
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:▼
2
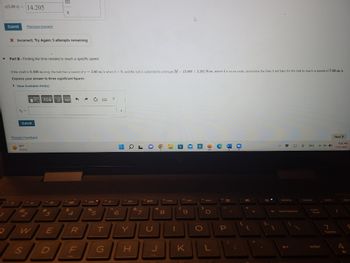
(5.00 s) 14.205
=
Submit
Previous Answers
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
t₁ =
Part B - Finding the time needed to reach a specific speed
If the shaft is 0.400 m long, the ball has a speed of v= 2.60 m/s when t= 0, and the rod is subjected to a torque M = (5.00t+2.30) N-m, where t is in seconds, determine the time it will take for the ball to reach a speed of 7.00 m/s.
Express your answer to three significant figures.
View Available Hint(s)
Submit
Provide Feedback
99°F
Sunny
2
S
15 ΑΣΦΑΛΗ vec
95
W
m
S
3
E
D
$
4
R
F
→ C
40
96
5
?
red-
T
6
5
OL
G H
&
7
U
s
to idd
8
1
(
9
DE
K
O
DI
PPI
O
L
e
P
H
0
{
2
+
C
=
(5)
.
A
#
delete
1
backspace
↓
ENG
home
lock
4x D
7
Next >
7:05 PM
7/12/2022
1
A
S
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
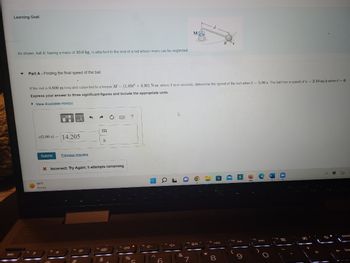
As shown, ball B, having a mass of 10.0 kg, is attached to the end of a rod whose mass can be neglected.
Part A - Finding the final speed of the ball
.
v(5.00 s) 14.205
Submit
If the rod is 0.600 m long and subjected to a torque M = (1.85t2 +4.30) N-m, where t is in seconds, determine the speed of the ball when t-5.00 s. The ball has a speed of v= 2.10 m/s when t = 0.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
► View Available Hint(s)
99 F
Sunny
Previous Answers
3
m
S
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
C
$
40
%
?
154
a
164-
J
4+
&
a
M
7
40
d
*
8
4
f10 DII
ha
delet
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 5kg block is pushed up along the slope as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction is uk =0.2. Determine the speed of the block when it moves 2 m up the slope using Newton's Second Law. (Don't use the required method for this question)arrow_forwardDetermine the power that must be supplied to the motor when t = 2 s. Express your answer in units of horsepower to three significant figures.arrow_forwarda horizontal force P = 25 lb is applied to block A Determine the acceleration of the block B. Neglect friction. a =arrow_forward
- A motorcycle and rider have a combined mass of 350kg. The vehicle's velocity is 100 km/hr. The rider is to go up a hill incline of 10 meters. The wheels each have a mass of 20 kg and a diameter of 500mm. The wheel design consists of 6 spokes with a mass of 0.5 kg for each spoke. a. Determine the vehicle's velocity at the top of the hill, assuming it was a rolling vehicle with engine being turned off. a. Indicate the vehicle's velocity at each meter through the climb. b. Explain the transfer energy and how this affects the behaviour of the system. At another point in its journey, the motorcycle and rider travel at 80 km/h around a left-hand bend of radius 30m. Calculate: a) The angular velocity of each wheel. b) The moment of inertia of each wheel. c) The angular momentum of the wheel prior to entering the bend. d) The magnitude of the gyroscopic torque produced on the bike as the rider is driving around the bend. What is the effect and why is it important to calculate the gyroscopic…arrow_forwardQ13. As shown in the image below, the force acting on the 23-kg box is F = (C.s) N, where constant C = 2 and s is displacement in m. If the box has initial velocity of 1.2 m/s when s = 0, determine the power of force Fwhen s = 2.7 m. The ground is smooth. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point, and proper Sl unit. S | s Your Answer: Answer units Farrow_forwardThe 1.334-Mg car is traveling along the curved road described by r = (50e28) m, where 0 is in radians. If a camera is located at A and it rotates with an angular velocity of Ó = 0.083 rad/s and an angular acceleration of ö = 0.304 rad/s? at the instant 0 = 0.879 rad, .determine the resultant friction force developed between the tires and the road at this instant %3D r= (50")marrow_forward
- The 40-kg crate is being hoisted by the motor. If at this instant shown the velocity of point P on the cable is 4 m/s and the speed is increasing at 2 m/s2 * what is the power input supplied to the motor if its efficiency is £ = 0.75? Neglect the mass of pulley and cable Vp ↓P = 4 m/s A Question 1: The 40-kg crate is being hoisted by the motor. If at this instant shown the velocity of point P on the cable is 4 m/s and the speed is increasing at 2 m/s², what is the power input supplied to the motor if its efficiency is = 0.75? Neglect the mass of pulley and cable. (a) 0.649 kW (b) 0.865 kW (c) 1.15 kW (d) 1.53 kWarrow_forwardDetermine the distance the ball is from the origin 3 s after being released from rest. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardHi, I have an engineering dynamics question.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY