
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
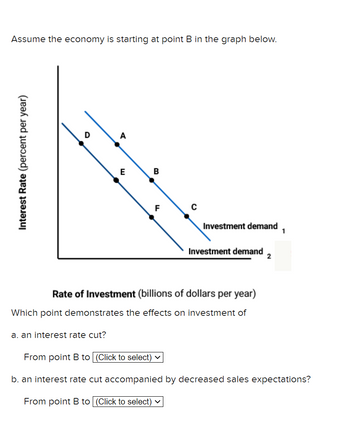
Transcribed Image Text:Assume the economy is starting at point B in the graph below.
Interest Rate (percent per year)
D
4
a. an interest rate cut?
E
B
F
Investment demand
Investment demand
Rate of Investment (billions of dollars per year)
Which point demonstrates the effects on investment of
2
1
From point B to (Click to select)
b. an interest rate cut accompanied by decreased sales expectations?
From point B to (Click to select)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 31 5 points Save Answ In year 2018, the government of Qatar spent is 143 billion Qatari Riyal (the national currency of Qatar). The GDP of Qatar in the same year is 1,121 billion Qatari Riyal. Qatar's desired consumption and desired investment during the year can be summarized by the following equations: cd = 1,000 – 5,000r, || /d = 800 – 3000r, %3D cd is the desired consumption in billions of Qatari Riyal, 7º if the desired investment in billions of Qatari Riyal, and r is the real interest rate in decimal form. where What is the equilibrium real interest rate, r*, in %? Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places. (E.g. 12.3456% should be entered as 12.35)arrow_forwardOn the following graph, show the impact of the increase in government purchases on the interest rate by shifting one or both of the curves. Supply X Demand 2 10 20 30 40 50 QUANTITY OF LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of dollars) 12 IN TEREST RATE 10 0 0 60 ģ Demand Supply ? Suppose that for each one-percentage-point increase in the interest rate, the level of investment spending declines by $1.25 billion. by According to the change you made to the loanable funds market in the previous scenario, the increase in government purchases causes the interest rate in the money market to from 6% to %. The change in the interest rate causes the level of investment spending to $ billion. by After the multiplier effect is accounted for, the change in investment spending will cause the quantity of output demanded to $ billion at each price level. The impact of an increase in government purchases on the interest rate and the level of investment spending is known as the effect. Place the purple line (diamond…arrow_forwardThe following table provides data for output (real GDP) and saving. a. Fill in the missing numbers (gray-shaded cells) in the table. Instructions: In the table, enter your answers for consumption as a whole number. Round your answers for APC and APS to 3 decimal places. Round your answers for MPC and MPS to 1 decimal place. If you are entering any negative numbers be sure to include a negative sign (-) in front of those numbers. Level of Output and Income (GDP = DI) Consumption Saving АРС APS MPC MPS 496 -0.033 -0.015 $480 $-16 1.033 520 528 -8 1.015 560 560 1.000 0.000 592 624 600 0.987 0.013 640 16 0.975 0.025 680 656 24 0.965 0.035 720 688 32 0.956 0.044 760 720 40 0.947 0.053 800 752 48 0.940 0.060arrow_forward
- In the market for loanable funds, the equilibrium interest rate is 3% and the equilirbium quantity of loanable funds is $500 billion.What's the likely result if bamks offer loans for an interest rate of 5%? a) the quantity of loans supplied by banks will be greater than the quantity of loans demanded from potential investors b) the government will issue more bonds to make up for the decreased number of loans c) there'll be an increase in borrowing d) the quantity of loanable funds demanded will increasearrow_forwardConsider an economy described as follows: Y = C+1+G Y= 8,000. G= 2,500. T 2,000. C- 1,000 + 2/3(Y-T). 1-1,200-100r. 'n this economy, compute private saving, public saving, and national saving. How much is the marginal propensity to consume? 1. 2. 3. Find the equilibrium interest rate.arrow_forwardHow do you explain why investment falls as interest rate risesarrow_forward
- Which of the following is most likely to cause a rightward shift of the investment demand curve? a. An increase in the market rate of interest b. An increase in income O c. A decrease in the market interest rate d. An improvement in business expectations e. A decrease in incomearrow_forwardQuestion 35 Suppose real estate analysts expect that 100,000 homes will be needed in a particular community by 2014. If the current number of homes in the community is only 50,000, we can expect to see a significant increase in the demand for investment. True O Falsearrow_forward#29arrow_forward
- K Consider the graph to answer the following questions: a. The shift from S, to S₂ represents in the supply of loanable funds. b. With the shift in supply, the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds c. With the change in the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds, the quantity of saving and the quantity of investment ▼ A CI Real Interest Rate Market for Loanable Funds L₂ L1 Loanable Funds ($ per year) S₁ Qarrow_forwardAnswer the following questions: Instructions: Enter your answers rounded to the nearest whole number. a. By how much will GDP change if firms increase their investment by $12 billion and the MPC is 0.80? billion b. If the MPC is 0.50? %24 billionarrow_forwardClassify each of the following scenarios listed in the table below using the macroeconomic definitions of saving and investment. Shen purchases a new townhouse in Hartford. Poornima borrows money to build an addition to a lab owned by her engineering firm. Manuel purchases a certificate of deposit at his bank. Valerie purchases stock in Tesqar, a biotech firm. Saving Investment Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education