
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please answer all parts of the question with step by step working and explanantions so i understand the questions and solution better thank you.
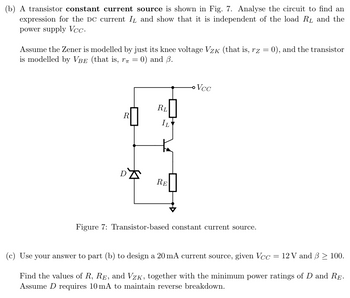
Transcribed Image Text:(b) A transistor constant current source is shown in Fig. 7. Analyse the circuit to find an
expression for the DC current IL and show that it is independent of the load RL and the
power supply Vcc.
Assume the Zener is modelled by just its knee voltage Vzк (that is, rz = 0), and the transistor
is modelled by VBE (that is, r = 0) and 3.
R
RL
IL
D
RE
Vcc
Figure 7: Transistor-based constant current source.
(c) Use your answer to part (b) to design a 20 mA current source, given Vcc : = 12 V and ẞ> 100.
Find the values of R, RE, and VZK, together with the minimum power ratings of D and RE.
Assume D requires 10 mA to maintain reverse breakdown.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For the circuit in Figure 1, the transistor is biased so that ICQ is 10 mA and VCEQ is 8 V. As a starting point, let VRE be 20% of VCC. Calculate the values needed for RE and RC.Assume β is 100. Select the nearest standard values for the twoCalculate the values of R1 and R2arrow_forwardComplete the given BJT circuit. Solve for the value of the resistors and the voltage supply that will satisfy the given DC loadline. Assume IC=IE and RC=RE. Show and label properly the required final circuit. 5 mA 2.5 mA * IC IC 0 15 V 30V VCE RB B +VCC C E RC B=100 RE ...arrow_forwardDetermine the resistor at the source Rs and bias voltage VBIAS necessary for the current source to operate with an output resistance of 500k2 and current of 0.2mA at a Vov-0.2V. Assume that the transistor has VA-20V and V.-0.5V. a. R.: b. Vbias VBIAS O Rsarrow_forward
- b)The transistor consists of three terminals. The main reason for designing configurations is that it requires four terminals in order to provide the input and the output connections of the circuit for effective amplification. Now in your own words describe how Bipolar Transistors Transistor ( BJT ) various configurations are designed with relating diagrams. In your own estimation evalute which one is most widely used when looking at appreciable output for an amplifier?arrow_forwardplease solve, with few steps as possible and show all formulasarrow_forward4. Circuit Analysis: 5. Given: Vd1 = Vbe = 0.7V. Icq = 0 Required: The dc voltages at the bases and emitters of the transistors Q1 andQ2 and VceQ for each transistor. wwww Vcc p +24 R1 1k Q1 R2 53 0 ci C2 Rg RL 120n Q2 R3 1karrow_forward
- The p-channel MOSFET in the circuit below has V = 1 V and k, = 2 mA/V² (A = 0). + 5 V 9 mA (. vout Q1 10 k VS -5 v a) Is this amplifier a common-source, common-drain, or common-gate configuration? b) Determine the d.c. biasing by calculating VsG and Vsp. c) What is the amplificr's gain A and output resistance Rout?arrow_forwardSince the transistors used in the circuit are b=200 and r0= ∞(endless);A) By analyzing the DC for each amplifier floor separatelyre1, re2 find resistance values.B) Draw the AC equivalent circuit of the amplifier circuit.C) For each floor Zi=?, Z0 =?D) For each amplifier floor Av1, Av2 find the tension gains.E) Avl find Vl voltage value by finding voltage gain.arrow_forwardFor the circuit shown. Sketch la vs V1 for the following values of V2 for V1 >0: V2 = 0V, V2 = 0.55V, V2=0.6V Assume that Is = 20fA, B = 100, VT = .025V (You may neglect early effect) On your graph label the models of operation that the transistor would be in and value(s) for the current when the transistor is in Forward Active. V2 laarrow_forward
- Draw ac equivalent circuits for the following amplifiers. Each circuit should include resistancesand one dependent voltage or current source. a) Common Drain b) Common Emitter with single emitter resistance RE c) Common Gate d) Common Source with RSAC and RSDCarrow_forwardConsider the following circuit with matched transistors. Assume a threshold voltage Ven = - Vtp = 1.5V. For an input voltage (V) of OV. Which statement is +2.5 V O vo 10 kN -2.5 V O A. Both transistors will be OFF O B. PMOS will cut OFF O C. NMOS will cut OFF O D. None of thesearrow_forwardThe MOSFET in the circuit below has V = 1 V, k, = 0.5 mA/V², and A= 0.04 V-1. + 5 V R. vout Q1 10 k vs -5 v a) Is this amplifier a common-source, common-drain, or common-gate configuration? b) Determine the resistance R so that the d.c. biasing has a drain current equal to 1 mA. What is VGs and Vps? Note, don't include A in the d.c. bias calculation. c) What is the amplifier's gain A, input resistance Rin, and output resistance Rout?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,