
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
A golf ball with mass 4.50 10-2 kg is struck with a club as shown in the figure above. The force on the ball varies from zero when contact is made up to some maximum value (when the ball is maximally deformed) and then back to zero when the ball leaves the club, as in the graph of force vs. time in the figure below. Assume that the ball leaves the club face with a velocity of +50 m/s.
(a) Find the magnitude of the impulse due to the collision.
kg · m/s
(b) Estimate the duration of the collision and the average force acting on the ball. (Assume the distance the ball travels on the face of the club is 2 cm, roughly the same as the radius of the ball.)
| duration | s |
| average force | N |
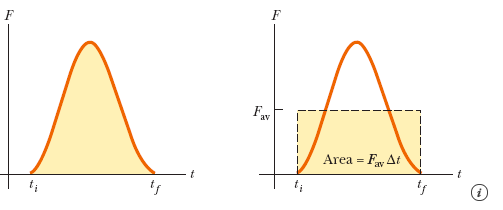
Transcribed Image Text:av
Area
F At
t;
ts
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- stretch 38. Realizing that he could not drive up a 30°, ice-covered hill because there was no friction, Sir Isaac Newton had stopped his cart, of total mass 500 kg, at the bottom. He was struck in the rear by a London stage coach, of total mass 1500 kg. trav- elling at 20 m/s. The two vehicles stuck together, with nothing breaking loose, and slid up the hill in a straight line. How far up the slope did the wreckage get before coming to rest? (SIN '70)arrow_forwardA baseball (m= 150 g) approaches a bat horizontally at a speed of 43.9 m/s (98.2 mi/h) and is hit straight back at a speed of 52.6 m/s (118 mi/h). If the ball is in contact with the bat for a time of 1.27 ms, what is the average force exerted on the ball by the bat? Neglect the weight of the bat, since it is so much less than the force of the bat. Choose the direction of the incoming ball as the positive direction. Number i Units VO Vfarrow_forwardA 0.7 ball falls down and hits the floor at a speed of 15 m/s. The ball then bounces back up at aspeed of 12 m/s. If the ball was in contact with the floor for 0.06 s, what was the average force from the floor on the ball?arrow_forward
- A 0.6 Kg football is thrown with a velocity of 22 m/s to left. A stationary receiver catches the ball and brings it to rest in 0.03 s. What is the force exerted on the ball by the receiver? Show the procedure, result with units and directionarrow_forwardA 78-kg fisherman in a 116-kg boat throws a package of mass m = 15 kg horizontally toward the right with a speed of vi = 4.4 m/s as in the figure below. Neglecting water resistance, and assuming the boat is at rest before the package is thrown, find the velocity of the boat after the package is thrown. magnitude m/s direction ---Select--- toward the right toward the left upwards downwardsarrow_forwardA hockey player slaps a puck into a cushion, which brings the puck to rest. If the puck's initial velocity was +40 m/s and it has a mass of 170 g, what force does the cushion apply to the puck? Assume the cushion acts on the puck for 0.03 s and the surface that the puck slides on is frictionless.arrow_forward
- A Maxim machine gun fires 431 bullets per minute. Each bullet has a mass of 12g and a velocity of 686m/s.What is the average force that the impact of these bullets exerts on a target? Assume the bullets penetrate the target and remain embedded in it. Calculate answer to one decimal.arrow_forwardBlocks A, B, and C are aligned along a straight line on a horizontal frictionless surface. The masses of the blocks are M, 3M and 4M, respectively. Block A is initially moving to the right along the same line at a speed v, as shown in the figure. Blocks B and C are initially at rest. Block A collides with and sticks to block B. The two blocks then collide with and stick to block C. What is the speed of * ?block C after the collisions Block A Block B Block C 8v v/4 0. v/3 O v/8 Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON