
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
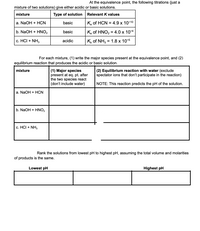
Transcribed Image Text:At the equivalence point, the following titrations (just a
mixture of two solutions) give either acidic or basic solutions.
mixture
Type of solution
Relevant K values
а. NaOH + HCN
basic
K, of HCN = 4.9 x 10-10
b. NaOH + HNO2
basic
Ka of HNO2 = 4.0 x 10-4
c. HCI + NH3
acidic
K, of NH3 = 1.8 x 10-5
For each mixture, (1) write the major species present at the equivalence point, and (2)
equilibrium reaction that produces the acidic or basic solution.
mixture
(1) Major species
present at eq. pt. after
the two species react
(don't include water)
(2) Equilibrium reaction with water (exclude
spectator ions that don't participate in the reaction)
NOTE: This reaction predicts the pH of the solution.
а. NaOH + HCN
b. NaOH + HNO2
c. HCI + NH3
Rank the solutions from lowest pH to highest pH, assuming the total volume and molarities
of products is the same.
Lowest pH
Highest pH
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which solution has the greatest buffer capacity? Which solution can react with the largest amount of added strong acid?arrow_forwardAcetic Acid: Ka = 1.7 x 10-5 Hydrofluoric Acid: Ka = 6.8 x 104 Propionic Acid: Ka = 1.3 x 10-5 A 20.0 mL sample of 0.120 M propionic acid was titrated by 0.150 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the following points. a) Before titration. b) After the addition of 10.0 mL of the base. c) At the equivalence point. d) After the addition of a total of 30.0 mL of the basearrow_forwardFor each combination of acid and base below, what is the relative pH at the equivalence point of the titration? 1) HCO₂H + NaOH: [Select] CIRC 2) HNO₂ + NH3: [Select] 3) H₂SO4 + LIOH: [Select] 4) HBr + KOH: [Select] <arrow_forward
- Calculate the pH of each of the following solutions a. 0.10 M propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH, Ka = 1.3 x 10-5 b. 0.10 M sodium propanoate, NaCH3CH2COO. c. A mixture containing 0.10 M propanoic acid and 0.10 M sodium propanoate d. Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of HCl is added to 1.00 L of a solution that contains 0.10 M propanoic acid and 0.10 M sodium propanoate e. Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of NaOH is added to 1.00 L of a solution that contains 0.10 M propanoic acid and 0.10 M sodium propanoatearrow_forwardC Determine the pH of each solution at the equivalence point. pH (NaOH titrant) pH (Ca(OH)2 titrant) Submit =arrow_forward2)Make a rough plot of pH versus milliliters of acid added for the titration of 50.0 mL of 1.0 M NaOH with 1.0 M HCl. Indicate the pH at the following points and tell how many milliliters of acid are required to reach the equivalence point. a)Before the titration starts b)At the equivalence point c)After an additional 10.0 mL of HCL is added after the equivalence point (i.e. equivalence point volume + 10.0 mL)arrow_forward
- I need help with 3. Determine the pH of the solution at the equivalence pointarrow_forwardIn a titration of a weak acid with a strong base, what is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point?arrow_forwardse or conjugate base. 12 2. A 50.0mL sample of an acid HA, of unknown molarity is titrated with 0.1000 M KOH. The pH of the resulting solution is measure with a pH meter and graphed below. Select the letter that corresponds to the following. Some letters may be used more than once. Some may not be used at all. 10+ a. the equivalence point: R 9 b. the half equivalence point: Q 8+ c. where [KOH] is greatest: 7+ P I of d. where [H+] is greatest: T e. where [HA]=[A-]: 5+ 4 f. where [A-] is the predominate species: 3+ 2 SO a. What is pH after 10.0mL of 0.15M NaOH solution has been added to 25.0 mL of 0.12M HF solution? Ka = 6.8 x 10-4. b. After adding NaOH, is the resulting solution a buffer solution? Explain. 3. Complete the following calculations. (P) (Q) 84 3 ST PRarrow_forward
- A triprotic acid is titrated with KOH. What species are NOT in solution to any large extent between the 1st and 2nd equivalence points? Select all that apply. O H3A O HA? O A³- K+ O OH H2Aarrow_forwardHCN is a weak acid with a Ka = 4.90 x 10-10. A 50.00 mL sample of this HCN solution (0.250 M) is titrated with 0.500 M NAOH. What is the pH at the equivalence point?arrow_forwardLet HA represent a weak acid. A 10.0 mL sample of 0.600M HA was titrated with 0.300 M NaOH. The table below is some of the data for this titration. Volume NaOH added (mL) 5.00 10.00 15.00 ? ? pH 6.98 7.46 7.93 ? ? Calculate the following: a) The volume of NaOH needed to reach the equivalence point is mL. (Report value to the correct number of significant figures.) b) The Ka for HA is Report value using no superscripts. For example, Kw = 1.0 x 10-14 or 1.0e-14 (Report value to the correct number of significant figures.) c) The Kp for A is Report value using no superscripts. For example, Kw = 1.0 x 10-14 or 1.0e-14 (Report value to the correct number of significant figures.) d) The pH of the solution at the equivalence point is e) On your sheet of paper, draw a reasonable diagram of the complete titration curve. Label both axis appropriately. Label the volumes and pH values at the MIDPOINT and the EQUIVALENCE POINT.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY