
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need help solving this statistics problem.
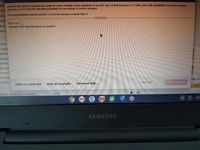
Transcribed Image Text:m
abil
Assume that random guesses are made for seven multiple choice questions on an SAT test, so that there aren=7 trials, each with probability of success (correct)
rey given byp%30.2. Find the indicated probability for the number of correct answers.
dult Find the probability that the number x of correct answers is fewer than 4.
cted
P(X<4) =
exac (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
ire a
ume
made
estion
oices 1
at there
ith prol
correct)
ne prob
Easy to
answers.
Clear all
Check answer
Help me solve this
View an example
Get more help -
Add to
A pharmaceutical company
n=41
1O
prese
SAMSUNG
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are a big soccer fan and you decide to gather information on the goal differential (goals scored - goals allowed) for your favorite team in the Premier League during the last season. You find that the average goal differential for home games (games that take place on the team's own stadium) was 1.37 and the average goal differential for away games (games that take place on the opponent team's stadium) was 0.32. With the data you have, if you regress goal differential (call it variable G) on a dummy variable (call it variable D) that takes the value 1 if the game is a home game and takes the value zero if the game is an away game, and obtain Ĝi = Bo + B₁ D₁, then, Bo will be equal to equal to and ₁ will bearrow_forwardImagine you are talking with a novice statistics student. How would you describe the method of determining if a variable is continuous versus discrete?arrow_forwardPlease help with this problem. Can you please explain using a calculator. Thank you.arrow_forward
- The American Heart Association is about to conduct an anti-smoking campaign and wants to know the fraction of Americans over 38 who smoke. Step 1 of 2: Suppose a sample of 273 Americans over 38 is drawn. Of these people, 79 smoke. Using the data, estimate the proportion of Americans over 38 who smoke. Enter your answer as a fraction or a decimal number rounded to three decimal places. Step 2 of 2: Suppose a sample of 273 Americans over 38 is drawn. Of these people, 79 smoke. Using the data, construct the 85% confidence interval for the population proportion of Americans over 38 who smoke. Round your answers to three decimal places. Lower end point, upper end pointarrow_forwardIf most of the scores in a large data set are about close together except for a few scores that are quite a bit higher, how would the mean and median of the data set compare and what shape would a histogram of the data set have? The mean would be smaller than the median and the histogram would be skewed with a long tail towards higher scores. The mean would be larger than the median and the histogram would be skewed with a long tail towards lower scores. The mean would be smaller than the median and the histogram would be skewed with a long tail towards lower scores. The mean would be larger than the median and the histogram would be skewed with a long tail towards higher scores. The mean would be equal to the median and the histogram would be symmetrical. None of the answers listed.arrow_forwardYou are a paranoid delusional statistician with far too much time on your hands. One day, you sit down to have a bowl of soup. This bowl of soup happens to be Tic-Tac-Toe themed, meaning that you have some noodles that are shaped like an X, and some that are shaped like an O. As you stir your soup, you notice that this bowl seems to have a particularly high number of X- shaped noodles in it. Being paranoid, you conclude that this has some meaning like someone is trying to give you a message, possibly warning you of the dangers of x-rays. You jump out of your seat and run to get your x-ray-proof cape, and then you pause for a moment and think that you should calculate a chi-square statistic for the frequency of X-shaped noodles before freaking out. First, you carefully separate each of the noodles by shape and count them. Here is what you find: Frequency of Noodles X-shaped 33 O-shaped 21 2. Write out the null and alternative hypotheses using symbols: Но: На:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman