
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337614085
Author: Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
In this figure, m∠BDA = ° and m∠BCA = ° ?
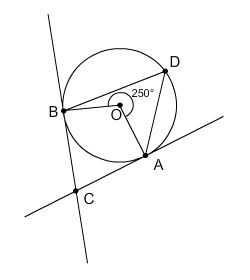
Transcribed Image Text:### Geometry Diagram Explanation
The image depicts a geometric figure involving a circle and several intersecting lines, accompanied by an angle measurement. Here is a detailed description of the components:
1. **Circle and Center**:
- The circle is centered at point \( O \).
2. **Points on the Circle**:
- There are four points on the circle, labeled \( A \), \( B \), \( C \), and \( D \).
- Lines extend from the points \( A \) and \( B \) away from the circle, intersecting outside the circle.
3. **Lines and Angles**:
- Line segments \( BA \) and \( AC \) form a secant-tangent combination, meeting at points \( B \) and \( A \) respectively, with \( C \) being another point of intersection on the extended line.
- Line segment \( BD \) extends from the circle through points \( B \), \( D \), \( and \) beyond.
4. **Interior Angle**:
- The angle \( \angle DOB \) is marked as \( 250^\circ \). This is the central angle formed by the points \( D \) and \( B \) with respect to the center \( O \).
### Graphical Interpretation:
This geometric figure can be utilized to illustrate several key concepts in geometry, such as:
- Central and inscribed angles.
- Intersecting lines creating various angles.
- Properties of circles involving tangent and secant lines.
Students can apply the principles of these geometric properties to solve for unknown measurements and to understand the relationships between different segments and angles in circles.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:9781285195698
Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:Cengage Learning