
Concept explainers
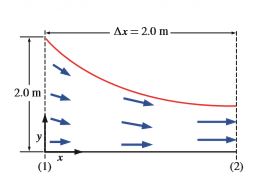
A two-dimensional converging duct is being designed for a high-speed wind tunnel. The bottom wall of the duct is to be flat and horizontal, and the top wall is to be curved in such a way that the axial wind speed u increases approximately linearly from u1 = 100 m/s at section (1) to u2 = 300 m/s at section 2. Meanwhile, the air density ? is to decrease approximately linearly from ?1 = 1.2 kg/m3 at section (1) to ?2 = 0.85 kg/m3 at section (2). The converging duct is 2.0 m long and is 2.0 m high at section (1). (a) Predict the y-component of velocity, ?(x, y), in the duct. (b) Plot the approximate shape of the duct, ignoring friction on the walls. (c) How high should the duct be at section (2), the exit of the duct?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 7 images

- Problem P68 (a) Determine the magnitude of the anchoring force needed to hold the horizontal bend and nozzle in place. The velocity at location 1 is known to be 2 m/s. The pressure at location 1 of the 300 mm diameter pipe is known to be 100 kPa. The discharge at section 2 is in the form of a free jet to the atmosphere. Ans: F = 8.345 kN 300 mm 160 mm Diameter Jet P₁ = 100 KPa Reducing Bend with Nozzle FRB/Farrow_forwardFast.arrow_forward9. Water at 20 C flows in a 10 cm diameter commercial steel pipe that 100m long with an average velocity of 8m/s. what is the frictional pressure drop for this pipe? a. 109 kPa b. 473 kPa c. 248 kPa d. 544 kPaarrow_forward
- H.W. 6.32 Q: in a (45°) bend a rectangular air duct of (1) m² cross-sectional area is gradually reduced to (0.5) m² area. Find the magnitude and direction of the force required to hold the duct in position if the velocity of flow at (1) m² section is (10) m/s and pressure is (2.943) N/cm². Take density of air as (1.16) kg/m³. 66arrow_forwardProblem 11.11 Air at 60°C flows through the very wide duct. Suppose that L = 210 mm. v = 18.9(106) m²/s. (Figure 1) Figure 0.5 m/s L x = 4m 1 of 1 0.5 m/s Part A Determine the required dimension a of the duct at x = 4 m so that the central core flow velocity maintains the constant free-stream velocity of 0.5 m/s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value Submit μA Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forwardConsider a system where a horizontal, laminar, separated flow of air and water at 100 kPa pressure and 20 C temperature are moving between two infinitely-sized parallel plates. The water flow is not forced, but is carried along by the air flow. The 'superficial velocity' of the air is 0.1 m/s (superficial velocity is volume flow rate / flow area, representing the average velocity of the flow). The depth of the water film is 2 mm and the thickness of the air layer is 5 mm. Use the multiphase balance equations and interfacial boundary conditions to derive the velocity profile in the air and water, with y=D0 being the interface between the two.arrow_forward
- help plssarrow_forwardA 2-ft-diameter hemispherical plexiglass "bubble" is to be used as a special window on the side of an above-ground swimming pool. The window is to be bolted onto the vertical wall of the pool and faces outward, covering a 2-ft-diameter opening in the wall. The center of the opening is 4.1 ft below the surface. Determine the (a) horizontal and (b) vertical components of the force of the water on the hemisphere. (a) FH = (b) Fy= lb (outward) (down on bubble)arrow_forwardThe floor of a classroom is made of 125-mm thick lightweight plain concrete. If the floor is slab having a length of 9 m and width of 10 m. Determine the force in kN caused by the liveload. Liveload for private room = 1.92 kPaarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





