
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305632134
Author: J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
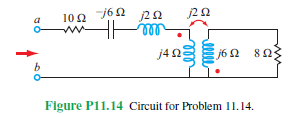
Determine (a) the input impedance and (b) the reflected
impedance, both at terminals (a,b) in the circuit of Fig. P11.14.
Transcribed Image Text:b
10 Ω
-760
1202
ΡΩ
4ΩΞ
60 80
Figure P11.14 Circuit for Problem 11.14.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I'm confused, please help with some explanation. Thank uarrow_forwardDesign a pulse train generator circuit using shift register for the following pulse train. ......1000110.........arrow_forwardCreate a sequence detector that detects the sequence 1001 or 0110 by using Verilog Code. Construct the modules for both the Moore and Mealy models. Demonstrate your simulation results using the following input sequence for the test fixture (test bench): x= 0010011010010110010110110100arrow_forward
- (B): Design a Moore FSM to detect the sequence (00) using T-FFs. Q4/ (A): Design a Mealy FSM for odd parity generator using JK-FFs.arrow_forwardReference 7 segment display: Solve for the segments: "d, e, and f." Show your work 1. KMAPs 2. Reduced equation to lite up the segment 3. Describe the operation of Lab 12 4. If you were to add a 4th seven-segment, Describe your design process.arrow_forwardReconsider Problem 3.29. If Va,VbandVc are a negative-sequence set, how would the voltage and current relationships change? (a) If C1 is the complex positive-sequence voltage gain in Problem 3.29 and (b) if C2 is the negative sequence complex voltage gain, express the relationship between C1andC2arrow_forward
- 3) or down. Explain how you come up with your answer in a step by step manner. Analyze the following ripple counters and check whether the counter is counting up a) Note that the LSB is Qa and MSB is QD. As usual LSB receives the count pulse. Qc Qo CK CK CK CK Count pulse R R R RESET- b) Note that the LSB is Qo and MSB is Q2. As usual LSB receives the count pulse. Qo Q1 Clk CIk Q. FF. Ck T FF1 Clk Q FF2arrow_forwardConsider the line of code below. analogWrite(11, 84); The voltage at pin 11 is turns on (at 5V for Uno) and off at 500 Hz. This PWM frequency is the default value for Arduino boards. How many microseconds is the voltage at pin 11 high?arrow_forwardVHDL Testbench Generate the following waveforms as part of a VHDL testbench using multiple processes. Note that cntr, and en signals are periodic signals and din and rst are not. Assume each time division is 10 ns. The ... represents the repeating pattern. Write your testbench as a parameterized waveform based on the parameter TD = 10 ns.arrow_forward
- Suppose you wish to increase the maximum clock frequency of the following circuit (without introducing timing violations or modifying the functional behavior of the circuit aside from introducing delay) through pipelining. Some potential locations for pipelining to be added to wires (labelled with numbers 1-10) are shown below: 1 D Q A DQ D Q 10 B D Q DQ C CLK Select all of the wires to which you would add pipeline registers. (Note, it is OK to increase the latency of the circuit, but not the functionality: for any sequence of input combinations, it should produce the same output combinations) If it is not possible, do not select any wires. 01 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 U 0 2 Harrow_forwardConsider a 1 into 4 de-multiplexer.The data input and selection line waveforms for the demultiplexer are given below. Draw the corresponding output waveforms (for D0 to D3). Data in SO DO D3 Note: You need to draw the waveforms on paper. Take the photo and then upload. A- B Iarrow_forwardIn a communication system the signal sent from point a to point b arrives by two paths in parallel. For path 1, the signal passes through two repeaters ( in series ). Each repeater has probability of failing ( becoming an open circuit ) of 0.1. For path 2, the signal passes through one repeater with a probability of failing of 0.08. All repeaters fail independently of each other. Find the probability that the signal will not arrive at point b. O 0.0152 O 0.016 0.008 0.09arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:Cengage Learning