
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
As the hydraulic cylinder rotates around O, the exposed length l of the piston rod is controlled
by the action of the oil pressure in the cylinder. If the cylinder rotates at the constant rate of
dθ/dt = 55 deg/s and l is decreasing at the constant rate of 155 mm/s, calculate the magnitudes
of the velocity v and acceleration a of end B when l = 125 mm.
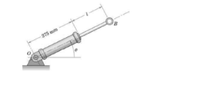
Transcribed Image Text:375 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- At the instant shown, the paper is being unrolled with a speed, vp = 7.5m/s and an acceleration ap = 1 m/s2. If, at this instant, the outer radius of the roll is r= 0.75 m, determine the angular velocity ωs and acceleration αs of the rollarrow_forwardAt the instant shown, the disk is rotating with an angular velocity of wo = 3 rad in the clockwise direction. Determine the x-component of the velocity vector of pin A (in m) at this instant. Consider r = 1.0 meters and 0 = 35°. A 2r B. a yarrow_forwardThe T shaped plate is rotating at a rate of w = 10 rad/s CCW (as shown) and deccelerating at a rate of a = -2.5 rad/s². The relevant dimensions of the plate are a = 3 in and b = 2 in. The plate is inclined at an angle = 15 deg at the instant shown. 1. What are the inertial velocity and acceleration vectors of points P and Q in terms of the unit vectors 6₁ and 6₂? 2. Which point has a greater velocity magnitude? acceleration magnitude? 3. How much of the acceleration is due to the Coriolis effect? 4. How many revolutions will the plate complete before reaching zero angular velocity? iz a b₂ 9 ......... b Q aarrow_forward
- disk rotate with angular speed w= 3rad/s, and is increasing with rate 0.6 rad/s. small ball A moves along radial slot with speed u=0.3 m/s relative to disk. ball speed u decreasing with rate of 0.2 m/s. find magnitude of absolute (total) velocity as well as acceleration of ball at instant.arrow_forwardThe triangular plate rotates about a fixed axis through point O with the angularproperties indicated. Determine the instantaneous velocity and acceleration of point A.Take all given variables to be positive.arrow_forwardA uniform plate has a weight of 50 lb. Link AB is subjected to a couple moment of M = 10 lb # ft and has a clockwise angular velocity of 2 rad>s at the instant u = 30°. Determine the force developed in link CD and the tangential component of the acceleration of the plate’s mass center at this instant. Neglect the mass of links AB and CD. PLEASE EXPLAIN THE N-T COORDINATE SYSTEM (HOW DO YOU KNOW WHICH WAY IS THE N-DIRECTION AND T-DIRECTION)arrow_forward
- draw velocity vectors for point O and C. Find the instantaneous center of the spoolarrow_forwardIf M = 2m, find the linear acceleration of the suspended body (in g).arrow_forwardA simple pendulum is pivoted at O and is free to swing in the vertical plane of the plate. If the plate is given a constant acceleration a = 4.2 m/s2 up the incline θ = 30°, find the steady angle β assumed by the pendulum after all initial start-up oscillations have ceased. Neglect the mass of the slender supporting rod.arrow_forward
- The power winches on the industrial scaffold en- able it to be raised or lowered. For rotation in the senses indicated, the scaffold is being raised. If each drum has a diameter of 200 mm and turns at the rate of 40 rev/min. determine the upward velocity u of the scaffold.arrow_forwardDetermine the constraint equation which relates the accelerations of bodies A and B. Assume that the upper surface of A remains horizontal. If B accelerates downward at 3.29 m/s?, find the acceleration of A (positive if downward, negative if upward). B Answer: aA = m/s?arrow_forwardATWOOD'S MACHINE Draw a free body diagram of m1 and another free body diagram of m2. Using these diagrams, apply Newton’s second law to each mass. Assume that the tension is the same on each mass and that they have the same acceleration. From these two equations, find an expression for the acceleration of m1 in terms of m1, m2, and g. Compare the expression to your result in Step 5 of Analysis.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY