches and a standard deviation of 9.5 inches. On what percentage of years can we expect there to be between 40.4 and 59.4 inches of rain in New York City? (A) 100% B) 99.7% C) 95% D) 68%arrow_forwardYou may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question. In order to estimate the average time spent per student on the computer terminals at a local university, data were collected for a sample of 81 business students over a one-week period. Assume the standard deviation is 1.4 hours. The standard error is 0.156. Find the approximate margin of error with a 0.95 probability. a) 0.259 b) 0.310 c) 1.645 d) 1.96arrow_forwardA bottled water distributor wants to determine whether the mean amount of water contained in 1-gallon bottles purchased from a nationally known water bottling company is actually 1 gallon. You know from the water bottling company specifications that the standard deviation of the amount of water is 0.03 gallon. You select a random sample of 45 bottles, and the mean amount of water per 1-gallon bottle is 0.996 gallon. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a. Is there evidence that the mean amount is different from 1.0 gallon? (Use a = 0.01.) Let u be the population mean. Determine the null hypothesis, Ho, and the alternative hypothesis, H, . Ho: H What is the test statistic? ZSTAT = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) What is/are the critical value(s)? (Use a = 0.01.) (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) What is the final conclusion? O A. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the mean…arrow_forward
- A variable of a population has a mean of µ = 82 and a standard deviation of o = 9. a. Identify the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 81. b. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable? c. Can you answer part (a) if the sample size is 25 instead of 81? Why or why not? a. What is the shape of the sampling distribution? normal uniform skewed O bimodal What is the mean of the sampling distribution? Hi = (Simplify your answer.) What is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution? (Simplify your answer.) b. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable? A. It was assumed that the variable was normally distributed. B. No assumptions were made because, for a relatively large sample size, the sampling distribution is normal, regardless of the distribution of the variable under consideratioarrow_forwardThe Acme Company manufactures widgets. The distribution of widget weights is bell-shaped. The widget weights have a mean of 50 ounces and a standard deviation of 4 ounces. Use the Standard Deviation Rule, also known as the Empirical Rule (see image below). Do not use normalcdf on your calculator. Suggestion: sketch the distribution in order to answer these questions. a) 95% of the widget weights lie between and b) What percentage of the widget weights lie between 46 and 58 ounces? c) What pagcentage of the widget weights lie below 62 ? % 34% 34% 2.35% 13.5% 2.35% 0.15% 13.5% -35 25 0.15% -1s 1s 25arrow_forwardThe Acme Company manufactures widgets. The distribution of widget weights is bell-shaped. The widget weights have a mean of 46 ounces and a standard deviation of 9 ounces. Use the Standard Deviation Rule, also known as the Empirical Rule (see image below). Do not use normalcdf on your calculator. Suggestion: sketch the distribution in order to answer these questions. a) 99.7% of the widget weights lie between b) What percentage of the widget weights lie between 37 and 73 ounces? c) What percentage of the widget weights lie above 28? 0.15% -3s 2.35% -25 13.5% -1s 34% 34% 1s 13.5% 2s 2.35% 3s and 0.15% % %arrow_forward
- Esp Heavy children: Are children heavier now than they were in the past? The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) taken between 1999 and 2002 reported that the mean weight of six-year-old girls in the United States was 49.3 pounds. Another NHANES survey, published in 2008, reported that a sample of 193 six-year-old girls weighed between 2003 and 2006 had an average weight of 52 pounds. Assume the population standard deviation is o =16 pounds. Can you conclude that the mean weight of six-year-old girls in 2006 is different from what it was in 2002? Use the a =0.01 level of significance and the critical value method. 00 Part: 0/ 5 Part 1 of 5 (a) State the appropriate null and alternate hypotheses. H.: OD O=0 dl. H : This hypothesis test is a (Choose one) test. 00arrow_forwardThe Acme Company manufactures widgets. The distribution of widget weights is bell-shaped. The widget weights have a mean of 60 ounces and a standard deviation of 3 ounces. Use the Standard Deviation Rule, also known as the Empirical Rule (see image below). Do not use normalcdf on your calculator. Suggestion: sketch the distribution in order to answer these questions. a) 99.7% of the widget weights lie between b) What percentage of the widget weights lie between 57 and 69 ounces? c) What percentage of the widget weights lie above 54 ? 0.15% -3s 2.35% -25 13.5% -1s 34% 34% 1s 13.5% 2s 2.35% 3s and 0.15% % %arrow_forwardIn the US women between the ages of 18 to 50 have shoe sizes that approximately follow a normal distribution. The approximate mean is shoe size 8.43 and the standard deviation is 1.35. Find the 90th percentile of this distribution, write the calculator function used to compute the result, and interpret it in a complete sentence.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman