
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
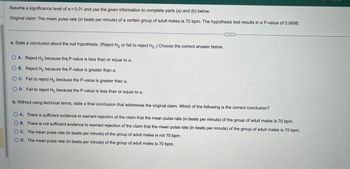
Transcribed Image Text:Assume a significance level of α = 0.01 and use the given information to complete parts (a) and (b) below.
Original claim: The mean pulse rate (in beats per minute) of a certain group of adult males is 70 bpm. The hypothesis test results in a P-value of 0.0698.
a. State a conclusion about the null hypothesis. (Reject Ho or fail to reject Ho.) Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Reject Ho because the P-value is less than or equal to a.
OB. Reject Ho because the P-value is greater than a.
OC. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value is greater than α.
D. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value is less than or equal to a.
b. Without using technical terms, state a final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Which of the following is the correct conclusion?
OA. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the mean pulse rate (in beats per minute) of the group of adult males is 70 bpm.
B. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the mean pulse rate (in beats per minute) of the group of adult males is 70 bpm.
C. The mean pulse rate (in beats per minute) of the group of adult males is not 70 bpm.
OD. The mean pulse rate (in beats per minute) of the group of adult males is 70 bpm.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A graduate student is designing a research study. She is hoping to show that the results of an experiment are statistically significant. What type of p-value would she want to obtain? a)A large p-value. b)A small p-value. c)The magnitude of a p-value has no impact on statistical significancearrow_forwardFind the test statistic: Determine the P-value: State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim:arrow_forwardThe p-value for a hypothesis test turns out to be 0.0534. At a 3% level of sigrnificance, what is the proper decision? O Reject Ho O Fail to reject Ho Check Answer e Type here to searcharrow_forward
- Claim: The mean systolic blood pressure of all healthy adults is less than than 120 mm Hg. Sample data: For 276 healthy adults, the mean systolic blood pressure level is 119.61 mm Hg and the standard deviation is 14.88 mm Hg. The null and alternative hypotheses are Ho: μ = 120 and H₁: μ< 120. Find the value of the test statistic. The value of the test statistic is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Carrow_forwardAnswer all parts pleasearrow_forwardClaim: The mean systolic blood pressure of all healthy adults is less than 125 mm Hg. Sample data: For 261 healthy adults, the mean systolic blood pressure level is 121.18 mm Hg and the standard deviation is 15.97 mm Hg. a. Express the original claim in symbolic form. Let the parameter represent a value with respect to systolic blood pressure of a healthy adult. B. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses.arrow_forward
- A group of students estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute? 75 88 48 77 50 33 69 72 78 59 73 82 100 101 75 D S Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: μ= 60 seconds OB. Ho: 60 seconds H₁ μ 60 seconds H₁: #60 seconds Determine the test statistic. lete (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardTest the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test. Ho: p=0.6 versus H₁: p > 0.6 n = 200; x = 125; a = 0.05 Click here to view page 1 of the table. Click here to view page 2 of the table. Calculate the test statistic, Zo- Zo = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. P-value= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Choose the correct result of the hypothesis test for the P-value approach below. OA: Reject the null hypothesis, because the P-value is greater than α. OB. Reject the null hypothesis, because the P-value is less than α. OC. Do not reject the null hypothesis, because the P-value is greater than α. O D. Do not reject the null hypothesis, because the P-value is less than a. #3 80 F3 E $ 4 000 F4 R % 5 F5 T MacBook Air < 6 F6 Y & 7 AA F7 U * 0 8 DII F8 ( 9 DD F9 C I 0arrow_forwardAssume a significance level of a = 0.1 and use the given information to complete parts (a) and (b) below. Original claim: The standard deviation of pulse rates of a certain group of adult males is more than 11 bpm. The hypothesis test results in a P-value of 0.3373. -C a. State a conclusion about the null hypothesis. (Reject Ho or fail to reject Ho.) Choose the correct answer below. O A. Reject Ho because the P-value is less than or equal to α. OB. Reject Ho because the P-value is greater than a O C. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value is greater than a O D. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value is less than or equal to a. b. Without using technical terms, state a final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Which of the following is the correct conclusion? O A. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the standard deviation of pulse rates of the group of adult males is more than 11 bpm. O B. The standard deviation of pulse rates of the group of adult males…arrow_forward
- Describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim. A furniture store claims that at least 40% of its new customers will return to buy their next piece of furniture. Describe the type I error. Choose the correct answer below. OA. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece of furniture is at least 0.40, but you fail to reject Ho: p20.40. OB. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece furniture is at least 0.40, but you reject Ho: p20.40. OC. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece of furniture is no more than 0.40, but you reject Ho: p ≤ 0.40. OD. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece f furniture is no more than 0.40, but you fail to reject Ho: p ≤0.40. Describe the type II error. Choose the correct answer…arrow_forwardA researcher is studying how much electricity (in kilowatt hours) people from two different cities use in their homes. Random samples of 11 days from Tampa (Group 1) and 16 days from New York City (Group 2) are shown below. Test the claim that the mean number of kilowatt hours in Tampa greater than the mean number of kilowatt hours in New York City. Use a significance level of a = 0.10. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed with unequal variances. Round answers to 4 decimal places. Tampa New York City 1015.4 1010 1010.3 1022.8 1001.7 1028.9 1001.7 1026.9 1022.6 1001.7 1020.2 1012.4 1021.9 1015.9 1018.9 1005.8 996.2 1006.1 1010.5 1012 1005.1 1025.9 1005.6 1020.2 985.3 994.9 1013.2 What are the correct hypotheses? Note this may view better in full screen mode. Select the correct symbols for each of the 6 spaces. Ho: Select an answer ✓ ? Select an answer ✓ H₁: Select an answer ✓ ? ✓ Select an answer ✓arrow_forwardA poll classified respondents by gender and political party, as shown in the table. A researcher wonders if gender and party affiliation are not independent. (Assume a significance level of α = 0.05) Complete parts a) through e) below. d) Find the P-value for this test. Calculate the chi-square statistic. x² = 2.339 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value for the test. Choose the correct answer below. 0.0823 0.3104 0.003 DRIO 40 40 25 Male Female 49 35 18 e) State an appropriate conclusion. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim. B. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim. C. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim. O D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman