
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
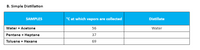
Transcribed Image Text:B. Simple Distillation
SAMPLES
°C at which vapors are collected
Distillate
Water + Acetone
56
Water
Pentane + Heptane
37
Toluene + Hexane
69
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which one of the following pairs of liquids might be used in carrying out solvent extractions? Explain your choice. 1. Benzene and hexane 2. Methylbenzene and water 3. Water and ethanol 4. Benzene and methylbenzenearrow_forwardAnswer to c is 1.56g. Please answer bottom question and disregard book pages.arrow_forwardSuppose that you have a 1:1 mixture of compounds that is comprised of compound X and compound Y. You desire pure compound X and are planning a recrystallization to enhance the purity. Which solvent below is optimal for your recrystallization? Ethanol (boiling point = 78 °C) Solubility At 0 °C 100 °C Compound X 0.05 g/mL 0.20 g/mL Compound Y 0.02 g/mL 0.40 g/mL Water (boiling point = 100 °C) Solubility At 0 °C 100 °C Compound X 0.02 g/mL 0.05 g/mL Compound Y 0.01 g/mL 0.10 g/mL Methanol (boiling point = 65 °C) Solubility At 0 °C 65 °C Compound X 0.04 g/mL 0.10 g/mL Compound Y 0.02 g/mL 0.30 g/mL Acetone (boiling point = 56 °C) Solubility At 0 °C 56 °C Compound X 0.10 g/mL 0.50 g/mL Compound Y 0.20 g/mL 0.50 g/mL Ethyl Acetate (boiling point = 77 °C) Solubility At 0 °C 77 °C Compound X 0.10 g/mL 0.60 g/mL Compound Y 0.30 g/mL 0.60…arrow_forward
- When would you use fractional distillation vs. fractional crystallization?arrow_forwardThe melting point (mp) range of reference compound A is 320-340°C. The mp range of a 1:1 mixture of a sample of A with a sample of unknown compound B is found to be 140-300°C. Do the samples consist of identical compounds? A)Yes, because the mp of the mixture is lower than the mp of pure A. B) Not enough information is given to answer the question C) Yes, because they melt over a broad range. D) No, because the mp of the mixture is lower than the melting point of pure A.arrow_forwardCircle the upper layer in each pair of mixed solvents: water and benzene water and carbon tetrachloride water and etherarrow_forward
- Using recrystallization techniques, a student attempts to purify 0.50 g of compound H. Based on the solubility of H in the chosen solvent at collection temperature, the maximum percent recovery is 82%. The student obtains 0.396 g of purified crystals. What is their percent recovery? Group of answer choices 41% 64% 79% 82% 97% none of thesearrow_forwardThe mixture contains benzoic acid, 2-napthol, and naphthalene. Dissolve the mixture in the polar solvent ether. When you react the mixture with 10% NaHCO3(sodium bicarbonatea weak base in aqueous solution) reacts with benzoic acid and forms sodium benzoate an ionic compound (similar to NaCl) that dissolves in aqueous solution (heavier than ether in density) and goes to the bottom of the centrifuge tube or to the bottom of the separatory funnel forming two layers. Then remove the bottom aqueous layer and collect in a beaker labeled as bicarbonate extract. Acidify the bicarbonate extract in the beaker to give benzoic acid. The top ethereal layer contains in the centrifuge tube or separatory funnel 2-napthol and naphthalene. To this top layer add 10% NaOH (sodium hydroxideis a strong base in aqueous solution reacts with only 2-napthol, a weak acid forming 2-napthoxide an ionic compound soluble in aqueous solution (similar to NaCl) that goes to the bottom of the centrifuge tube or to…arrow_forwarda. b. C. How are fractional distillation and steam distillation similar? How are fractional distillation and steam distillation different? Kabing works as a The vapor pressure of benzaldehyde at 97 °C is about 60 mm Hg. Assume atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. If you collected 20 g of distillate from your steam distillation, how much of it was benzaldehyde? Show your calculation. (MW)APA =gA (MW)BPB gвarrow_forward
- Simple Distillation The temperature was 76o C when the first drop of distillate was collected. Liquid was collected and the temperature gradually rose to 124 o C. Fraction 2 was taken when liquid was distilling at 124o C. Fractional Distillation The temperature was 77o C when the first drop of distillate was collected. Liquid was collected until the temperature reached 78 o C, then the temperature dropped. The temperature of the hot plate was increased and a second fraction of liquid was collected at 126 o C. a.) Based on the boiling points observed when the fractions were collected, what is the identity of the unknown compound isolated in fraction 1 and Fraction 2?arrow_forward5.0 mL of 1-butanol was mixed with 10 mL of HCl. The reaction was put on an ice bath and 4 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid was added. This mixture was refluxed for 45 min and then the product was co-distilled with water using a simple distillation apparatus. Water and the product are immiscible. 1-butanol has a molar mass of 74.12 g/mol, a density of 0.810 g/mL, and a boiling point of 118 C. The product has a molar mass of 92.57 g/mol, a density of 0.880 g/mL, and a boiling point of 78 C. What is the nucleophile in this reaction? What is the role of H2SO4 in this reaction? Calculate the theoretical yield for this reaction. Give your answer in grams. Select the following statements that can be said about the reaction shown.arrow_forwardAfter the ethyl acetate is evaporated, Q and R (a mixture of liquids) remain. A) What criteria does this mixture have to satisfy to be separated by simple or fractional distillation? Homogenous or Heterogeneous B) What kind of distillation would you carry out? Fractional or Simple C)What reason(s) would make the mixture suitable to be separated using the distillation chosen in (b)? A) boiling point difference only B) boiling point difference and composition C) composition onlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY