
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
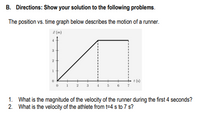
Transcribed Image Text:B. Directions: Show your solution to the following problems.
The position vs. time graph below describes the motion of a runner.
z (m)
3
t (s)
t (s)
3
1. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the runner during the first 4 seconds?
2. What is the velocity of the athlete from t=4 s to 7 s?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Include a picture or description of your coordinate system (origin, positive direction).arrow_forward2. The position of a drone as a function of time is given by *(t) = ( 8 i + 1.5 k) + (-3 î + 2 j) t – 0.5 t2 j The units are missing in the constant coefficients above, i.e., "0.5" should be "0.5 m/s2". Include the correct units on all the constant coefficients in your answers below. a. What is the x-position of the drone as a function of time? b. What is the y-position of the drone as a function of time? c. How far away is the drone from its starting position at t = 3s? d. What is the acceleration vector? е. What is the velocity vector as a function of time? (One way to do this is to take the time derivative of the position vector.) f. Make a sketch of the x, y, and z positions of the drone as function of time. You just need the general shape. time time timearrow_forwardV 0 A C. B 2. Two identical objects, A and B, move along straight, parallel, horizontal tracks. The graph above represents the velocity as a function of time for the two objects. a. At approximately which time or times, if any, are the objects moving at the same speed? If the objects are never moving with the same speed during the interval shown, indicate this explicitly. Briefly explain your answer. b. At approximately which time or times, if any, are the objects moving with the same acceleration? If the objects are never moving with the same acceleration during the interval shown, indicate this explicitly. Briefly explain your answer. At approximately which time intervals is object B moving at a greater speed than A? If the object B are never moving with the same speed during the interval shown, indicate this explicitly. Briefly explain your answer. d. If Object B has an initial position of Xb = -4.5m and Object A started at the origin, at approximately which time or times, if any,…arrow_forward
- Help me pleasearrow_forwardWrite the actual function that you expect the velocity to obey as a function of time (recall that the initial velocity was 17 m/s). Your function should be a function of time (i.e. the t variable should be left as an independent variable) but all other values should be filled in with numbers. Based on your answer above, what type of curve would you expect the position vs. time function to obey? i.A constant (horizontal) curve? ii.A linear curve? iii.A quadratic (parabolic) curve? iv.Another type of curve, such as cubic, exponential, sine, square root, etc...? Circle an answer from above and explain how you use your answer to the above question and the relationship between position and velocity to arrive at your conclusion.arrow_forwardA honda civic starts moving from rest with constant acceleration of 4 m/s^2 for 5 seconds. a. Is it going to cover equal disteances every second during those 5 seconds? b. How much distance would the car cover in those five seconds of motion? show calculations c. What would be the instantaneous velocity of the car after five seconds of motion?arrow_forward
- A cat walks in a straight line, which we shall call the -axis, with the positive direction to the right. As an observant physicist, you make measurements of this cat's motion and construct a graph of the feline's velocity as a function of time (Figure 1). I. Calculate the area under the graph between t = 0 and t = 6.0 s. (Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.) II. For the time interval t = 0 to t = 6.0 s, what is the magnitude of the average velocity of the cat? (Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.) III. Use constant-acceleration equations to calculate the distance the cat travels in this time interval. (Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.)arrow_forwardAn object is held 10 m above the ground. It is tossed upward at 5 m/s. Describe the object's motion in words. Write an equation of motion for the object. How long does it take for the object to hit the ground? How far above the ground is the object in 1.5 sec?arrow_forwardConclusion: Write a single paragraph describing the how the velocity of the car changes as time passes. Be sure to include your equation and the acceleration in your description.arrow_forward
- Problem-Solving Technique: Draw a labeled picture. Put a coordinate system on the picture indicating the location of the origin and the positive direction. Show the solution in a step-by-step orderly fashion. Write any equation you use in symbolic form before substituting in numbers. 1. Ann is traveling at 30 m/s (80 mi/hr) west when she passes a police car. She immediately begins slowing down at a rate of 2.5 m/s for 4 seconds. How far has she traveled for this time? a. Fill in the information that is given in the problem. Put a question mark for any quantity that is not given in the problem. Vox = v. = b. Determine the distance she traveled in this time. Start with the equation in sy numbers you used including units. olic form and show thearrow_forwardinclude a picture or description of your coordinate system (origin, positive direction).arrow_forwardHi! Please help with a-c. Thank you in advancearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON