
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
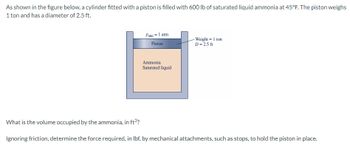
Transcribed Image Text:As shown in the figure below, a cylinder fitted with a piston is filled with 600 lb of saturated liquid ammonia at 45°F. The piston weighs
1 ton and has a diameter of 2.5 ft.
Patm = 1 atm
Piston
Ammonia
Saturated liquid
Weight = 1 ton
D = 2.5 ft
What is the volume occupied by the ammonia, in ft³?
Ignoring friction, determine the force required, in lbf, by mechanical attachments, such as stops, to hold the piston in place.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- As shown in the figure below, a piston-cylinder assembly contains 1 kg of water at T1=200° C and P1 = 1.5 bar holding the piston against the stops. The atmospheric pressure is 1 bar, and you can assume the piston's weight is negligible. The water is slowly cooled until the piston just begins to move downward in the cylinder. What is the pressure (P2), temperature (T2), and volume (V2) of water at this point? (°C), V2 = P2 = (m³) The cooling continues until water has entirely turned into saturated liquid. What is the pressure(P3) and temperature (T3), and volume (V3) of water at this point? (°C), V3 = P3 = (bar), T2 = (bar), T3 = Qtotal Calculate the total work done on the moving boundary of this system during the two processes. W total (kJ) Calculate the total heat transfer during the two processes. (kJ) On paper draw the P-v diagram for water going through the above processes. Show your detailed work on paper. hint: you must also find v1, u1, and u3. Patm = 1 bar Piston (m³) Stopsarrow_forwardA spherical balloon is filled with 6 kg of hydrogen gas (H2) at 2 bar and 20 °C. Which nearly gives the diameter of the balloon in meters when it reaches an altitude where the pressure and temperature are 0.2 bar and -60 °C ? Note: 1 bar=100kPaa. а. 1.23 O b. 7.97 О с. 5.61 O d. 2.13arrow_forwardb. Two cylinders are filled with liquid water (p = 998 kg/m³), and connected by a pipe line with a closed valve. Cylinders A (inside diameter = 42.75 cm) and B (inside diameter = 55 cm) contain 125 kg and 450 kg of water, respectively. The height h as indicated in Fig. 3 is 0.85 m. Determine the pressure (in kPa) of cylinder A and cylinder B on either side of the valve. If the valve is opened such that water flows to an equilibrium between the two cylinders, find the final pressure (in atm) at the valve location. Assume Po= 100 kPa. k Po B g Figure 3 Po Aarrow_forward
- Q2: A gas is contained in a vertical, frictionless piston-cylinder device. The piston has a mass of 3.2 kg and a cross-sectional area of 35 cm2. A compressed spring above the piston exerts a force of 150 N on the piston. If the atmospheric pressure is 95 kPa, determine the pressure inside the cylinder.arrow_forwardQ1) The heat capacity at constant volume of hydrogen sulfide at low pressures is given by Eq. Q1-1: Co[kJ/(mol•°C)] = 0.0252 + 1.547 × 10-T – 3.012 × 10-9T² Eq. Q1-1 ........ Where, Tis temperature in °C. A quantity of H2S is kept in a piston-fitted cylinder with initial temperature, pressure, and volume equal to 25°C, 2.0 atm, and 3.0 liters, respectively. i- Calculate the heat (kJ) required to raise the gas temperature from 25°C to 1000°C, if the heating takes place at constant volume (i.e., if the piston does not move). ii- For a closed system at constant pressure with negligible kinetic and potential energy changes, the specific heat is determined by Eq. Q1-2: Cp = Cy + 0 008314 Eq. Q1-2 calculate the heat (J) required to raise the gas from 25°C to 1000°C at constant pressure. What would the piston do during this process? Given the gas constant = 0 08206 atm. Lit/ (mol. K)arrow_forwardNeed help with this engineering problem. Which unit could be used in the Ideal Gas law equation to get specific volume in ft3/lbm? absolute pressure in lbf/ft2, Temperature in °R and the gas constant in ft·lbf/lbm·°R absolute pressure in lbf/ft2, Temperature in °F and the gas constant in ft·lbf/lbm·°R absolute pressure in lbf/ft2, Temperature in °R and the gas constant in ft·lbm/lbf·°R barometric pressure in lbf/ft2, Temperature in °R and the gas constant in ft·lbf/lbm·°R gauge pressure in lbf/ft2, Temperature in °F and the gas constant in ft·lbf/lbm·°Rarrow_forward
- A piston and cylinder device contains 0.15 kg of water at 25◦C (state 1). As shown in the figure, the piston weighs 500 N and has a cross-sectional area of 0.01 m2. Atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. Heat is transferred to the cylinder from a reservoir at 200◦C, raising the piston. When the piston touches the stops, the volume inside the cylinder is Vmax= 0.165 m^3 (state 2). Heat continues to be transferred until the control mass reaches the boundary temperature (state 3). Determine: a) The initial pressure of the water (kPa) b) The temperature (Celsius) when the piston hits the stops c) The total work (kJ) d) The total heat transfer (kJ) e) The total entropy production for the entire process (kJ/K)arrow_forwardKindly solve this problem with complete solution so that I can Understand. Correct Final answer: 0.96 or 0.95arrow_forwardIn the relation ∆u = mcv ∆T, what is the correct unit of cv — kJ/kg-°C or kJ/kg-K?.arrow_forward
- Can you please indicate ALL necessary processess, units, and cancellations and derivations?arrow_forwardIf you add the diagram it would be well and good. The question is from thermodynamics.arrow_forwardTwo pounds of gas R = 26ft-lbf/lbm-R and k=1.10 undergo a polytropic process from 15psia, 100F to 75psia 3.72ft3. Determine the value of "n" or the polytropic index (unitless)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY