
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
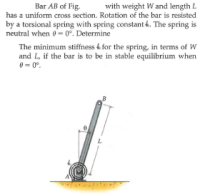
Transcribed Image Text:Bar AB of Fig.
with weight W and length L
has a uniform cross section. Rotation of the bar is resisted
by a torsional spring with spring constant 4. The spring is
neutral when 0- 0°. Determine
The minimum stiffness & for the spring, in terms of W
and L, if the bar is to be in stable equilibrium when
0 = 0°.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The weight of the uniform bar AB is W. The stiffness of the ideal spring attached to B is k, and the spring is unstretched when =80. If W=kL, the bar has three equilibrium positions in the range 0, only one of which is stable. Determine the angle at the stable equilibrium position.arrow_forwardThe bar ABC is supported by three identical, ideal springs. Note that the springs are always vertical because the collars to which they are attached are free to slide on the horizontal rail. Find the angle at equilibrium if W = kL. Neglect the weight of the bar.arrow_forwardFind the equilibrium positions of the 30-lb homogeneous bar and investigate their stability.arrow_forward
- The spring attached to the homogenous bar of weight W is undeformed when =0. Determine the smallest spring stiffness k for which the =0 equilibrium position will be stable. Use W = 10 lb, a = 24 in., and b = 6 in. Assume that the spring remains horizontal, which is a valid approximation if is small.arrow_forwardhas an unstretched length The spring in Fig. of 2 ft. Find the spring constant required for equilibrium at an angle 0 = 30° if Wg = 300 lb, Wp = 500 Ib, and L = 4 ft. Assume that the weights of the bars are negligible. A L WB L/2 WD Sarrow_forwardNeed help please. Round answers to 3 sig figs please.arrow_forward
- L from Pivot 1. A uniform bar with mass M =3.25 kilograms is the top end of the bar. A cable connects to the bar as shown in the diagram. the 75.0 40.0° a. Calculate the tension in the cable required to keep tne bar in static equilibrium. Pivot preso your your answe stem right when n terr b. Calculate the force (both magnitude and direction) exerted by the pivot.arrow_forwardProblem. Consider the following problem. Find the displacement of node 4. Assume F2=200 N, F3=300 N, F4=400 N and Kı= 100, K2= 200, and K3= 300 N/mm. F. 3 2 3 4 Note: The stiffness matrix of individual springs should be first written, then the equilibrium equations at each node should be written, expanded in terms of nodal displacement, and used to perform the assembly of the global stiffness matrix of the problem. Then, the appropriate boundary conditions should be applied and the nodal displacement vector should be found. Every step should be shown; missing any step would result in point deduction even if the final answer is correct.arrow_forwardहै A ★F B The structure shown above is in static equilibrium. The structure is made of square segments 1.5m on each side. Support A is a pin joint and support B is on rollers. An external force F=150.0 N is applied to the structure. What is the reaction force at B?arrow_forward
- Need help. Please round answers to 3 sig figsarrow_forwardA rear suspension system for a front wheel-drive vehicle is shown here. Spring EF is offset behind member CD. The normal force due to contact between the wheel and the road is 4200 N. Assume the weight of the wheel and suspension system components is negligible. Determine the magnitude of the member CD. Is the member in tension or compression? Determine the support reactions at A. Determine the unstretched length of the spring EF given a spring constant of 150 kN/m.arrow_forwardA straight pole of length l = 7 ft and weight W = 25 lbf leans against the corner of a wall of height h = 5 ft as shown. A rope at the bottom prevents the pole from sliding. All surfaces are smooth (no friction). Determine the force F in the rope that produces static equilibrium.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L