
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Assume two countries: H and F. If the world terms of trade for a country are somewhere between the domestic cost ratio of H and that of F, then
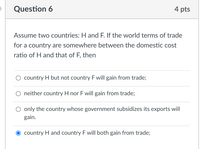
Transcribed Image Text:Question 6
4 pts
Assume two countries: H and F. If the world terms of trade
for a country are somewhere between the domestic cost
ratio of H and that of F, then
O country H but not country F will gain from trade;
neither country H nor F will gain from trade;
O only the country whose government subsidizes its exports will
gain.
country H and country F will both gain from trade;
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Trade theories suggest that both countries gain from trade. In a 2-country, 2-good model, we assume the 2 states—Futland and Tandam share a common currency (allowing us to ignore exchange rate), they both have the same wages, and they both produce two goods: bicycles and boots. The units of labour requirement are shown below, assuming constant returns to scale. Production Techniques: Units of labour hour required per unit output Tandom Futland Bicycles 90 hours 120 hours Boots 30 hours 50 hours Define opportunity cost. Using the table above, calculate the opportunity cost of bicycles in terms of boots and the opportunity cost of boots in terms of bicycles for each of the countries.arrow_forwardThe gains from expanding trade are probably most important for the low-income economies in the world as opposed to the gains though trade benefitting the USA. Why might this be so? Offer at least three different reasons comparing and contrasting the USA economy with that of smaller nations.arrow_forward"Poor countries like Malawi have no absolute advantages. They have poor soil, low investments in formal education and hence low-skill workers, no capital, and no natural resources to speak of. Because they have no advantage, they cannot benefit from trade." How would I respond to this statement?arrow_forward
- Assume that the comparative-cost ratios of two products-baby formula and tuna fish-are as follows in the nations of Canswicki and Tunata: Canswicki: 1 can baby formula = 3 cans tuna fish Tunata: 1 can baby formula = 5 cans tuna fish a. In what product should each nation specialize? Canswicki should produce [(Click to select), and Tunata should produce [(Click to select) ♥ b. Would the following terms of trade be acceptable to both nations? i. 1 can baby formula = 2 cans tuna fish: (Click to select) ii. 1 can baby formula = 3.5 cans tuna fish: (Click to select) iii. 1 can baby formula = 6 cans tuna fish: (Click to select)arrow_forwardFrom an economic point of view, India and China are somewhat similar: Both are huge, low-wage countries, probably with similar patterns of comparative advantage, which until recently were relatively closed to international trade. China was the first to open up. Now that India is also opening up to world trade, how would you expect this to affect the welfare of China? Of the United States? (Hint: Think of adding a new economy identical to that of China to the world economy.) A. From China's perspective, the world relative supply curve will shift to the left. This shift will improve China's terms of trade. The U.S. purchases of Chinese exports will hurt the U.S. by decreasing the relative price of goods that the U.S. exports. B. From China's perspective, the world relative supply curve will shift to the right. This shift will worsen China's terms of trade. The U.S. purchase of Chinese exports will benefit the U.S. by increasing the relative price of goods that the U.S. exports. C. From…arrow_forwardWould the U.S. government gain any advantage from using tariffs or quotas to restrict imports?arrow_forward
- Choose four countries. One country in North America, another country in Central America, another country in the Caribbean and another country in South America and indicate, using the gravity model, which factors should increase or reduce trade between those countries. After that, choose a country in Europe and indicate, using the Gravity Model, how the intensity of trade changes with five countries. You must take into account the concept of the gravity model and the factors that affect trade such as language, culture, trade agreements, among others. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardWhich of the following has not been a facilitating factor in world trade? general declines in tariffs import quotas dramatic improvements in communications technology O improvements in transportation technology.arrow_forwardAmerican firms outsource many jobs to other, lower cost countries. How can this outsourcing actually lead to increased employment here in the USA? How can there be any economic gains for a country from both importing and exporting the same good, like cars?arrow_forward
- Finally, Canada and Australia are both English-speaking countries with not-too dissimilar population sizes. However, Canada’s trade is twice as large as that of Australia’s. to what extent, does comparative advantage help explain this?arrow_forwardDescribe benefits from international trade.arrow_forwardAs you may have heard, Russia decided to invade its neighbor, which has led to international condemnation (albeit not on all fronts). The EU, a former major importer of gas from Russai, went ahead with sanctions. Imagine, if you will, that the respective heads of state get together and try to negotiate a trade agreement to end sanctions. They each have three possible choices: (a) Maintain tariffs against the other nation (T); (b) Seek mediation from the WTO, which would implement an international trade agreement at a small cost (M); (c) Unilaterally remove tariffs (F). The payoff matrix is as given below. Is there a dominant strategy for either player? Find all the (pure strategy) Nash equilibria in the game. How would this change if, instead, the mediation is costless and yields a payoff of 50 to each nation (assuming mutually successful mediation) and a payoff of 0 (if the other nation chooses otherwise)? **arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education