
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A projectile is thrown at an angle theta above horizontal. The speed at B (maximum height) is equal to VB. Determine the distance AC if theta=30 degrees and VB=12m/s.
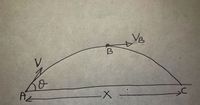
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates a projectile motion diagram, highlighting key variables and trajectory points. Here's the transcription and explanation:
1. **Initial Point (A):**
- An object is launched from point A with an initial velocity denoted as \( V \).
- The launch angle relative to the horizontal is \( \theta \).
2. **Trajectory Path:**
- The path from A to C is curved, representing the parabolic trajectory of the projectile under the influence of gravity.
3. **Midpoint (B):**
- At point B, the projectile is at the highest point in its trajectory.
- The horizontal velocity at this point is denoted as \( V_B \).
4. **Horizontal Distance (X):**
- The horizontal displacement from point A to the point directly below B is marked as \( X \).
5. **End Point (C):**
- The projectile lands at point C along the horizontal axis.
This diagram is a classic representation used to analyze the motion parameters of projectiles in physics, considering initial velocity, angles, and the effects of gravity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particle moving in the x-y plane has a position vector given by r = 3/2t² i + 2/3t³j, where r is in inches and t is in seconds. Calculate the radius of curvature p of the path for the position of the particle when t = 2.0 sec. Sketch the velocity v and the curvature of the path for this particular instant. 6. Answer: p= i in.arrow_forwardW S →E VIE 0 VbE A boat is crossing the river. By making angle theta = 25 degree with North direction as shown in the figure, the boat can travel due north. If the speed of the boat with respect to the river is 3 m/s. Determine the speed of the river (in m/s) with respect to the earth. Answer to 2 decimal placesarrow_forwardA ball is tossed from an upper-story window of a building. The ball is given an initial velocity of 8.50 m/s at an angle of 18.0°C below the horizontal. It strikes the ground 5.00 s later. Answer (a) How far horizontally from the base of the building does the ball strike the ground? (b) Find the height from which the ball was thrown. (c) How long does it take the ball to reach a point 10.0 m below the level of launching? Use 4 decimal places.arrow_forward
- I need to solve v(sub y)=v(sub 0)sin θ(sub 0)-gt to find the time that it takes the projectile to reach maximum height (so I believe I'm solving for t?). I have previously found v(sub 0y) in part (a), but I'm unsure what v(sub 0) and v(sub y) are. How do I find those variables?arrow_forwardA pursue at radius 2.00 m and a wallet at radius 3.00 m travel in uniform circular motion on the floor of a merry-go-round as the ride turns. They are on the same radial line. At one instant, the acceleration of the pursue is (2.00 m/s^2)i + (4.00 m/s^2)j. At the instant and in unit-vector notation, what is the acceleration of the wallet?arrow_forwardIarrow_forward
- The banded archerfish is a species of fish that lives in mangrove estuaries in Asia and Oceania. It has a unique and highly effective hunting strategy: it shoots an incredibly precise stream of water out of its mouth at almost ten meters per second, knocking insects and other small animals into the water from nearby branches! Pom Fbug (t) Ө = Our hero, a hungry archerfish, has spotted a big, delicious bug sitting on a branch a height ħ above the surface of the water. The archerfish can shoot its water jet at a speed of vo. The archerfish wants to knock the bug sideways off of the branch, so it decides to shoot so that its water jet is moving horizontally at the moment when it strikes the bug. The final goal of this problem is to find the horizontal distance, d, from the branch, and the angle above horizontal, 0, at which archerfish should shoot. d (a) What are the position and velocity of the water droplet as a function of time and the position and velocity of the bug as a function of…arrow_forwardA squirrel runs along an overhead telephone wire that stretches from the top of one pole to the next. It is initially at position x: = 2.01 m, as measured from the center of the wire segment. It then undergoes a displacement of Ax = -6.// m. What is the ' sauirrel's final position xe?arrow_forwardMr. M is walking to Mr. T’s house. He take the shortcut across an open field. His first displacement is 140 m[E35N]. He then walks 200.0m[E]. What is Mr. M’s total displacement?arrow_forward
- .With w = 500 rad/s, for V = 10 - j 20, find v(4 ms) إختر أحد الخيارات V 2.4- .a V 6.13 .b V 19.8 - .C angle (-63°) V 22 .d × V 10.4 .earrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardThis problem will involve deriving a formula or two for a projectile launched from one height and angle and landing at a different height on Earth. Begin with a projectile launched at angle 0 above horizontal from a height y₁ with initial velocity Vo. The projectile lands at a point with height y₂. These are the given quantities: vo, 0, y₁, y2 and g. Construct formulae for each of the following, as. a function of given quantities the horizontal distance traveled. the maximum height reached. the time taken. the angle of impact. (find the final velocity components first).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON