
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Need help with Number 7 A to F if possible but if you can do A TO D too that's fine.

Transcribed Image Text:b.
a.
6.
Use the limit comparison test to determine the convergence of the series.
2
¹3"-5
b.
a.
b.
C.
d.
n=1
00
a.
b.
74√/1²-²
n=1
∞0
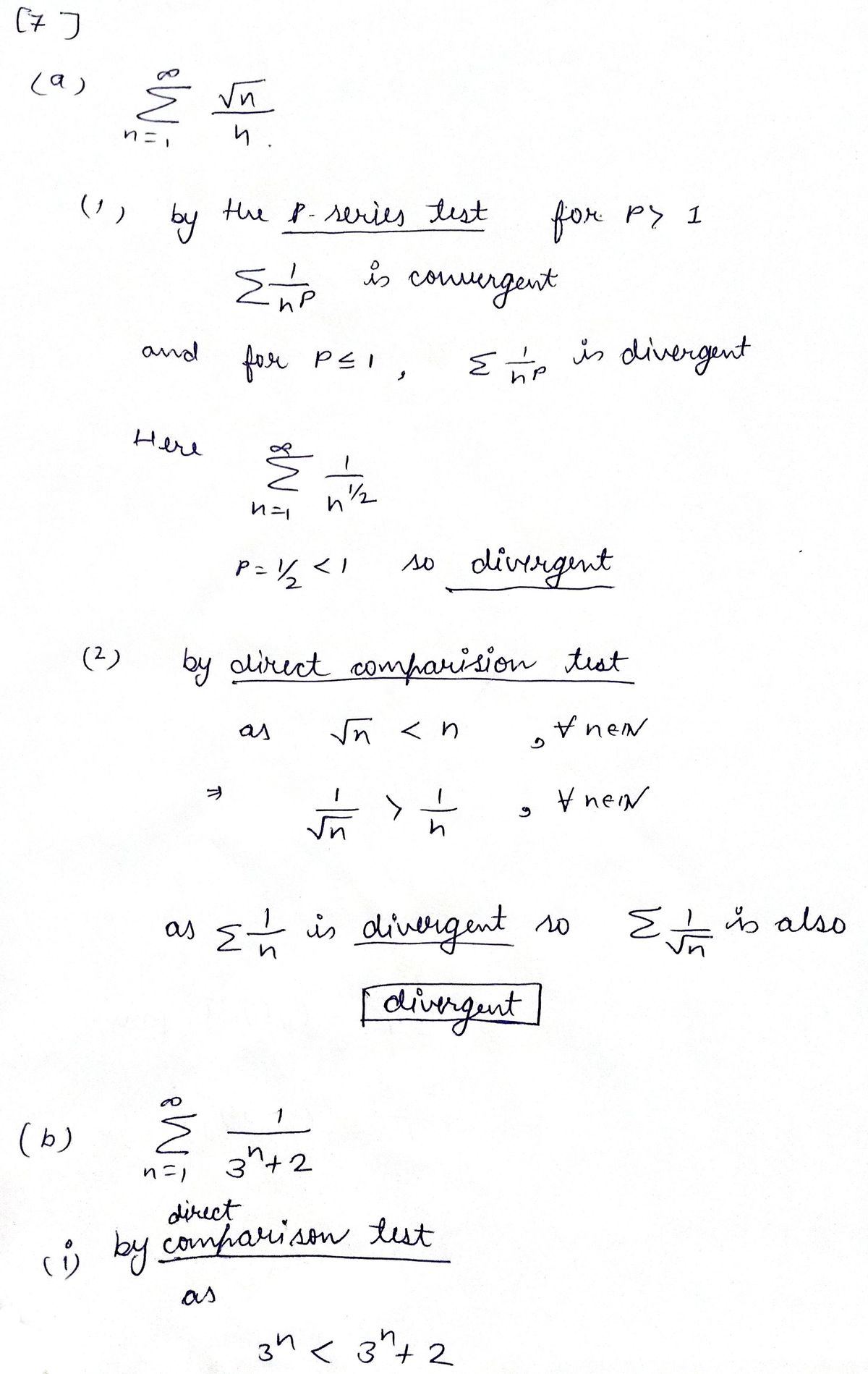
7. For each of the series below, use at least two of the tests to determine the convergence of the
series. Each test should be used at least once. Choose from: nth-term test, p-series test,
integral test, limit comparison test, geometric series test, telescoping series test, direct
comparison test. Clearly indicate which tests you are using.
Σ(-3)
n=0
n=1
L√n
n
18 IMS IM8
n=1
00
tan
e. Σ=1
f. Σn=1
g. Σ=1
n=1
1
¹3" +2
n=1 n² +
∞
n
'2n + 3
00
Ic
n=1
n
∞
c. Σ=1
n=0
n
² + 1)²
n-1
n² √√n
n+4n
n=1
n+6n
1
1+=
n n
COSNT
d. Σ(-1)"e-n²
(−1)n+1 √n
Vn
C.
\n+
e. Σ(-1)"+¹ arctan n
f. Σ=1(-1)" sin
1
n=n(n² +1)
h.
i.
j.
k.
8. Determine the convergence or divergence of the series. If the series converges, does it
converge absolutely or conditionally?
(−1)″ n²
n² +1
00
i.
j.
n=4
Σ
n=1\n+1
00
n=1
I.
I.E=1
m. 2n=1
Σ=
1
3n²-2n-15
100
n. Σn=₁ sin
WW
1
n=1
3
n(n+3)
n=0
(2k-1)(k²-1)
(k+1)(k²+4)
e1/n
n
(−1)n+¹
n=1
k. † (-1)"
In n
n=2
1
n+2
1
n
n+¹ In(n+1)
·
COSNT
n+1
n+1
(−1)¹+¹ √√n
n+2
m. Σã=₁(−1)n-¹e²/n
n. Σ=1
(-1)^nn
n!
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- i need this answer for with four decimals. Can you please help?arrow_forwardIf "y" varies directly with "x," and y = 6 when x = -7, what is "y" when x = 4? Enter the number that belongs in the green box. Reduce to simplest form. y = Enterarrow_forwardOnly need help on the very last part after p valuearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

