
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Blocks A and B are connected by a cord which passes over pulleys and through a collar C. The system is released from rest when x= 1.7 m. As block A rises, it strikes collar C with perfectly plastic impact (e= 0). After impact, the two blocks and the collar keep moving until they come to a stop and reverse their motion. As A and C move down, C hits the ledge and blocks A and B keep moving until they come to another stop. Determine (a) the velocity of the blocks and collar immediately after A hits C, (b) the distance the blocks and collar move after the impact before coming to a stop, (c) the value of x at the end of one complete cycle.
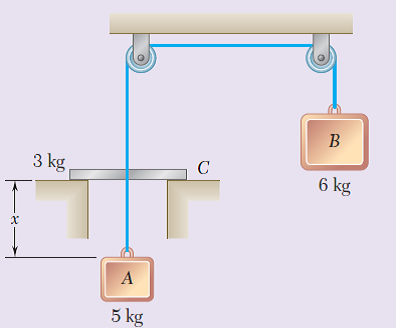
Transcribed Image Text:B
3 kg
6 kg
A
5 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Bullet B has a mass 15 g and blocks A and C both have a mass 2 kg. The coefficient of friction between the blocks and the plane is Hx = 0.25. Initially the bullet is moving at vo and blocks A and C are at rest (Fig. 1). After the bullet passes through A it becomes embedded in block C and all three objects come to stop in the positions shown (Fig. 2). Determine the initial speed of the bullet vo- B Vo - (1) 100 mm 150 mm B PC Aarrow_forwardAt the instant illustrated assigned as point A, a 3 kg box is pushed against spring A so it can travel along the floor and reach spring B. Spring A's undeformed length is 0.7 m. Spring B is initially undeformed. The spring constant of spring A is 600 N/m and spring B is 800 N/m. The package is released from rest. Assume that the package maintains contact with the floor at all times. The coefficient of sliding friction is 0.4 across the whole floor. Point B is the instant wherein the package touches the end of undeformed spring B. Point C is the instant the package temporarily stops as it reaches the other end of the deformed spring B.1. What's the work done by friction from point A to B?2. What's the sum of the work done by gravity and spring from point A to B?3. What's the velocity of the box at the instant it touches the end of undeformed spring B?4. What's the maximum deformation of spring B as the box reaches point C?arrow_forwardThe Skier starts from rest at point A. Determine the horizontal distance X traveled after he leaves the ramp and the landing speed. Neglect friction. The Skier starts from rest at point A. Determine the horizontal distance traveled after he leaves the ramp and the landing speed. Neglect friction. X=10.2 m, vc=24.2 ms X=7.81 m, vc=18.1 ms X=13.1 m, vc=24.9 ms X=8.96 m, vc=−21.2 msarrow_forward
- Which of the following is TRUE about Block A?A. Block A is at rest and is not impending to moveB. Block A is sliding up with increasing velocityC. Block A is impending to slide upD. Block A is sliding up with uniform velocityarrow_forwardAt an intersection near the a Toyota Prius (vehicle B, weight WB = 3,000 lb) is traveling north at VB₁ = 65 mph while a Ford F-150 (vehicle A, weight W₁ = 5,010 lb) travels VA1 = 35 mph south- east (0 = 20°) when they slam into each other. They become entangled and move as one after the collision. Determine: a) The velocity (magnitude and direction) of the combined vehicles after the crash b) The efficiency of the collision. 0 VA1 CI CD VB1 V2arrow_forwardแสดงวิธีทำให้ดูหน่อยครับarrow_forward
- 12. A 60 Ib suitcase slides from rest 5 meters down the smooth ramp. Determine the distance Rwhere it strikes the ground at B. How long does it take to go from A to B? 5m 30 2.5 marrow_forwardThe figure below shows an experiment with two marbles. Marble A was launched towards marble B with launch angle a and initial speed vo = |vo| > 0. At the same instant, marble B was released to fall from rest at Rtan a units directly above a spot R units horizontally downrange from A. Show that the marbles collide regardless of the initial speed vo. B R tan a -----arrow_forward3. include free body diagramarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY