
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
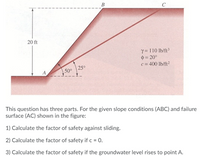
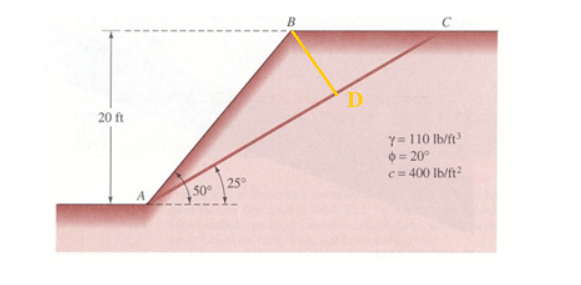
Transcribed Image Text:This image presents a slope stability analysis problem for educational purposes. The diagram shows a slope composed of three points: A, B, and C, with a failure surface labeled as AC. The slope is inclined at angles of 50° at point A and 25° between points B and C, with a vertical height of 20 ft from point A upwards to the surface level.
Material properties are given as:
- Unit weight (γ) = 110 lb/ft³
- Angle of internal friction (φ) = 20°
- Cohesion (c) = 400 lb/ft²
The task involves three parts:
1) Calculate the factor of safety against sliding for the given conditions.
2) Calculate the factor of safety if the cohesion (c) is equal to 0.
3) Calculate the factor of safety if the groundwater level rises to point A.
This educational problem focuses on understanding slope stability, the role of cohesion and internal friction in resisting sliding, and the impact of groundwater conditions on the factor of safety.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please round to the nearest One (i.e., 1). PLEASE DO NOT USE COMMA (S) ON YOUR ANSWER!!! Moist unit weight of soil, gamma = 112 pcf %3D Saturated unit weight of soil, gammasat = 124 pcf Cohesion of soil, c 0 psf The factor of safety, FS = 2 The internal friction angle of soil is 30 degrees B = 5 ft, D, = 5 ft, h = 3 ft A strip footing is shown below. Determine the followings: Unit weight of soil = y c' Qal Groundwater table Ysat B 1. Ultimate bearing capacity, qu = psf 2. Allowable bearing capacity, qa = psfarrow_forwardTa Hypothetical Case: Slope Soils Natural or man-made slope Potential failure plane 01 35° |0₁-652 0₁ = 52 kPa a = 35° 03= 12 kPa Horizontal Slope failure (landslide) will be triggered at any point along the potential failure plane when the shear stress exceeds the shear strength of the soil mobilized in the opposite direction.arrow_forwardA level site underlain by fully saturated clays is cut over a few days as shown in the figure below. The water table is located at the ground surface across the site. Determine the resistingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning