
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Q Search
ansport Review Questions
Home
Insert
Draw
View
Help
Open in Desktop App
O Tell me what you want to do
I
e Av A
E E E E
Calibri Light
v 20
В
U
...
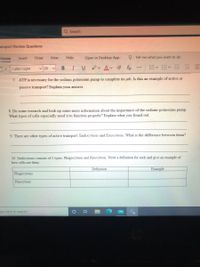
7. ATP is necessary for the sodium potassium pump to complete its job. Is this an example of active or
passive transport? Explain your answer.
8. Do some research and look up some more information about the importance of the sodium-potassium pump.
What types of cells especially need it to function properly? Explain what you found out.
9. There are other types of active transport: Endocytosis and Exocytosis. What is the difference between them?
10. Endocytosis consists of 2 types: Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis. Write a definition for each and give an example of
how cells use them.
Definition
Example
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
pe here to search

Transcribed Image Text:Q Search
nsport Review Questions
Home
Insert
Draw
View
Help
Open in Desktop App
O Tell me what you want to do
I.
ev Av A
m< m< 向 制川4
Calibri Light
v 20
B
...
tive
cnort
Cell Transport: Active Transport Review Questions
1. In your class pictorial notes, which ion was represented by the black circle? (Give the actual name and
symbol.)
2. In your class pictorial notes, which ion was represented in the diagram by the orange square? (Give the
actual name and symbol.)
3. Which ions (and how many) are moving outside of the cell during the sodium potassium pump's cycle?
4. Which ions (and how many) are moving inside of the cell during the sodium potassium pump's cycle?
5. Describe the concentration gradient. What ions have a higher concentration OUTSIDE the cell? What
ions have a higher concentration INSIDE the cell?
6. Are the ions moving up their concentration gradient (towards the higher concentration side)? Or are they
moving down their concentration gradient (towards the least concentrated side)? Explain your answer.
here to search
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hello, please answer the following Physiology question completely and correctly. Thank you. Physiology Question: "Explain the difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport. Further explain the difference between primary and secondary active transport." "arrow_forwardExplain why, when a concentration gradient exists on two sides of membrane, that the spontaneous movement of solute molecules is from areas of high concentration towards low concentration. (hint: think of thermodynamics)arrow_forwardIf a skeletal muscle has depleted its stores of ATP how will the altered transport properties of the following transporters affect cytosolic ion concentrations (increase, decrease, no change) relative to normal? Skeletal Muscle Cell With Depleted ATP Stores Ion transporter Cytosolic K+ Cytosolic Na+ Cytosolic Ca2+ NKA NCX SERCAarrow_forward
- Explain the difference between active transport across the cell membrane and passive transport.arrow_forwardMatch the following statement related to membrane transport processes to the appropriate term or terms: passive transport, facilitated transport, active transport. A transporter (or carrier) protein is necessary. (Select all that apply.) passive transport facilitated transport active transport O Oarrow_forwardDescribe the process of active transport as carried out by ion pumps. Your answer must include a discussion of all concentration gradients (ΔC), whether molecules are moving down and/or against ΔC, and the energy (ATP) requirements for active transport. Explain why energy is required or not required. Lastly, name a known ion pumparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education