
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
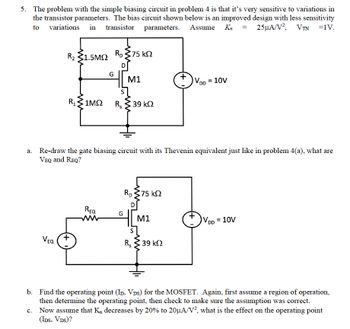
Transcribed Image Text:5. The problem with the simple biasing circuit in problem 4 is that it's very sensitive to variations in
the transistor parameters. The bias circuit shown below is an improved design with less sensitivity
to variations in transistor parameters. Assume Kn = 25μA/V², VTN =1V.
R2 31.5ΜΩ
VEQ
C.
G
Ro 375 ΚΩ
REQ
R, 31ΜΩ R, 3 39 ΚΩ
M1
a. Re-draw the gate biasing circuit with its Thevenin equivalent just like in problem 4(a), what are
VEQ and REQ?
G
Ro 375 ΚΩ
S
R₂
M1
+
39 ΚΩ
VDD = 10V
+
VDD
= 10V
b. Find the operating point (ID, Vòs) for the MOSFET. Again, first assume a region of operation,
then determine the operating point, then check to make sure the assumption was correct.
Now assume that K₁ decreases by 20% to 20µA/V², what is the effect on the operating point
(IDS, VDS)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a full-bridge dc-dc converter using PWM bipolar voltage switching, analytically obtain the value of (V/V) which results in the maximum (peak-peak) ripple in the output current i,. Calculate this ripple in terms of Va, La, and farrow_forwardExplain the concept of Moore's Law and its implications for the semiconductor industry. Assess whether it is still relevant in the era of nanometer-scale transistors.arrow_forwardConsider an n-channel MOSFET. What voltage (positive or negative) should be applied to the gate to induce a conducting channel connecting the source and drain? Why?arrow_forward
- State and explain the relation of drain current versus gate to source voltage for an MOSFET.arrow_forwardA PWM signal changes with a voltage of -15 and 15 volts while it is desirable to produce an effective (average) voltage of the PWM signal of 9 volts. The duty cycle that must be generated isarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,