
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
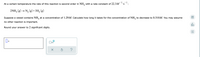
Transcribed Image Text:- 1
At a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is second order in NH, with a rate constant of 22.3M
-1
2NH, (g) → N, (g)+3H, (g)
Suppose a vessel contains NH, at a concentration of 1.29M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of NH, to decrease to 0.310M. You may assume
no other reaction is important.
dlo
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
Ar
S
x10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- At a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is first order in HI with a rate constant of 7.09 s 2HI (g) - H, (g) +1, (g) Suppose a vessel contains HI at a concentration of 0.350M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of HI to decrease by 83.0%. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Submit Assign MacBook Air F7 吕口。 D00 F4 F5 F3 吕 Xarrow_forwardAt a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is first order in N₂O5 with a rate constant of 0.0125 s¯¹: 2N₂O5 (g) → 2N₂O4 (8) + 0₂ (8) Suppose a vessel contains N₂O5 at a concentration of 1.14M. Calculate the concentration of N₂O5 in the vessel 88.0 seconds later. You may assume no of reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardConsider this reaction: 2H,PO, (ag) – P,0, (aq)+ 3H,0 (aq) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (0.392 M-1.s Suppose a vessel contains H, PO, at a concentration of 0.520 M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of H, PO, to decrease to 12.0% of its initial value. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- 5. You studied the chemical reaction, 2NO2(g) → 2NO(g) + O2(g), at 25°C by monitoring the concentration of NO2(g) as a function of time and constructed the following graph. y= 0.5408x + 125.0 R2=0.998 Time (s) What is the rate constant for this reaction at 25°C? Include the proper units. (W/T) [(3)ONI/Tarrow_forwardAt a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is second order in NH OH with a rate constant of 0.0123 M¹s¹: NH,OH (aq) → NH, (aq)+H,O(aq) Suppose a vessel contains NH OH at a concentration of 0.690 M. Calculate the concentration of NH OH in the vessel 790. seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Xarrow_forwardConsider this reaction: 2SO3 (g) →2SO₂(g) + O₂(g) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (0.894 M¹-s¹) [S0₂] Suppose a vessel contains SO3 at a concentration of 0.390 M. Calculate the concentration of SO3 in the vessel 8.60 seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. M Explanation Check 0 10 Q Search a Ⓒ2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use O Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Consider this reaction: 2NH, (g) - N2 (g) +3H, (g) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate =(0.0103 s")[NH,] S Suppose a vessel contains NH, at a concentration of 0.170M. Calculate the concentration of NH, in the vessel 68.0 seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. OM x10arrow_forwardAt a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is second order in H₂CO3 with a rate constant of 2.75Ms H₂CO3(aq) → H₂O (aq) + CO₂ (aq) Suppose a vessel contains H₂CO3 at a concentration of 0.130M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of H₂CO3 to decrease to 0.0286 M. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. X ? Sarrow_forwardConsider this reaction: 2C1,0, g) → 2C1, (6) + 50, (g) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (0.36 Ms)[C1,0,1 %3D Suppose a vessel contains Cl,0, at a concentration of 0.630 M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of Cl,0, to decrease to 5.0% of its initial value. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- At a certain temperature this reaction follows second-order kinetics with a rate constant of 1.0M 2NH, (g) - N, (2) + 3H, (g) Suppose a vessel contains NH, at a concentration of 1.07M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of NH, to decrease by 91.%. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardThe decomposition of N,0, can be described by the equation 2N,0,(soln) – 4 NO,(soln) + 0,(g) Consider the data in the table for the reaction at 45 "C in carbon tetrachloride solution. t (8) IN3Ogl (M) 1.934 175 1.732 446 1.461 825 1.151 Given the data, calculate the average rate of reaction for each successive time interval. What is the average rate of reaction for the time interval from 0 s to 175 s? average rate of reaction: M/s What is the average rate of reaction for the time interval from 175 s to 446 s? average rate of reaction: M/s What is the average rate of reaction for the time interval from 446 s to 825 s? average rate of reaction: M/sarrow_forwardConsider this reaction: 2SO3 (g) →2SO₂ (g) + 0₂ (8) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate= (0.00626 s¹)[03] Suppose a vessel contains SO3 at a concentration of 0.250M. Calculate the concentration of SO3 in the vessel 99.0 seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. M x10 X Śarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY