
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
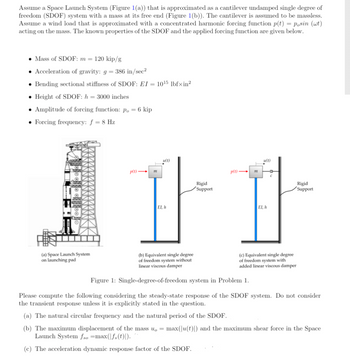
Transcribed Image Text:Assume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of
freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless.
Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = p.sin (wt)
acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below.
• Mass of SDOF: m = 120 kip/g
• Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec²
Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI=
Height of SDOF: h= 3000 inches
• Amplitude of forcing function: p. = 6 kip
Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz
O
RESIS
POLIS
O
(a) Space Launch System
on launching pad
p(t)->
1015 lbfxin²
111
u(t)
El, h
(b) Equivalent single degree.
of freedom system without
linear viscous damper
Rigid
Support
p(t)→
111
u(t)
EI, h
C
Rigid
Support
(c) Equivalent single degree
of freedom system with
added linear viscous damper
Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1.
Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider
the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question.
(a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF.
(b) The maximum displacement of the mass u, = max(|u(t)|) and the maximum shear force in the Space
Launch System fso =max(|fs (t)).
(c) The acceleration dynamic response factor of the SDOF.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- SOLVE STEP BY STEP The simple portico in the figure consists of a rigid lintel of length L supported by two cylindrical pillars of equal length and material. A triangular distributed load of maximum value q_0 is imposed on the lintel. Calculate the ratio between the cross sections of the columns so that buckling starts in both at the same time. Ignore the shortening of the pillars do 1 2arrow_forwardA cylindrical pressure vessel having a radius r = 14 in. and wall thickness t = 0.375 in. is subjected to internal pressure p = 375 psi. In addition, a torque T = 90 kip-ft acts at each end of the cylinder (see figure). (Assume that the structures behave linearly elastically and that the stresses caused by two or more loads may be superimposed to obtain the resultant stresses acting at a point. Consider both in-plane and out-of-plane shear stresses unless otherwise specified.) (a) Determine the maximum tensile stress omay and the maximum in-plane shear stress Tmay in the wall of the cylinder. (Enter the magnitudes in ksi.) o, = ksi Tmax ksi (b) If the allowable in-plane shear stress is 4.5 ksi, what is the maximum allowable torque T? (Enter the magnitude in kip-ft.) kip-ft (c) If T = 150 kip-ft and allowable in-plane shear and allowable normal stresses are 4.5 ksi and 11.5 ksi, respectively, what is the minimum required wall thickness (in inches)? in.arrow_forward1) Find the transfer function from the force F (applied at x= L/3 the bar) to the motion Y of the location x=2L/3 a bar (with fixed-fixed) boundary conditions. Consider only the first mode of vibration with zero damping. The mass of the rod is M, mass-density of the rod is p, its length is L, Young's modulus is E, and cross-sectional area is A. 2) Find the response Y(t) for a unit step input with zero initial conditions. F(t) Y(t) →L/3 → 2L/3arrow_forward
- 1)arrow_forwardQuestion 5 T/2 В 1200 Nm A homogeneous steel shaft (G=83GPA) is loaded as shown in the above Figure. Assuming T = 300 N-m, determine the torsional force in N-m in Member BC. Note: Include sign (+/-), assuming the direction of Torsion (T) at D is positive Given: AB: Length = 1.75m, Diameter = 75mm BC: Length = 1.50m, Diameter = 60mm AB: Length = 1.00m, Diameter = 40mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning