
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
![Assume the readings on thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. Find the probability that a randomly selected thermometer reads between -1.99 and -0.67 and draw a sketch of the region.
**Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below.**
**Options:**
- **A.** A normal distribution curve with the region between -1.99 and -0.67 shaded on the left side of the mean.
- **B.** A normal distribution curve with the region between -1.99 and -0.67 shaded on both sides of the mean.
- **C.** A normal distribution curve with the region between -1.99 and -0.67 shaded on the right side of the mean.
The probability is [ ].
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
*Click to select your answer(s).*
(Note: In option C, the shaded region correctly highlights the area between -1.99 and -0.67 on the left side of the mean on the normal distribution curve, indicating the probability of this range.)](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/0cb90495-7be7-4df7-831c-cee0d9583d28/e5a65f31-8c32-4fff-8c18-c72b2d74e31d/c5oe84a_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Assume the readings on thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. Find the probability that a randomly selected thermometer reads between -1.99 and -0.67 and draw a sketch of the region.
**Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below.**
**Options:**
- **A.** A normal distribution curve with the region between -1.99 and -0.67 shaded on the left side of the mean.
- **B.** A normal distribution curve with the region between -1.99 and -0.67 shaded on both sides of the mean.
- **C.** A normal distribution curve with the region between -1.99 and -0.67 shaded on the right side of the mean.
The probability is [ ].
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
*Click to select your answer(s).*
(Note: In option C, the shaded region correctly highlights the area between -1.99 and -0.67 on the left side of the mean on the normal distribution curve, indicating the probability of this range.)
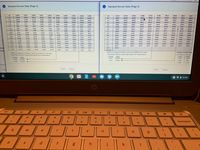
Transcribed Image Text:The image shows a laptop screen displaying two pages of a Standard Normal Table, commonly used in statistics to find the probabilities associated with a standard normal distribution (Z-scores).
### **Standard Normal Table (Page 1):**
- **Z-Score Values:** Range from -1.6 to 0.0, with increments of 0.1.
- **Probability Values:** Displayed as four-digit numbers representing cumulative probabilities for each Z-score.
- **Table Layout:** The leftmost column represents the Z-score, and the subsequent columns correspond to the second decimal place of the Z-score.
- **Example Entry:** For a Z-score of -1.6 and 0.05, the cumulative probability is 0.0548.
- **Note:** For Z-scores below -3.49, use an area of 0.0001.
- **Interpolation Example:**
- Z = -1.645, Area = 0.0500
- Z = -2.575, Area = 0.0050
### **Standard Normal Table (Page 2):**
- **Z-Score Values:** Range from 2.0 to 3.4, with increments of 0.1.
- **Probability Values:** Displayed as four-digit numbers similar to page 1.
- **Layout:** The format mirrors page 1, with Z-scores in the leftmost column.
- **Example Entry:** For a Z-score of 2.0 and 0.03, the cumulative probability is 0.9778.
- **Note:** For Z-scores above 3.49, use an area of 0.9999.
- **Interpolation Example:**
- Z = 1.645, Area = 0.9500
- Z = 2.575, Area = 0.9950
### **Common Critical Values Table:**
- **Confidence Level 90%:** Critical Z = 1.645
- **Confidence Level 95%:** Critical Z = 1.960
- **Confidence Level 99%:** Critical Z = 2.576
### **Additional Notes:**
- The tables provide a quick reference to find probabilities and Z-scores without the need for calculation.
- “Print” and “Done” buttons are visible, indicating options for output or closure of the screen.
This setup aids in the understanding of how Z-scores relate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Draw a graph and find the probability of a bone density test score greater than -1.62. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. O A. 1.62 Q The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) OB. Q -1.62 -1.62 ♫ OD. Q -1.62 1.62 Εarrow_forward8arrow_forwardAssume the readings on thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. Find the probability that a randomly selected thermometer reads between -1.03 and -0.51 and draw a sketch of the region. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. OA. -1.03 -0.51 Q The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) O B. 4 -1.03 -0.51 Q G O C. A -1.03 -0.51arrow_forward
- Assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Find the probability that a given score is between - 2.18 and 3.86 and draw a sketch of the region. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. O A. В. OC. O D. -2.18 3.86 2.18 3.86 -2.18 3.86 -2.18 3.86 The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Click to select your answer(s). 山T00④ NOV 2. 1377 14 X P W MacBook Air esc 80 888 F3 F4 F7 FB F9 F10 $4 & 4 80 Q E Y A F G H. K /2x cv C V B D. 林 wwww wwwwwarrow_forwardWhich statement is true about a normal distribution? O Knowing a data set is normal has no importance in the mathematical and scientific community. O Knowing a data set is normal is only important in producing nicely shaped graphs. O None of the answers listed O Knowing a data set is normal is important in the mathematical and scientific community. 77°F S rcharrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- Engineers want to design seats in commercial aircraft so that they are wide enough to fit 99% of all males. (Accommodating 100% of males would require very wide seats that would be much too expensive.) Men have hip breadths that are normally distributed with a mean of 14.9 in. and a standard deviation of 0.9 in. Find Pog- That is, find the hip breadth for men that separates the smallest 99% from the largest 1%. The hip breadth for men that separates the smallest 99% from the largest 1% is Pgg = in. %3D (Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardUse a calculator or computer software to generate a normal quantile plot for the data in the accompanying table. Then determine whether the data come from a normally distributed population. Click the icon to view the data set. Generate a normal quantile plot for the data. Choose the correct graph below. OA. 3.00 2.00- 1.00- 0.00- -1.00- Q Q -2.00 -3.00 100 200 300 400 500 0 X Value OB. 3.00 2.00- 1.00- 0.00- -1.00- -2.00- -3.00- ... 0 100 200 300 400 500 X Value Q Q G O C. 3.00 2.00 P 1.00 0.00- -1.00- -2.00- 0 100 200 300 400 500 X Value -3.00+ Determine whether the data come from a normally distributed population. Choose the correct answer below. OA. The distribution is not normal. The points are not reasonably close to a straight line. OB. The distribution is normal. The points show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern. OC. The distribution is not normal. The points show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern. OD. The distribution is normal. The…arrow_forwardq6arrow_forward
- Assume the readings on thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. Find the probability that a randomly selected thermometer reads between - 1.94 and -1.06 and draw a sketch of the region. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. O A. O B. O C. W W -1.94 -1.06 -1.94 -1.06 -1.94 -1.06 The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardAssume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Draw a graph and find the probability of a bone density test score greater than 0. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. O A. OB. C. ntents a Library The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer All parts showing Clear All Check Anwrarrow_forwardAssume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Draw a graph and find the probability of a bone density test score between 1.83 and 1.83. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. O A. -1.83 1.83 B. -1.83 *** 1.83 O C. -1.83 1.83 O D. -1.83 1.83arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman