
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
SOLVE CAREFULLY!! Please Write Clearly and Box the final Answer for Part C, and Part D , with THE CORRECT UNITS) Thank you. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units.
DRAW the kinematic diagram and label it for this problem as well Thank you
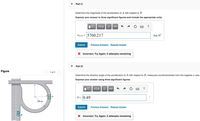
Transcribed Image Text:Part C
Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of A with respect to B.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
vec
aA/B = 5760.217
km/h?
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
Part D
Figure
1 of 1
Determine the direction angle of the acceleration of A with respect to B, measured counterclockwise from the negative x axis.
Express your answer using three significant figures.
VO AEO vec
?
0 = 0.49
100 m
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
- - - - - - -

Transcribed Image Text:At the instant shown in (Figure 1), car A has a speed of
23 km/h, which is being increased at the rate of
300 km/h² as the car enters the expressway. At the
same instant, car B is decelerating at 250 km/h² while
traveling forward at 100 km/h.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two cars A and B are traveling in the lane of an adjacent highway at the position and speed shown in the figure (this instant is called t = 0). Car A is moving at an equivalent speed of 0.54 m/s, and Car B is 0.36 m/s. It moves at a constant deceleration rate of 6 m/s2 (a) Find when and where A overtakes B. (b) Find the speed of each car at that moment.arrow_forward9arrow_forwardA car moved on a horizontal path from rest at constant acceleration from point A until it reached its maximum speed when passing by At point b it took 4 seconds, and after point B it continued its movement but at a slowdown of -3 m / s2 until it stopped at c Categorical The idling distance of 13.5 m. Find: 1. The distance the car traveled while accelerating from a to b 2. The car's rate of acceleration (acceleration) 3. The car's maximum speed from point b 4. The time the car took when slowing down from b to carrow_forward
- 2/203 Car A is traveling at the constant speed of 60 km/h as it rounds the circular curve of 300-m radius and at the instant represented is at the position 6 = 45°. Car B is traveling at the constant speed of 80 km/h and passes the center of the circle at this same instant. Car A is located with respect to car B by polar coordinates r and 0 with the pole moving with B. For this instant determine vAB and the val- ues of i and ở as measured by an observer in car B. Ans. VAB = 36.0 m/s i = -15.71 m/s, 6 = 0.1079 rad/sarrow_forwardCar A is traveling at the constant speed of 48 km/h as it rounds the circular curve of radius r - 310 m and at the instant represented is at the position 8 - 43°. Car B is traveling at the constant speed of 58 km/h and passes the center of the circle at this same instant. Car A is located with respect to car B by polar coordinates r and with the pole moving with B. For this instant determine VA/B and the values of it and as measured by an observer in car B. Answers: VA/B- ŕ- 0- i 27.4 i -14.4 0.075 0 m/s m/s rad/sarrow_forwardAt the instant shown in (Figure 1) , the car at A is traveling at 10 m/sm/s around the curve while increasing its speed at 5.1 m/s2m/s2. The car at B is traveling at 28.5 m/sm/s along the straightaway and increasing its speed at 2 m/s^2. First Question: Determine the direction angle of the relative velocity with respect to B at this instant, measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis. Second Question: Determine the magnitude of the relative acceleration of A with respect to B at this instant. Third Question: Determine the direction angle of the relative acceleration with respect to B at this instant, measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis.arrow_forward
- At the instant illustrated, car B has a speed of 40 km/h and car A has a speed of 55 km/h. Determine the values of i and 0 for this instant where r and O are measured relative to a longitudinal axis fixed to the road of car B as indicated in the figure.arrow_forwardCar A is traveling at the constant speed of 45 km/h as it rounds the circular curve of radius r = 380 m and at the instant represented is at the position 0 = 40°. Car B is traveling at the constant speed of 54 km/h and passes the center of the circle at this same instant. Car A is located with respect to car B by polar coordinates r and with the pole moving with B. For this instant determine VA/B and the values of r and as measured by an observer in car B. Answers: VA/B = r = 0 = i i 8 m/s m/s rad/s Barrow_forwardFigure shows two trains that are moving on the same direction from a same initialposition of O. The speed of the trains at the point O is given by v A =27 m/s and v B = 8m/s. If the train B is decelerating at a B = -2.3 m/s 2 to stop at the next station whiletrain A continues the traveling with a constant speed, calculate the distance betweenboth trains at the instant the train B stops at the station. Use s A and s B to describe thedistance of the trains from the initial position of O.arrow_forward
- please double check your answerarrow_forwardCompute it, Thanksarrow_forwardOn a curvy road, a motorist applies breaks and the speed of the vehicle is reduced uniformly from 60 km/h at point A to 40 km/h at point B; points A and B are 120 m apart. If the vehicle has a resultant acceleration of 2.5 m/s2 at point A, calculate the radius of the curvature of the road at this point. Calculate also the acceleration of the vehicle at point B where the road has a radius of curvature equal to 90 m. (complete steps)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY