
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
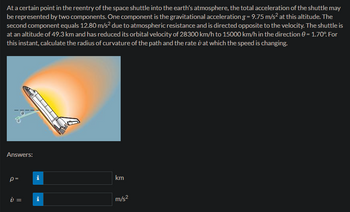
Transcribed Image Text:At a certain point in the reentry of the space shuttle into the earth's atmosphere, the total acceleration of the shuttle may
be represented by two components. One component is the gravitational acceleration g = 9.75 m/s² at this altitude. The
second component equals 12.80 m/s² due to atmospheric resistance and is directed opposite to the velocity. The shuttle is
at an altitude of 49.3 km and has reduced its orbital velocity of 28300 km/h to 15000 km/h in the direction = 1.70°. For
this instant, calculate the radius of curvature of the path and the rate at which the speed is changing.
Answers:
p=
i =
Mi
km
m/s²
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If you are sitting at the equator on Earth, what would your average speed be knowing that the radius of the Earth is 6.37 x 106 m? What would your acceleration on Earth be?arrow_forwardThe shuttle orbiter A is in a circular orbit of altitude 200 mi, while spacecraft B is in a geosynchronous circular orbit of altitude 22,300 mi. Find the relative position vector of A to B. Use g0 = 32.23 ft∕sec^2 for the surface-level gravitational acceleration and R = 3959 mi for the radius of the earth.arrow_forwardThe International Space Station orbits the Earth in a circle with a radius of approximately 6688185 m (which is only a few hundred miles above Earth's surface). At that distance, the acceleration due to gravity is only 8.87m / (s ^ 2) what is the velocity of the space station in this orbit? Your answer should be in units of m / sarrow_forward
- A spy satellite is in circular orbit around Earth. It makes one revolution in 8.90 h. Mass of Earth is 5.974 × 1024 kg, radius of Earth is 6371 km and Gravitational constant G is = 6.674 × 10−11 N·m2/kg2. a. How high above Earth’s surface is the satellite? answer in km b. What is the satellite’s acceleration? answer in m/s^2arrow_forwardA projectile is shot straight up from the earth's surface at a speed of 1.00×104 km/hr .How high does it go?arrow_forwardA 100.0 kg rocket is launched at 8.00 km/s directly up from the earth surface. What altitude does it reacharrow_forward
- In the figure, three 7.82 kg spheres are located at distances d₁ = 0.226 m, and d₂ = 0.204 m. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the net gravitational force on sphere B due to spheres A and C? (a) Number (b) Number IN M. d₁ A B ∙d₂ Units Units N ° (degrees)arrow_forwardThe astroid belt of our solar system is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. An astronomer is studying an interesting asteroid and has determined that one orbit around the Sun takes it 2.83 years. How far is the asteroid from the Sun? The following constants may be helpful. Earth's distance from the Sun = 1 AU = 1.5 x 1011 m MSun = 2.0 x 1030 kg G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 / kg2 1 year = 3.15 x 105 s A)1.5 AU (2.25 x 1011 m) B) 2.0 AU (3.00 x 1011 m) C) 2.5 AU (3.75 x 1011 m) D) 3.2 AU (4.80 x 1011 m) E) 4.8 AU (7.20 x 1011 m)arrow_forwardThe earth rotates once per day about an axis passing through the north and south poles, an axis that is perpendicular to the plane of the equator. Assuming the earth is a sphere with a radius of 6.38 x 106 m, determine the speed and centripetal acceleration of a person situated (a) at the equator and (b) at a latitude of 18.0 ° north of the equator. Re (a) v= i Units ac = Units (b) v = i Units ac = Units > > >arrow_forward
- An Earth satellite moves in a circular orbit 687 km above Earth's surface with a period of 98.30 min. What are (a) the speed and (b) the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the satellite?arrow_forwardAn Earth satellite moves in a circular orbit 714 km above Earth's surface with a period of 98.86 min. What are (a) the speed and (b) the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the satellite? (a) Number Units (b) Number i Units >arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON