
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:(b) What is the point estimate of the difference between the two population means? (Use mean score first round mean score fourth round.)
For which round is the population mean score lower?
The mean of the fourth round scores was lower than the mean of the first round scores.
The mean of the first round scores was lower than the mean of the fourth round scores.
(c) What is the margin of error for a 90% confidence interval estimate for the difference between the population means? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Could this confidence interval have been used to test the hypothesis in part (a)? Explain.
Yes. One could check to see if the 90% confidence interval includes a difference of zero. If the interval does not contain zero, the difference is not statistically significant.
Yes. One could check to see if the 90% confidence interval includes a difference of one. If the interval does not contain one, the difference is not statistically significant.
Yes. One could check to see if the 90% confidence interval includes a difference of zero. If the interval contains zero, the difference is not statistically significant.
Yes. One could check to see if the 90% confidence interval includes a difference of one. If the interval contains one, the difference is not statistically significant.
No. One can not use a confidence interval to test hypothesis in part (a) because hypothesis tests and confidence intervals are two different things.
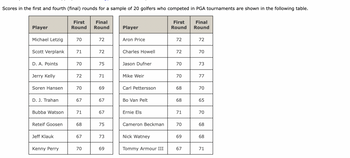
Transcribed Image Text:Scores in the first and fourth (final) rounds for a sample of 20 golfers who competed in PGA tournaments are shown in the following table.
Player
Michael Letzig
Scott Verplank
D. A. Points
Jerry Kelly
Soren Hansen
D. J. Trahan
Bubba Watson
Reteif Goosen
Jeff Klauk
Kenny Perry
First Final
Round Round
70
71
70
72
70
67
71
68
67
70
72
72
75
71
69
67
67
75
73
69
Player
Aron Price
Charles Howell
Jason Dufner
Mike Weir
Carl Pettersson
Bo Van Pelt
Ernie Els
Cameron Beckman
Nick Watney
Tommy Armour III
First
Round
72
72
70
70
68
68
71
70
69
67
Final
Round
72
70 - 73
77
70
65
70
68
68
71
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are interested in estimating the the mean weight of the local adult population of female white-tailed deer (doe). From past data, you estimate that the standard deviation of all adult female white-tailed deer in this region to be 23 pounds. What sample size would you need to in order to estimate the mean weight of all female white-tailed deer, with a 96% confidence level, to within 4 pounds of the actual weight?Sample Size: ????arrow_forwardHere are summary statistics for randomly selected weights of newborn girls: n=198, x =32.7 hg, s = 7.8 hg. Construct a confidence interval estimate of the mean. Use a 98% confidence level. Are these results very different from the confidence interval 30.4 hgarrow_forwardTo assess how women are doing in the workforce, we have gathered data from 120 firms with 100 to 500 employees, and have recorded how many of the top 25 highest paid employees are female. Use the data provided in the image. Q1 What is the overall proportion of females in the top 25? Answer is .5093 Q2 What is the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval for the mean proportion of females in the top 25? Answers are not: .4895 or .4634 or .0541 or .0550 or .0542 Q3 What is the upper bound of the 95% confidence interval for the mean proportion of females in the top 25? Answers are not: .0020 or .6794 or .0597 or .0587 or .0746 or .0983arrow_forwardThe electric cooperative needs to know the mean household usage of electricity by its non commercial customers in kilawatts per day. They would like the estimate to have a maximum era of 0.14 kW. A previous study found that for a average family the variance is 5.29 kW and the mean is 19.9 kW per day. If they are using 80% level of confidence how large of a sample is required to estimate the mean usage of electricity ? Round your answer up to the next integerarrow_forwardC2. Average years of education are reported by social class based on data from the GSS 2018. Mean Standard Deviation 12.19 Lower class 3.08 102 13.16 Working class 2.93 523 14.60 Middle class 2.88 498 15.21 Upper class 3.01 34 Construct the 95% confidence interval for the mean number of years of education а. for lower- and working-class respondents. 1 Construct the 99% confidence interval for the mean number of years of education for lower-class and middle-class respondents. As our confidence in the result increases, how does the size of the confidence interval Change? Explain why this is so.arrow_forwardhere are summary statistics for randomly weights of newborn girls. n=203, x=32.4hg s=6.4 hg. Construct a confidence interval estimate of the mean. Use a 90% confidence level. Are these results very different from the confidence interval 30.9 hg< <32.9 hg with only 15 sample values, x=31.9 hg and s=2.2hg?arrow_forwardWhat z score would be used to calculate the margin of error for a 98% confidence interval for the mean? 2.33 1.75 2.05 correct answer is not givenarrow_forwardHere are the summary statistics for randomly selected weights of newborn girls: n =247, x= 32.2 hg, s= 6.8hg . Construct a confidence interval estimate of the mean. Use 90% confidence level. Are these results very different from the confidence interval 31.0 hg < u < 33.2 hg with only 18 sample values, x= 32.1 hg and s=. 2.7 hg ? What is the confidence interval for the population mean u ? _ hg < u< hg _ (round to one decimal places as needed ? Are the results between the two confidence intervals very different ? a. Yes, because the confidence interval limits are not similar. b. No. because the confidence interval limits are similarc. Yes, because one confidence interval does not contain the mean of the other confidence intervald.arrow_forwardHere are summary statistics for randomly selected weights of newborn girls: n = 167, x= 30.6 hg, s= 6.2 hg. Construct a confidence interval estimate of the mean. Use a 99% confidence level. Are these results very different from the confidence interval 29.2 hg <<32.2 hg with only 13 sample values, x= 30.7 hg, and s= 1.8 hg? What is the confidence interval for the population mean µ? hgarrow_forwardYou may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question. Consider the following results for independent samples taken from two populations. Sample 1 Sample 2 n1 = 400 n2 = 300 p1 = 0.49 p2 = 0.32 (a) What is the point estimate of the difference between the two population proportions? (Use p1 − p2. ) (b) Develop a 90% confidence interval for the difference between the two population proportions. (Use p1 − p2. Round your answer to four decimal places.) to (c) Develop a 95% confidence interval for the difference between the two population proportions. (Use p1 − p2. Round your answer to four decimal places.) toarrow_forwardCan someone please help me to solve the following question showing all work.arrow_forward4..arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman