
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
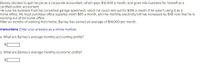
Transcribed Image Text:Barney decides to quit his job as a corporate accountant, which pays $12,000 a month, and goes into business for himself as a
certified public accountant.
He runs his business from his converted garage apartment, which he could rent out for $315 a month if he wasn't using it as a
home office. He must purchase office supplies worth $85 a month, and his monthly electricity bill has increased by $40 now that he is
working out of his home office.
After six months of working from home, Barney has earned an average of $14,000 per month.
Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number.
a. What are Barney's average monthly accounting profits?
2$
b. What are Barney's average monthly economic profits?
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that Maria is starting a food ordering and delivery company. Customers order meals online. Employees prepare the meals and deliver them to customers. Maintenance of the online platform for ordering meals costs the company $5 per day. The company also rents space where orders are prepared. Rent costs $50 per day. To make the deliveries, the business also rents two delivery cars that cost $10 each per day. The costs of ingredients for preparing different numbers of meals are provided in the table below. Maria also has to hire between 0 and 10 workers (depending on the number of meals she chooses to make) to buy ingredients, prepare meals, and deliver the orders. She will pay each employee $120 per day. The first two columns of the table below show how many meals different number of workers can prepare and deliver. Price per meal $50 Workers (Labor L) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Meals (Output Q) ol- 30 42 52 60 67 73 79 85 90 95 MPL FC Cost of ingredients $10 $75 $100 $121 $138 $152…arrow_forwardSuppose your current job pays you $225,000 a year. However, you are considering starting your own company. Based upon your research, you estimate your first-year total revenue to be $4,700,000. There are however several costs of running the company during this first year, such as the cost of materials which will equal $1,300,000, employees who will receive in total $1,500,000, utilities which will cost $750,000, and rent that will be paid to the landlord that equals $1,000,000. Based on this information, solve for both your accounting profit and economic profit during this first year. Also, based upon these profit values, state whether you are better off starting this company or staying in your current job.arrow_forward11 Suppose Jill Johnson operates her pizza restaurant in a building she owns in the center of the city. Similar build- ings in the neighborhood rent for $4,000 per month. Jill is considering selling her building and renting space in the suburbs for $3,000 per month, but she decides not to make the move. She reasons: "I would like to have a restaurant in the suburbs, but I pay no rent for my restaurant now, and I don't want to see my costs rise by $3,000 per month." Evaluate Jill's reasoning.arrow_forward
- You own a company that produces widgets. You currently produce 100 widgets; each widget sells for $100 and costs $80 to produce. You are considering increasing your company's production by one unit, upping the total to 101 widgets. At this level of production, total revenue will increase to $10,100, and total costs will increase to $8,120. Based on the given information, and considering you are a good entrepreneur and economist who wants to maximize profit, you should... A. Sell less than 100 units B. Not produce unit 101 C. Produce unit 101 D. Produce 150 unitsarrow_forwarddefinition of economic costsarrow_forwardBarney decides to quit his job as a corporate accountant, which pays $12,000 a month, and goes into business for himself as a certified public accountant. He runs his business from his converted garage apartment, which he could rent out for $315 a month if he wasn’t using it as a home office. He must purchase office supplies worth $85 a month, and his monthly electricity bill has increased by $40 now that he is working out of his home office. After six months of working from home, Barney has earned an average of $17,000 per month. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. What are Barney’s monthly explicit costs? $ b. What are Barney’s monthly implicit costs? $ c. What are Barney’s monthly economic costs? $arrow_forward
- Suppose Nicholas owns a business making Christmas tree ornaments. Currently, he makes 300 ornaments a month. At this level of production, each additional ornament takes him 30 minutes to make and costs him $5 in materials. Nicholas makes his ornaments in a small studio that he rents for $300 a month. Nicholas can easily increase or decrease the amount of time he spends making ornaments, and he can easily go to the store to buy additional materials to make the ornaments, but he has a year-long lease on his studio, so he has to pay his monthly rent no matter how many ornaments he produces each month. Nicholas values his time at $10 per hour. Other than his time, the cost of the materials and the rent on his studio, Nicholas has no additional production costs. a At Nicholas's current level of production, what is the marginal cost of making an additional ornament each month? b. At Nicholas's current level of production, what is the monthly average fixed cost of each ornament? c. Assuming…arrow_forwardImagine a very talented young person who has just graduated from high school and has been offered a 4-year contract worth ten million dollars to play professional basketball for the LA Bakers, and has also received an offer of acceptance to UCLA with full fellowship. The fellowship covers her tuition, room, and board, along with a generous monthly stipend of 2500 dollars for living expenses for 4+1 years. Which of the following is true for this scenario? ( Remember: the cost of something is what you give up to get it!)A) The cost of the four years of college education for this person is very high, in the range of millions of dollars.B) The cost of the four-years of college education for this person is almost zero because of the generous fellowship and financial aid package she has received.C) The cost of the four years of college education for this is person is the sum of the tuition, room, and board expenses, plus the monthly stipend of 2500 dollars for 4 years.D) The rational choice…arrow_forwardMichael runs a small pottery firm. He hires one helper at $14,000 per year, pays annual rent of $8,000 for his shop, and spends $24,000 per year on materials. He has $50,000 of his own funds invested in equipment (pottery wheels, kilns, and so forth) that could earn him $7,500 per year if alternatively invested. He has been offered $35,000 per year to work as a potter for a competitor. He estimates his entrepreneurial talents are worth $4,000 per year. Total annual revenue from pottery sales is $75,000. Michael's accounting profit is $. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest dollar and include a negative sign if necessary.)arrow_forward
- Dexter set up a computer repair business out of his home office. Based on the square footage of his office, he allocates a fixed cost of $400 per month in mortgage expenses. He also has a monthly internet bill of $45 and a monthly phone bill of $35. While repairs vary greatly, Dexter estimates an average of $19 in expenses per repair and charges a flat $49 fee per repair for his labor. 3a. How many computers does Dexter need to repair each month to break even?__________3b. What is Dexter’s profit / loss if he only repairs 8 computers in a month?__________3c. What fee would Dexter need to charge to break even at 8 repairs?arrow_forwardGomez runs a small pottery firm. She hires one helper at $12,000 per year, pays annual rent of $5,000 for her shop, and spends $20,000 per year on materials. She has $40,000 of her own funds invested in equipment (pottery wheels, kilns, and so forth) that could earn her $4,000 per year if alternatively invested. She has been offered $15,000 per year to work as a potter for a competitor. She estimates her entrepreneurial talents are worth $3,000 per year. Total annual revenue from pottery sales is $72,000. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. Calculate the accounting profit and the economic profit for Gomez's pottery firm. Accounting profit = $ Economic profit = $arrow_forwardEdward the entrepreneur takes 2 hours to cut a lawn, and he cuts 1,000 lawns per year. He uses solar-powered equipment (truck and mower) that will last forever- and can be sold at any time for $40,000. Edward could earn $11 per hour as a pedicurist. The interest rate is 10 percent. Given his current output level, compute his average cost of cutting lawns. $20 $24 $22 $28 $26arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education