
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
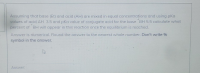
Transcribed Image Text:Assuming that base (B:) and acid (AH) are mixed in equal concentrations and using pKa
values of acid AH 3.5 and pka value of conjugate acid for the base BH 5.5 calculate what
percent of BH will appear in this reaction once the equilibrium is reached.
Answer is numerical. Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Don't write %
symbol in the answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The conjugate base that is produced after the first ionization step of carbonic acid when it has reacted with ethyl amine (CH3CH2NH2) would be _________. H2CO3 CH3CH2NH3+ HCO3- CO3-2 CH2CH2NH Given a Ksp of 4.96 X 10-9 for limestone (calcium carbonate), the calcium concentration in a limestone solution will be__________ the Ksp. greater than less than the same as cannot be determinedarrow_forwardCalculate the concentrations of the weak acid and conjugate base for the best possible buffer at pH 3.50 knowing that the concentration of the more concentrated species between the two will be 0.2 M. Choose the buffer system you think would be best between the following three. You will need to look up literature values for the Ka/pKa on your own. Remember that a strong buffer has similar concentrations of the buffering components. Formic acid/formate Acetic acid/acetate Hypobromous acid/Hypobromitearrow_forwardPhenol red is a common acid-base indicator. It has a pKa equal to 8.000. It's undissociated form is yellow and its anionic form is violet. What color would a solution containing phenol red solution if the pH is 7.50? yellow yellow-orange red-orange red-violet violetarrow_forward
- Weak Acids and Buffers Write out the simple equilibrium of a weak acid (HA), labeling the conjugate acid and the conjugate base. ● Write out the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation and use this expression to define the meaning of the characteristic pką value.arrow_forwardDetermine the Kb for a base by constructing an ICE table and using this information to construct and solve the equilibrium constant expression. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. 1 2 NEXT > The pH for a 0.0160 M solution of CH:CH.NH: is 8.600. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine the unknown concentrations of all reactants and products. CH:CsH&NH:(aq)+ H:O(1) OH-(aq) +CH:CeH&NH;*(aq) Initial (M) |Change (M) Equilibrium (M) 5 RESET 0.0160 8.60 -8.60 0.93 -0.93 2.50 x 109 -2.50 x 109 3.98 x 10 -3.98 х 10° 5.4 -5.4arrow_forwardComplete the following table, which lists information about the measured acid dissociation constants of three unknown weak acids. Note: be sure each number you put in the table has the correct number of significant digits. acid B C Ka M 0 7.28 x 10 pK 1.17 11.3 0 relative strength (Choose one) ✓ (Choose one) ✓ (Choose one) ✓ O *10 X ?arrow_forward
- Provide your view on this? Strong bases have weak conjugate acids with high pKa values, usually > 12.arrow_forwardSolve correctly please.arrow_forward1. The pKa of HX is 9.34. Calculate the pH of a 0.418 M solution of HX. 2. A weak monoprotic acid, HA dissociates by 2.416 % and has a pH of 3.61. Calculate the Ka value for the acid HA. Record your answer in scientific notation to 3 sig figs.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY