
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
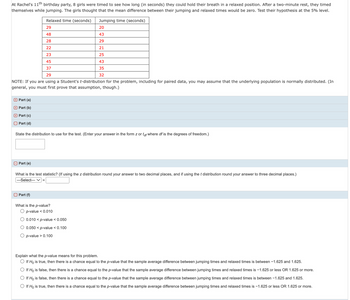
Transcribed Image Text:At Rachel's 11th birthday party, 8 girls were timed to see how long (in seconds) they could hold their breath in a relaxed position. After a two-minute rest, they timed
themselves while jumping. The girls thought that the mean difference between their jumping and relaxed times would be zero. Test their hypothesis at the 5% level.
Relaxed time (seconds)
29
48
28
22
23
45
37
29
NOTE: If you are using a Student's t-distribution for the problem, including for paired data, you may assume that the underlying population is normally distributed. (In
general, you must first prove that assumption, though.)
Part (a)
Part (b)
Part (c)
Part (d)
State the distribution to use for the test. (Enter your answer in the form z or tof where df is the degrees of freedom.)
Part (e)
What is the test statistic? (If using the z distribution round your answer to two decimal places, and if using the t distribution round your answer to three decimal places.)
---Select--- =
Part (f)
What is the p-value?
O p-value < 0.010
O 0.010 < p-value < 0.050
Jumping time (seconds)
20
43
29
21
25
43
35
32
0.050 <p-value < 0.100
O p-value > 0.100
Explain what the p-value means for this problem.
O If Ho is true, then there is a chance equal to the p-value that the sample average difference between jumping times and relaxed times is between -1.625 and 1.625.
O If Ho is false, then there is a chance equal to the p-value that the sample average difference between jumping times and relaxed times is -1.625 or less OR 1.625 or more.
O If Ho is false, then there is a chance equal to the p-value that the sample average difference between jumping times and relaxed times is between -1.625 and 1.625.
If Ho is true, then there is a chance equal to the p-value that the sample average difference between jumping times and relaxed times is -1.625 or less OR 1.625 or more.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a fishing lodge brochure, the lodge advertises that 75% of its guests catch northern pike over 20 pounds. Suppose that last summer 71 out of a random sample of 86 guests did, in fact, catch northern pike weighing over 20 pounds. Does this indicate that the population proportion of guests who catch pike over 20 pounds is different from 75% (either higher or lower)? Use ? = 0.05. (a) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. H0: p = 0.75; H1: p > 0.75H0: p ≠ 0.75; H1: p = 0.75 H0: p < 0.75; H1: p = 0.75H0: p = 0.75; H1: p ≠ 0.75H0: p = 0.75; H1: p < 0.75 (b) What sampling distribution will you use? The Student's t, since np > 5 and nq > 5.The standard normal, since np > 5 and nq > 5. The Student's t, since np < 5 and nq < 5.The standard normal, since np < 5 and nq < 5. What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to two decimal places.) (c) Find the P-value of the test…arrow_forwardAt Rachel's 11th birthday party, 8 girls were timed to see how long (in seconds) they could hold their breath in a relaxed position. After a two-minute rest, they timed themselves while jumping. The girls thought that the mean difference between their jumping and relaxed times would be zero. Test their hypothesis at the 5% level. Relaxed time (seconds) 29 48 28 22 23 45 37 29 NOTE: If you are using a Student's t-distribution for the problem, including for paired data, you may assume that the underlying population is normally distributed. (In general, you must first prove that assumption, though.) Part (a) Part (b) Part (c) + Part (d) Part (e) Part (f) Part (g) Part (h) Indicate the correct decision ("reject" or "do not reject" the null hypothesis), the reason for it, and write an appropriate conclusion. (i) Alpha (Enter an exact number as an integer, fraction, or decimal.) απ (ii) Decision: O reject the null hypothesis Jumping time (seconds) 20 43 29 21 25 43 35 32 do not reject the…arrow_forwardX10.2.21-T Twenty years ago, 56% of parents of children in high school felt it was a serious problem that high school students were not being taught enough math and science. A recent survey found that 247 of 700 parents of children in high school felt it was a serious problem that high school students were not being taught enough math and science. Do parents feel differently today than they did twenty years ago? Use the a=0.01 level of significance. Because npo (1- Po) = 172.5 > 10, the sample size is less than 5% of the population size, and the sample can be reasonably assumed to be random, the requirements for testing the hypothesis are satisfied. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) What are the null and alternative hypotheses? versus H,: Ho: (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)arrow_forward
- A standardized math test of fifth grade students produces a mean ?μ = 100 with a ?σ = 18. A sample of n = 36 students participated in "boost" training for their math skills. The sample M = 104 with S = 24. Did this "boost" training significantly improve students' math performance? Use ?α = .01.arrow_forwardWould you favor spending more federal tax money on the arts? Of a random sample of n1 = 204 women, r1 = 70 responded yes. Another random sample of n2 = 178 men showed that r2 = 48 responded yes. Does this information indicate a difference (either way) between the population proportion of women and the population proportion of men who favor spending more federal tax dollars on the arts? Use ? = 0.05. (a) What is the level of significance?State the null and alternate hypotheses. H0: p1 = p2; H1: p1 > p2H0: p1 = p2; H1: p1 < p2 H0: p1 = p2; H1: p1 ≠ p2H0: p1 < p2; H1: p1 = p2 (b) What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making? The standard normal. We assume the population distributions are approximately normal.The Student's t. The number of trials is sufficiently large. The standard normal. The number of trials is sufficiently large.The Student's t. We assume the population distributions are approximately normal. What is the value of the sample…arrow_forwardA survey was conducted two years ago asking college students their top motivations for using a credit card. To determine whether this distribution has changed, you randomly select 425 college students and ask each one what the top motivation is for using a credit card. Can you conclude that there has been a change in the claimed or expected distribution? Use a=0.10. Complete parts (a) through (d). New Survey Frequency, f 111 97 Response Old Survey % Rewards 29% 23% Low rates Cash back Discounts Other 22% 108 8% 46 18% 63 UD. XX O D. X Xo 2 OC. X >Xo OC. X>x (c) Calculate the test statistic. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) %3D (d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Then interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. V the claimed or ▼enough evidence to conclude that the distribution of motivations Ho At the 10% significance level, there expected distribution.arrow_forward
- In a fishing lodge brochure, the lodge advertises that 75% of its guests catch northern pike over 20 pounds. Suppose that last summer 59 out of a random sample of 85 guests did, in fact, catch northern pike weighing over 20 pounds. Does this indicate that the population proportion of guests who catch pike over 20 pounds is different from 75% (either higher or lower)? Use a = 0.05. (a) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. O Ho: p = 0.75; H1: p 0.75 (b) What sampling distribution will you use? O The Student's t, since np 5 and ng > 5. O The standard normal, since np 5 and nq > 5. What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to two decimal places.) (c) Find the P-value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)arrow_forwardWould you favor spending more federal tax money on the arts? Of a random sample of n1 = 215 women, r1 = 63 responded yes. Another random sample of n2 = 185 men showed that r2 = 49 responded yes. Does this information indicate a difference (either way) between the population proportion of women and the population proportion of men who favor spending more federal tax dollars on the arts? Use ? = 0.05.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman