
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
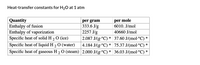
Transcribed Image Text:Heat-transfer constants for H2O at 1 atm
Quantity
Enthalpy of fusion
Enthalpy of vaporization
Specific heat of solid H 2 0 (ice)
per mole
6010. J/mol
per gram
333.6 J/g
2257 J/g
40660 J/mol
2.087 J/(g.°C) * 37.60 J/(mol-°C) *
Specific heat of liquid H 2 0 (water)
4.184 J/(g.°C) * 75.37 J/(mol-°C) *
Specific heat of gaseous H 2 0 (steam) 2.000 J/(g°C) * 36.03 J/(mol-°C) *

Transcribed Image Text:At 1 atm, how much energy is required to heat 79.0 g H,O(s) at – 18.0 °C to H,O(g) at 157.0 °C? Use the heat transfer
constants found in this table.
q =
kJ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Measurements show that the energy of a mixture of gaseous reactants increases by 301. kJ during a certain chemical reaction, which is carried out at a constant pressure. Furthermore, by carefully monitoring the volume change it is determined that – 104. kJ of work is done on the mixture during the reaction. Calculate the change in enthalpy of the gas mixture during the reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. O exothermic ? Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? O endothermicarrow_forwardA 3.971 g sample of a new organic material is combusted in a bomb calorimeter. The temperature of the calorimeter and its contents increase from 24.87 ∘C to 28.06 ∘C. The heat capacity (calorimeter constant) of the calorimeter is 36.35 kJ/ ∘C, what is the heat of combustion per gram of the material?arrow_forwardCalculate the energy required to heat 1.80kg of ammonia from 21.5°C to 41.0°C . Assume the specific heat capacity of ammonia under these conditions is ·4.70J·g−1K−1 Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
- 10.00 g of Compound X with molecular formula C4H8 are burned in a constant-pressure calorimeter containing 50.00 kg of water at 25 °C. The temperature of the water is observed to rise by 2.151 °C. (You may assume all the heat released by the reaction is absorbed by the water, and none by the calorimeter itself.) Calculate the standard heat of formation of Compound X at 25 °C. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardLet's use our knowledge of constant volume (bomb) calorimetry to determine the heat energy in a given food sample, say a hamburger. A typical hamburger has a serving size of 105 g and consists of approximately 20% protein (21.0 g), 33% fat (34.7 g), and 47% carbohydrate (49.3 g). Assume that the heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter is 8.39 kJ K-¹, and the increase in water temperature was 13.2 K. Q5.38 Homework Unanswered How many Calories (Cal) are in the hamburger described above? Respond with the correct number of significant figures in scientific notation (Use E notation and only 1 digit before decimal e.g. 2.5E5 for 2.5 x 105) Type your numeric answer and submit Unanswered • 4 attempts left Submitarrow_forwardA system does 516516 kJ of work and loses 236236 kJ of heat to the surroundings. What is the change in internal energy, Δ?Δ�, of the system? Note that internal energy is symbolized as Δ?Δ� in some sources.arrow_forward
- An ideal gas sealed in a rigid 3.13-L cylinder, initially at pressure Pi=12.70 atm, is cooled until the pressure in the cylinder is Pf=1.18 atm. What is the enthalpy change for this process?What is the change in internal energy for this process?arrow_forwardIf we measure the heat change (q) of everything in a system except the calorimeter, we can use the first law of thermodynamics (∆Euniverse = 0) to calculate the heat change of the calorimeter (qcal). In this reaction, we combine 5.85 g of 63.7 ºC water with 6.63 g of 18.9 ºC water in a calorimeter. Since some of the heat is absorbed by the calorimeter, the final temperature of the water is 28.8ºC. Since the hot and cold water are combined, the final temp of the water is the final temp for the hot water and the cold water. Calculate the heat change of the calorimeter in J. Remember that all of the heat changes must add up to zero so you can calculate the heat change of the hot water (qhotwater) and the heat change of the cold water (qcoldwater) using for each where Cs = 4.186 J/gºC. The first law of thermodynamics tells us that all of these changes sum up to zero so Enter your answer to one decimal place (tenths)arrow_forwardAnswer the questions that are attachedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY