
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
At a certain time a particle had a velocity of 18 m/s in the positive x-direction, and 2.4 s later its velocity was 30 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the average acceleration of the particle during this 2.4 s interval.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
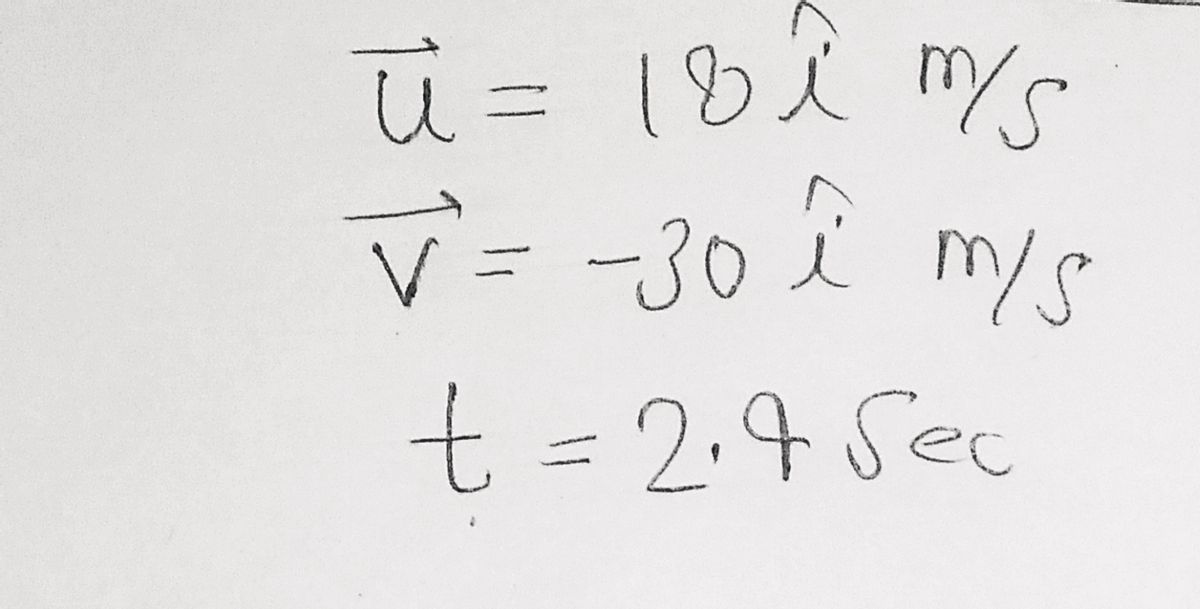
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particle moves in one dimension, and its position as a function of time is given by x = (2.1 m/s)t + (−3.0 m/s2)t2. (a) What is the particle's average velocity from t = 0.45 s to t = 0.55 s? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)(b) What is the particle's average velocity from t = 0.49 s to t = 0.51 s? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)arrow_forwardIn heavy rush-hour traffic, you drive in a straight line at 12 m/s for 1.5 minutes, then you have to stop for 3.5 minutes, and finally, you drive at 15 m/s for another 2.5 minutes. Plot a position-versus-time graph for this motion. Your plot should extend from t = 0 minutes to t = 7.5 minutes. Assume x=0 and t=0 at the start of your motion.arrow_forwardA brick is dropped from the roof of a tall building. After it has been falling for a few seconds, it falls 41.0 mm in a 1.00-ss time interval.What distance will it fall during the next 1.00 s? Ignore air resistance.arrow_forward
- A particle has an acceleration of + 6.24 m/s2 for 0.300 s. At the end of this time the particle’s velocity is + 9.31 m/s. (a) Write given quantities. (b) Calculate the particle’s initial velocity.arrow_forwardAn express train passes through a station. It enters with an initial velocity of 22.0 m/s and decelerates at a rate of 0.150 m/s² as it goes through. The station in 210.0 m long. How fast is it going when the nose leaves the station?arrow_forwardThe function x (t) = -2.1le-1.93t describes the position, in meters, of a particle on the x-axis as a function of time t, in seconds. Find the particle's velocity at time t = 3.05 s.arrow_forward
- A ball of moist clay falls 17.7 m to the ground. It is in contact with the ground for 21.0 ms before stopping. (a) What is the average acceleration of the ball during the time it is in contact with the ground? (Treat the ball as a particle.) (b) Is the average acceleration up or down?arrow_forwardA particle moves in one dimension, and its position as a function of time is given by x (2.0 m/s)t + (-3.6 m/s²)e². (a) What is the particle's average velocity from t 0.45 s to t = 0.55 s? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s (b) What is the particle's average velocity from t = 0.49 s to t = 0.51 s? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s MacBook Air 888 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 @ #3 $4 3 4 Q W E R T Garrow_forwardA particle is initially traveling east at 5 m/s , then it begins to have an acceleration of 10 m/s2 in the north direction. What can you say about its velocity after a long period of time.arrow_forward
- Part (a) What is the velocity, in meters per second, of the particle at the time t1 = 3.0 s? v(t) = ______ m/s Part (b) What is the velocity, in meters per second, of the particle when it is at the origin (x = 0) at time t0 > 0? v(t0) = ______ m/sarrow_forwardYour motion begins at rest and consists of acceleration at 2.0 m/s^2 for 10 seconds, then a period of7.5 seconds with no acceleration, then deceleration at -1.0 m/s^2 for 20 seconds, resulting in a finalspeed of zero. The total distance traveled is 450 m. What is your average speed during this motion? Group of answer choices 10 m/s 42 m/s 12 m/s 16 m/s zeroarrow_forwardA driver applies the brakes on his car reducing its speed from 31.0 m/s to 11.0 m/s in a time 5.0 secs while traveling a distance of 121 m. What is that magnitude of the car's average acceleration during the 5.0 sec period?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON