
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
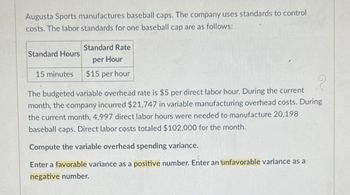
Transcribed Image Text:Augusta Sports manufactures baseball caps. The company uses standards to control
costs. The labor standards for one baseball cap are as follows:
Standard Hours
15 minutes
Standard Rate
per Hour
$15 per hour
The budgeted variable overhead rate is $5 per direct labor hour. During the current
month, the company incurred $21,747 in variable manufacturing overhead costs. During
the current month, 4,997 direct labor hours were needed to manufacture 20,198
baseball caps. Direct labor costs totaled $102,000 for the month.
Compute the variable overhead spending variance.
Enter a favorable variance as a positive number. Enter an unfavorable variance as a
negative number.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Dawson Toys, Limited, produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently created a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the following standards for the Maze toy: Direct materials: 8 microns per toy at $0.32 per micron Direct labor: 1.4 hours per toy at $7.40 per hour During July, the company produced 4,600 Maze toys. The toy's production data for the month are as follows: Direct materials: 73,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.30 per micron. 27,000 of these microns were still in inventory at the end of the month. Direct labor. 6,940 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $55,520. Required: 1. Compute the following variances for July: (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) a. The materials price and quantity…arrow_forwardDawson Toys, Limited, produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently created a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the following standards for the Maze toy: Direct materials: 7 microns per toy at $0.33 per micron Direct labor: 1.2 hours per toy at $7.10 per hour During July, the company produced 5,200 Maze toys. The toy's production data for the month are as follows: Direct materials 71,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.31 per micron. 25,500 of these microns were still in inventory at the end of the month. Direct labor. 6,640 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $51,128. Required: 1. Compute the following variances for July: (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) a. The materials price and quantity…arrow_forwardDawson Toys, Limited, produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently created a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the following standards for the Maze toy: Direct materials: 6 microns per toy at $0.33 per micron Direct labor: 1.3 hours per toy at $6.80 per hour During July, the company produced 5,000 Maze toys. The toy's production data for the month are as follows: Direct materials: 79,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.32 per micron. 41,500 of these microns were still in inventory at the end of the month. Direct labor: 7,100 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $52,540. Required: 1. Compute the following variances for July: (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) a. The materials price and quantity…arrow_forward
- Hear Smart manufactures headphone cases. During September 2018, the company produced and sold 105,000 cases and recorded the following cost data: STANDARD COST INFORMATION QUANTITY COST Direct Materials 2 Parts $0.15 per part Direct Labor 0.02 hours 8.00 per hour Variable Manufacturing Overhead 0.02 hours 10 per hour Fixed Manufacturing Overhead ($28,500 for static budget volume of 95,000 units and 1,900 hours, or $15 per hour) ACTUAL COST INFORMATION Direct Materials (209,000 parts @ $0.20 per part) $ 41,800 Direct Labor (1,600 hours @ $8.15 per hour) 13,040 Variable Manufacturing Overhead 9,000 Fixed Manufacturing Overhead 26,000 REQUIREMENTS Compute the cost and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor. For manufacturing overhead, compute the variable overhead…arrow_forwardDawson Toys, Limited, produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently created a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the following standards for the Maze toy: Direct materials: 6 microns per toy at $0.33 per micron Direct labor: 1.1 hours per toy at $6.70 per hour During July, the company produced 5,000 Maze toys. The toy's production data for the month are as follows: Direct materials: 80,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.31 per micron. 42,500 of these microns were still in inventory at the end of the month. Direct labor. 5,800 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $40,600. Required: 1. Compute the following variances for July: (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) a. The materials price and quantity…arrow_forwardComputer World, Inc. manufactures computer parts and keyboards. The annual production and sales of computer parts is 1,000 units, while 1,200 keyboards are produced and sold. The company has traditionally used direct labor hours to allocate its overhead to products. Computer parts require 3 direct labor hours per unit, while keyboards require 2.5 direct labor hours per unit. The total estimated overhead for the period is $114,000. The company is looking at the possibility of changing to an activity-based costing system for its products. What is the predetermined overhead allocation rate using the traditional costing system?arrow_forward
- Sardi Inc. is considering whether to continue to make a component or to buy it from an outside supplier. The company uses 13,100 of the components each year. The unit product cost of the component according to the company's cost accounting system is given as follows: Direct materials $ 8.90 Direct labor 5.90 Variable manufacturing overhead 1.70 Fixed manufacturing overhead 3.70 Unit product cost $ 20.20 Assume that direct labor is a variable cost. Of the fixed manufacturing overhead, 20% is avoidable if the component were bought from the outside supplier. In addition, making the component uses 2 minutes on the machine that is the company's current constraint. If the component were bought, time would be freed up for use on another product that requires 4 minutes on this machine and that has a contribution margin of $5.30 per unit. When deciding whether to make or buy the component, what cost of making the component should be compared to the…arrow_forwardCWB Inc. produces stuffed bunnies. The company normally produces and sells 78,000 stuffedbunnies each year at a selling price of $50 per unit. The company's unit costs at this level ofactivity are given below: Direct materials $9.30Direct labor 8.00Variable manufacturing overhead 2.00Fixed manufacturing overhead 6.00 ($468,000 total)Variable selling expenses 1.50Fixed selling expenses 6.00 ($468,000 total)Total cost per unit $32.80 The company has 500 completed stuffed bunnies on hand that have someirregularities and are therefore considered to be "seconds." Due to the irregularities, it will beimpossible to sell these units at the normal price through regular distribution channels. Whatunit cost figure is relevant for setting a minimum selling price? Briefly explain why. How to do it and what does unit cost figure mean?arrow_forwardInnova uses 1,100 units of the component IMC2 every month to manufacture one of its products. The unit costs incurred to manufacture the component are as follows. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Total Direct material Direct labor Overhead costs include variable material handling costs of $6.50, which are applied to products on the basis of direct material costs. The remainder of the overhead costs are applied on the basis of direct labor dollars and consist of 60.00% variable costs and 40.00% fixed costs. A vendor has offered to supply the IMC2 component at a price of $290.00 per unit. (a) Material handling Prepare the incremental analysis for the decision to make or buy IMC2. Assume that no fixed costs will be eliminated if production is outsourced. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 12.25. Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding the number e.g. -45 or parentheses e.g. (45).) Variable overhead Fixed overhead Purchase price Total unit cost $55.34 $ No…arrow_forward
- The Gidget Company produces a variety of styles of gidgets, and measures total output as the standard hours allowed for actual output. Gidget Company's manufacturing overhead budget calls for $50,000 of fixed overhead for the year plus $10 per direct labor hour. Last year the Gidget Company produced 11,000 standard hours of output. Actual manufacturing overhead for the year amounted to $53,000 of fixed overhead and the Gidget Company used 8,000 direct labor hours. The Gidget Company uses standard direct labor hours allowed as a basis for allocating overhead and uses 10,000 direct labor hours as its denominator volume. Calculate the production volume variance:arrow_forwardCozy, Inc., manufactures small and large blankets. It estimates $350,000 in overhead during the manufacturing of 75,000 small blankets and 25,000 large blankets. What is the predetermined overhead rate if a small blanket takes 1 machine hour and a large blanket takes 2 machine hours?arrow_forwardThe following details taken from the books of DiDi Sdn Bhd for the year ending 31 December 2020. DiDi Sdn Bhd Statement Profit or Loss for the year ending 31 December 2020 (extract) RM RM Gross profit 44,700 Add : Discount received 410 Profit on sale of van 620 1,030 45,730 Less: Expenses Motor expenses 1,940 Wages 17,200 General expenses 830 Bad debts 520 Increase in allowance for doubtful debts 200 Depreciation : van 1,800 22,490 23,240 Statement of Financial Position as at 31 December 2019 2020 RM RM RM RM Non-current Assets Vans at cost 15,400 8,200 less Depreciation (5,300) (3,100) 10,100 5,100 Current Assets Inventory 18,600 24,000 Trade accounts receivables less provision*…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education