
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
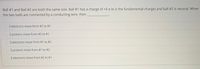
Transcribed Image Text:Ball #1 and Ball #2 are both the same size. Ball #1 has a charge of +6 e (e is the fundamental charge) and ball #2 is neutral. When
the two balls are connected by a conducting wire, then
3 electrons move form #2 to #1
3 protons move from #2 to #1
3 electrons move from #1 to #2
O3 protons move from #1 to #2.
6 electrons move from #2 to #1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Anthea rubs two latex balloons against her hair, causing the balloons to become charged negatively with 2.0 x 10-6 C. She holds the balloons distance of 0.70 m apart. What is the electric force between the two balloons? 3.7*10^4 N 8*10^-12 N O 5*10^-2 N O 7.3*10^-2 Narrow_forwardÀ student observes a demonstration involving an interaction between a neutral metallic sphere suspended from a string and a negatively charged insulating rod. The student makes the following statement: "As the negatively charged rod nears the sphere, it causes the electrons in the sphere to move away from the rod. The side of the sphere nearest Insulating to the rod becomes positively charged while the other side becomes negatively charged. So the sphere will be attracted toward the rod. If they touch, the sphere will swing back since they will both become neutral." Neutral conducting sphere rod What, if anything, is wrong with this statement? If something is wrong, explain the error and how to correct it. If the statement is valid, explain why.arrow_forwardA proton is launched from an infinite plane of charge with surface charge density -4.30×10-6 C/m2. If the proton has an initial speed of 3.00×107 m/s, how far does it travel before reaching its turning point? 3.50×10-7 m 19.3 m 6.44×10-7 m 38.7 marrow_forward
- Metal spheres A and B are identical except that sphere A has a charge of -2.0 nCnC while sphere B has a charge of +4.0 nCnC. Part A If the spheres are brought into contact, do electrons move from A to B or from B to A? Electrons move from A to B Electrons move from B to Aarrow_forwardTwo small balls with a mass of 2 g each are hanging on two separate strings 0.5 m (50 cm) long attached to a common point. They are given an identical negative charge and spread apart to a distance 6 cm from each other. What will happen in an identical situation if the mass of the balls is cut in half?arrow_forwardConsider the arrangements of an electron and two protons shown below: O (a) P O a> c> b O b>c> a O O a-b-c In each case rank the magnitude of the net electrostatic force on the electron, greatest first. none of these Oc>b>a Oc-b>a Ob>a>c c=a> b D a>b>c P d D d Parrow_forward
- Red blood cells often become charged and can be treated as point charges. Healthy red blood cells are negatively charged, but unhealthy cells (due to the presence of a bacteria, for example) can become positively charged. In the figure, three red blood cells are oriented such that they are located on the corners of an equilateral triangle. The red blood cell charges are A = 1.90 pC, B = 6.50 pC, and C = -4.80 pC. Given these charges, what would the magnitude and direction of the electric field be at cell A? (1 pC = 1 x 10-12 c.) Magnitude- Direction-arrow_forwardΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔ $6.4 mc 0.25m + tab +1.2 MC ! 1 45° Q 2 W 3 Charges are placed on the corners of a right triangle. 45-45-90 0.35m #3 450 a E S4 % L 5 triangle Precise infinitely MacBook Pro 16.0 mc & 23 0.25m what is the instantaneous electrostatic force on the -6.0 mC charge? include a magnitude and direction (an angle)arrow_forwardThis time your object has a mass of 20.4 kg. Now imagine taking all the protons out of the object and stuffing them into a box. Also take all the electrons out of the object and stuff them in a second box. How much charge is contained in the box with all the protons? Question 2 options: 3.90E+09 C 4.89E+08 C 9.77E+08 C 1.95E+09 Carrow_forward
- Two pith balls, each of mass m = 0.2 × 10−3 kg are suspended from the same point by silk threads each 0.4 m long. An equal charge q is given to each of the pith balls, which causes them to separate by a distance d until the threads are at an angle of 40 degrees to each other. Calculate the magnitude of the charge on each ball.arrow_forwardFour identical metallic objects carry the following charges: +1.23, +6.89, -4.44, and -9.28 μC. The objects are brought simultaneously into contact, so that each touches the others. Then they are separated. (a) What is the final charge on each object? (b) How many electrons (or protons) make up the final charge on each object? (a) Number i (b) Number IN Units Unitsarrow_forwardBead A has a mass of 15 g and a charge of -5.2 nC . Bead B has a mass of 22 g and a charge of -11.7 nC . The beads are held 15 cm apart (measured between their centers) and released.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON