
Concept explainers
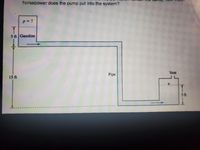
Gasoline at 77°F flows from a pressurized upper tank to a vented lower tank as shown in the figure below. A length of 1-inch Schedule 40 pipe connects the two tanks a
Calculate the air pressure (in psi) above the gasoline in the upper tank that will result in a flow rate of 35 gpm into the lower tank for the dimensions shown The head loss due to pipe friction is 52.8 feet and you DO NOT need to calculate this!
As the upper tank drains does the air pressure in the upper tank need to be neld constant to maintain the flow rate at 35 gpm? Briefly explain your answer.
C The pressurized upper tank is converted to an atmospheric tank and a pump is installed in the system. If flow rate and pipe friction remain the same, how much horsepower does the pump put into the system?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- Problem 3. Outcome 5. Please show all work. Air at standard pressure but with T= 50°C flows through the ducting system shown in the figure. The gauge measures the pressure difference between the downstream and upstream points. All duct sections have circular cross section. Use the following geometry: D₁ = 60 mm, D, = 200 mm, L= 2 m. At this temperature, ai = 1.95 x 10-5 kg/m-s. Also recall that Rai = 287 J/kg-K. The center pipe is smooth with e0. Ap Voo D2 L D₁ Dz Figure for problem 3. The velocity entering the system, Voo; is measured to be 20 m/s. Estimate the Ap = Pdownstream Pupstream measured by the pressure gauge.arrow_forwardTopic is fluid mechanics. Please show all steps on how to determine the flowrates in pipes 2 and 3, and how to find the total required power in the system shown. Thank you.arrow_forwardFor the flow configuration shown, you are required to design a pump station to transfer water from the bottom tank to the upper tank. In your own words, explain the steps that are needed to be followed for the design of the pump system. Your answer should be typed and not more than one page. The pipe equivalent roughness is 1.5 mm. And a valve with a k=10 is located just upstream of the lower reservoir (other losses are negligible). Take p=1000 kg/m”, g = 9.81 m/s?, and u = 1.179 x 102 kg/m.s.arrow_forward
- Can you do Part D of this question. Parts A - C have already been done.arrow_forwardHydraulicsarrow_forwardTranscribed Image Text:As part of a processing of biofuels, water is pumped into a circular tank with a diameter Dt. as shown in Figure Q3. The flowrate into the tank is Q₁ and the flowrate out is Q₂. When the vessel is heated, water evaporates. The average velocity at which the vapour rises across the entire tank is vevap- You may assume that water has a density of Pw, and vapour has a density of Pv. Acceleration due to gravity is g. 2₁ Vevap Q₂ => D₂ Figure Q3: Water being pumped through a heated evaporation tank. Find anexpressio for the rate of chnage of the mass of water in the tank At time t= 0 the height of water in the tank is h0. Find an expression for the height as a function of time h(t) An alarm is triggered when the pressure at the bottom of the tank exceeds P alarm. Find an expression for the time at which the alarm goes offarrow_forward
- Question # 3 A 150 mm diameter pipe reduces in diameter abruptly to 100 mm. If the pipe carries water at 30 litres s', calculate the pressure loss across the contraction and express this as a percentage of the loss to be expected if the flow was reversed. Take the coefficient of contraction as 0.6.arrow_forwardPlease give a detailed Handwritten solution.arrow_forwardThe pressure through a section of pipe is 23 PSI and the velocity of the fluid is 3 ft/sec. If the velocity was increased to 5 ft/sec, what would the pressure drop be?arrow_forward
- Couarrow_forwardI need help with this question: Q. A sprinkler system pumps water through a large pipe inlet with a diameter (d1). The then breaks into N narrow Pipes (which have a diameter, d2, and a length, L2), before the water is released to the atmosphere, as shown in the figure. The entrance to the small pipe from the large pipe has a loss coefficient of KL. You may assume the flow is laminar and fully developed everywhere in the system, and that any changes in height are neglible. (The viscosity is NOT negligible) a) Find an expressin for the velocity of water leaving the sprinkler b) Find an Expression for the gauge pressure at point A, a distance L1 upstream of the narrow pipes. Express your answer in terms of the flowrate, Q. c) The inner diameter of the first segment of the pipe is d1 = 10mm, the inner diameter of the second set of pipes is d2 = 1mm, with N = 25. The flowrate through the sprinkler is Q = 0.2 L/s. Flow in pipes typically becomes turbulent when the Reynolds number exceeds…arrow_forwardDetermine the power requirement of the pump shown in Figure 3.0, assuming it has an efficiency of 88%. The system has a loss coefficient of 3.0 up to point A, and K =1.2 from point B to point C. Neglect any losses through the exit nozzle. Additionally, compute the pressures at points A and B. Water 15 m 2 cm 4 cm dia. 5 cm dia. Figure 3.0 400 kPaarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





