
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
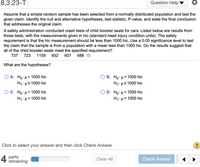
Transcribed Image Text:8.3.23-T
Question Help
Assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a normally distributed population and test the
given claim. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion
that addresses the original claim.
A safety administration conducted crash tests of child booster seats for cars. Listed below are results from
those tests, with the measurements given in hic (standard head injury condition units). The safety
requirement is that the hic measurement should be less than 1000 hic. Use a 0.05 significance level to test
the claim that the sample is from a population with a mean less than 1000 hic. Do the results suggest that
all of the child booster seats meet the specified requirement?
737
723
1159
652
607
688 D
What are the hypotheses?
A. Ho: µ = 1000 hic
H1: µ2 1000 hic
В. Но: и< 1000 hic
H1: µ2 1000 hic
D. Hо: и> 1000 hic
< 1000 hic
C. Ho: µ = 1000 hic
H1: µ< 1000 hic
H1:µ<
Click to select your answer and then click Check Answer.
4
parts
remaining
Clear All
Check Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a normally distributed population and test the given claim. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. A simple random sample of 25 filtered 100 mm cigarettes is obtained, and the tar content of each cigarette is measured. The sample has a mean of 19.4 mg and a standard deviation of 3.61 mg. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the mean tar content of filtered 100 mm cigarettes is less than 21.1 mg, which is the mean for unfiltered king size cigarettes. What do the results suggest about the effectiveness of the filters? a) What are the hypotheses? b) Identify the P-value. c) State the final conclusion. A. Fail to reject H0. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean tar content of filtered 100 mm cigarettes is less than 21.1 mg. B. Fail to reject H0. There is insufficient evidence to support…arrow_forwardA data set includes data from student evaluations of courses. The summary statistics are n= 92, x = 3.57, s = 0.61. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the population of student course evaluations has a mean equal to 3.75. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.arrow_forwardUse the pulse rates in beats per minute of a random sample of adult females listed in the data set that is available below to test the claim that the means is less than 74 b. p.m. Use a 0.10 significance level.arrow_forward
- A data set includes data from student evaluations of courses. The summary statistics are n = 93, x = 3.66, s = 0.62. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the population of student course evaluations has a mean equal to 3.75. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? OA. Ho: H=3.75 H₁: 3.75 Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) *B. Hoi k = 3.75 H₁: 3.75 OD. Ho: 3.75 H₁: 3.75arrow_forwardA data set includes data from student evaluations of courses. The summary statistics are n = 97, x = 3.68, s = 0.66. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the population of student course evaluations has a mean equal to 3.75. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: H= 3.75 О в. Но: и-3.75 H1: u#3.75 H4: µ 3.75 Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Ho. There is evidence to conclude that the original claim that the mean of the population of student course evaluations is equal to 3.75 correct.arrow_forwardAn article reports that men over 6 feet tall earn more than men under 6 feet, with these numbers: average 6 foot plus male’s salary $55,000, average male’s salary under 6 foot tall of $47,000, with a p-value of 0.45. Based on that reported p-value, and using the common definition of "statistical significance," which is the case? With that p value, the results are not significant. With that p value, the differences are very close, but not statistically significant. The salary differences are not statistically significant. The salary differences are statistically significant.arrow_forward
- A data set lists earthquake depths. The summary statistics are n=500, x=6.37 km, s=4.17 km. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim of a seismologist that these earthquakes are from a population with a mean equal to 6.00. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.arrow_forwardA data set includes data from student evaluations of courses. The summary statistics are n=97, x=4.19, s=0.58. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the population of student course evaluations has a mean equal to 4.25. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.arrow_forwardA data set includes data from student evaluations of courses. The summary statistics are n=91, x=3.92, s=0.61. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the population of student course evaluations has a mean equal to 4.00. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.arrow_forward
- A data set lists earthquake depths. The summary statistics are n= 500, x = 6.37 km, s = 4.51 km. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim of a seismologist that these earthquakes are from a population with a mean equal to 6.00. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. %3D What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: H#6.00 km H1:H=6.00 km O B. Ho: H= 6.00 km Hi :H>6.00 km O C. Ho: H= 6.00 km H1: µ<6.00 km OD. Ho:H=6.00 km H:µ#6.00 km Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Ho. There is evidence to conclude that the original claim that the mean of the population of earthquake depths is 6.00 km correct. Click to select your answer(s). esc & %23 $ 4 5 6 2 3 R T Y J K…arrow_forwardA data set includes data from student evaluations of courses. The summary statistics are n= 95, x= 3.33, s= 0.66. Use a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that the population of student course evaluations has a mean equal to 3.50. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: H= 3.50 О в. Но: и33.50 H1: µ3.50 Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. v Ho. There is v evidence to conclude that the mean of the population of student course evaluations is equal to 3.50 v correct.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman